Abstract
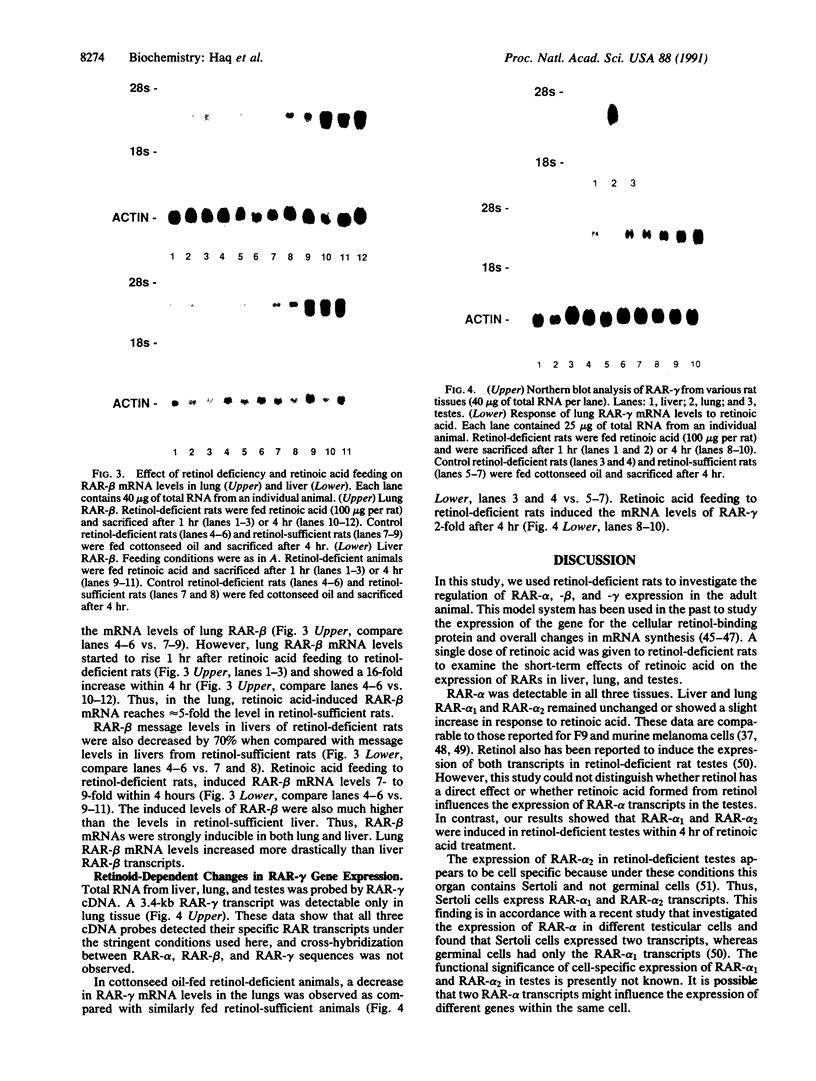
The multitude of biological effects of the vitamin A metabolite, retinoic acid, are mediated by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs), which are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. RAR-alpha, -beta, and -gamma are encoded by three genes from which multiple isoforms can be generated. Recent studies suggest that the expression of at least some RAR isoforms can be regulated by retinoic acid in certain cell lines. Here we examined regulation of RAR expression in the adult animal. RARs were analyzed by Northern blots from lung, liver, and testes of retinol-deficient rats. Retinol deficiency caused a 65-70% decrease in the mRNA levels of lung and liver RAR-beta, whereas no change was observed in RAR-alpha and -gamma mRNA levels in these organs. In the testes of retinol-deficient animals, two transcripts, RAR-alpha 1 (3.7 kb) and RAR-alpha 2 (2.8 kb), were detected as compared with one RAR-alpha 1 (3.7 kb) transcript in retinol-sufficient testes. When retinol-deficient rats were orally administered 1 dose of retinoic acid (100 micrograms per rat), lung RAR-beta mRNA levels started to increase after 1 hr and reached a 16-fold higher level after 4 hr; after 4 hr these retinoic acid-fed rats also showed a 7-fold increase in liver RAR-beta mRNA levels as compared with levels in the retinol-deficient rats. In contrast, liver, lung, and testes RAR-alpha transcripts remained either unchanged or showed only a slight increase in response to retinoic acid. RAR-gamma was constitutively expressed in lung, and its mRNA levels were induced 2-fold by retinoic acid. These results show tissue diversity in the rapid induction of RAR-beta and RAR-gamma by retinoic acid in the adult animal and suggest distinct roles for the various receptor isoforms in the control of the retinoid response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne S., Chomienne C., Daniel M. T., Ballerini P., Berger R., Fenaux P., Degos L. All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1704–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F. Retinoic acid: biochemistry and metabolism. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986 Oct;15(4 Pt 2):741–747. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F., Riaz-ul-Haq Vitamin A mediated gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1990;1(1):61–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford J. L., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Lotan R. Modulation by retinoids of mRNA levels for nuclear retinoic acid receptors in murine melanoma cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1546–1555. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Bougueleret L., Grzeschik K. H., Tiollais P. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration in a sequence homologous to v-erb-A and steroid receptor genes in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):70–72. doi: 10.1038/322070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Stoner C. M., Gudas L. J., Chambon P. Differential expression of genes encoding alpha, beta and gamma retinoic acid receptors and CRABP in the developing limbs of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):702–705. doi: 10.1038/342702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Leroy P., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. I. A systematic study of their differential pattern of transcription during mouse organogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1133–1151. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichele G., Tickle C., Alberts B. M. Studies on the mechanism of retinoid-induced pattern duplications in the early chick limb bud: temporal and spatial aspects. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1913–1920. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Shago M., Zirngibl R., Tate P., Rossant J., Varmuza S. Identification of a novel isoform of the retinoic acid receptor gamma expressed in the mouse embryo. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2335–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graupner G., Wills K. N., Tzukerman M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. Dual regulatory role for thyroid-hormone receptors allows control of retinoic-acid receptor activity. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):653–656. doi: 10.1038/340653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haq R., Chytil F. Retinoic acid rapidly induces lung cellular retinol-binding protein mRNA levels in retinol deficient rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):712–716. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Husmann M., Graupner G., Pfahl M. A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong W. K., Lippman S. M., Itri L. M., Karp D. D., Lee J. S., Byers R. M., Schantz S. P., Kramer A. M., Lotan R., Peters L. J. Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 20;323(12):795–801. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009203231205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Gudas L. J. Cyclic AMP analogs and retinoic acid influence the expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha, beta, and gamma mRNAs in F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):391–396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Krust A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Zelent A., Leroy P., Staub A., Chambon P. Murine isoforms of retinoic acid receptor gamma with specific patterns of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Griswold M. D. The regulation of retinoic acid receptor mRNA levels during spermatogenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1679–1688. