Abstract
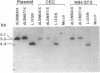
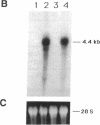
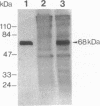
In aiming to develop a gene therapy approach for hemophilia B, we expressed and characterized human factor IX in rat capillary endothelial cells (CECs). Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived retrovirus vectors that contain human factor IX cDNA linked to heterologous promoters and the neomycin-resistant gene were constructed and employed to prepare recombinant retroviruses. Rat CECs and NIH 3T3 cells infected with these viruses were selected with the neomycin analogue, G418 sulfate, and tested for expression of factor IX. A construct with the factor IX cDNA under direct control by long terminal repeat gave the highest level of expression (0.84 and 3.6 micrograms per 10(6) cells per day for CECs and NIH 3T3 cells, respectively) as quantitated by immunoassays as well as clotting activity assays. A single RNA transcript of 4.4 kilobases predicted by the construct and a recombinant factor IX of 68 kilodaltons identical to purified plasma factor IX were found. The recombinant human factor IX produced showed full clotting activity, demonstrating that CECs have an efficient mechanism for posttranslational modifications, including gamma-carboxylation, essential for its biological activity. These results, in addition to other properties of the endothelium, including large number of cells, accessibility, and direct contact with the circulating blood, suggest that CECs can serve as an efficient drug delivery vehicle producing factor IX in a somatic gene therapy for hemophilia B.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Hock R. A., Austen D., Smith K. J., Brownlee G. G., Verma I. M., Miller A. D. Towards gene therapy for hemophilia B. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Feb;4(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentano D., Thompson A. R., Darlington G., Woo S. L. Expression of human factor IX in rabbit hepatocytes by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer: potential for gene therapy of hemophilia B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6141–6145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J. H., Read M. S., Brinkhous K. M., Verma I. M. Phenotypic correction of factor IX deficiency in skin fibroblasts of hemophilic dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Kumar A., Joseph M., Halfpap L., Insley M., Berkner K., Kurachi K., Woodbury R. Expression of active human factor IX in transfected cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):271–273. doi: 10.1038/316271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichek D. A., Nussbaum O., Degen S. J., Anderson W. F. Enhancement of the fibrinolytic activity of sheep endothelial cells by retroviral vector-mediated gene transfer. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):533–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T. Progress toward human gene therapy. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1275–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.2660259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachiya H. L., Takayama S., White M. F., King G. L. Regulation of insulin receptor internalization in vascular endothelial cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6417–6424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirosawa S., Fahner J. B., Salier J. P., Wu C. T., Lovrien E. W., Kurachi K. Structural and functional basis of the developmental regulation of human coagulation factor IX gene: factor IX Leyden. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4421–4425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K. Recombinant antihemophilic factors. Biotechnology. 1991;19:177–195. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7506-9120-8.50014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumoto H., Hirosawa S., Salier J. P., Hagen F. S., Kurachi K. Human genes for complement components C1r and C1s in a close tail-to-tail arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7307–7311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Progress toward human gene therapy. Blood. 1990 Jul 15;76(2):271–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel E. G., Plautz G., Nabel G. J. Site-specific gene expression in vivo by direct gene transfer into the arterial wall. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1285–1288. doi: 10.1126/science.2119055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer T. D., Thompson A. R., Miller A. D. Production of human factor IX in animals by genetically modified skin fibroblasts: potential therapy for hemophilia B. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):438–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Louis D., Verma I. M. An alternative approach to somatic cell gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Johnston D. E., Jefferson D. M., Mulligan R. C. Correction of the genetic defect in hepatocytes from the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4421–4425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Ping A. J., Krauss J. C., Mayo-Bond L., Rogers C. E., Anderson D. C., Todd R. F. Correction of CD18-deficient lymphocytes by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1413–1416. doi: 10.1126/science.1972597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao S. N., DeSilva A. H., Kurachi S., Samuelson L. C., Kurachi K. Characterization of a mouse factor IX cDNA and developmental regulation of the factor IX gene expression in liver. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jan 23;65(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. F., von Rüden T., Kantoff P. W., Garber C., Seiberg M., Rüther U., Anderson W. F., Wagner E. F., Gilboa E. Self-inactivating retroviral vectors designed for transfer of whole genes into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]