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb A. J., Apiwatanaporn P., Olson J. A. Induction of rapid, synchronous vitamin A deficiency in the rat. J Nutr. 1974 Sep;104(9):1140–1148. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.9.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Hoffmann B., Pfahl M. Genomic organization of the retinoic acid receptor gamma gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):573–578. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Krust A., Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Kastner P., Dierich A., Chambon P. Multiple isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha are generated by alternative splicing and differential induction by retinoic acid. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F. Spatial distribution of cellular protein binding to retinoic acid in the chick limb bud. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):733–735. doi: 10.1038/335733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F. The role of retinoid-binding proteins in the generation of pattern in the developing limb, the regenerating limb and the nervous system. Development. 1989;107 (Suppl):109–119. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.Supplement.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. A., Ziegler L. M., Napoli J. L. Retinoic acid, dibutyryl-cAMP, and differentiation affect the expression of retinoic acid receptors in F9 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4804–4808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori M., Chytil F. Mechanism of vitamin A action. Gene expression in retinol-deficient rats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14370–14374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M., Tzukerman M., Zhang X. K., Lehmann J. M., Hermann T., Wills K. N., Graupner G. Nuclear retinoic acid receptors: cloning, analysis, and function. Methods Enzymol. 1990;189:256–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)89297-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale C. W., Jr, Petkovich M., Gates P. B., Chambon P., Brockes J. P. Identification of a novel retinoic acid receptor in regenerative tissues of the newt. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):654–657. doi: 10.1038/341654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern C. P., Daly A. K., Latham J. A., Todd C. The biological activity of retinoids in melanoma cells. Induction of expression of retinoic acid receptor-beta by retinoic acid in S91 melanoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees J. L., Daly A. K., Redfern C. P. Differential expression of the alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors in tissues of the rat. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):917–919. doi: 10.1042/bj2590917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. R., Lloyd R. S., Chytil F. Rat cellular retinol-binding protein: cDNA sequence and rapid retinol-dependent accumulation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3209–3213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Pang K., Sundin O., Wedden S. E., Thaller C., Eichele G. Molecular approaches to vertebrate limb morphogenesis. Development. 1989;107 (Suppl):121–131. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.Supplement.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerbell D., Maden M. Retinoic acid, a developmental signalling molecule. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Apr;13(4):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90006-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON J. N., HOWELL J. M., PITT G. A. VITAMIN A AND REPRODUCTION IN RATS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Feb 18;159:510–535. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takase S., Ong D. E., Chytil F. Cellular retinol-binding protein allows specific interaction of retinol with the nucleus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2204–2208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takase S., Ong D. E., Chytil F. Transfer of retinoic acid from its complex with cellular retinoic acid-binding protein to the nucleus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jun;247(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Alberts B., Wolpert L., Lee J. Local application of retinoic acid to the limb bond mimics the action of the polarizing region. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):564–566. doi: 10.1038/296564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Crawley A., Farrar J. Retinoic acid application to chick wing buds leads to a dose-dependent reorganization of the apical ectodermal ridge that is mediated by the mesenchyme. Development. 1989 Aug;106(4):691–705. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.4.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de The H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Differential expression and ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha and beta genes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):429–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ul Haq R., Chytil F. Early effects of retinol and retinoic acid on protein synthesis in retinol deficient rat testes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90558-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]