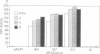Abstract
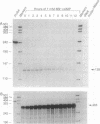
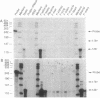
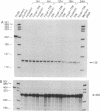
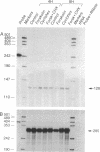
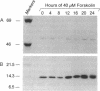
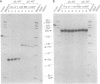
Adrenodoxin reductase (AR; ferridoxin: NADP+ oxidoreductase, EC 1.18.1.2) is a flavoprotein that mediates electron transport from NADPH to all known mitochondrial forms of cytochrome P450. AR mRNA was found in all human adult and fetal tissues examined; however, it was vastly more abundant in tissues that synthesize steroid hormones. The ratio of the 18- form of mRNA lacking 18 alternately spliced bases to the 18+ form was approximately 100:1 and remained constant irrespective of the tissue or hormonal manipulation, indicating that the alternate splicing is a passive nonregulated event. AR protein was unchanged by forskolin treatment of human JEG-3 cytotrophoblast cells for 24 h, but the mRNA diminished. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and cycloheximide had no effect, even though these agents had the expected effects on P450scc and adrenodoxin mRNAs. cAMP decreased the abundance of AR mRNA expressed from both transfected plasmids and the endogenous gene, indicating the effect was post-transcriptional. AR gene transcription in JEG-3 cells and promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase constructs transfected into JEG-3 cells were unresponsive to forskolin. Powerful basal transcription elements were identified between -46 and -214 bases from the principal transcriptional initiation site, a region containing six elements closely resembling the binding site for transcription factor SP1.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Seilman S., Amelizad Z., Oesch F., Wolf C. R. Identification of human cytochromes P-450 analogous to forms induced by phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene in the rat. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):869–876. doi: 10.1042/bj2320869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentano S. T., Picado-Leonard J., Mellon S. H., Moore C. C., Miller W. L. Tissue-specific, cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-induced, and phorbol ester-repressed transcription from the human P450c17 promoter in mouse cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1972–1979. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. Y., Wu D. A., Lai C. C., Miller W. L., Chung B. C. Cloning and structure of the human adrenodoxin gene. DNA. 1988 Nov;7(9):609–615. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. Y., Wu D. A., Mohandas T. K., Chung B. C. Structure, sequence, chromosomal location, and evolution of the human ferredoxin gene family. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;9(3):205–212. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Voutilainen R., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8962–8966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan V. M., Vickery L. E. Expression of human ferredoxin and assembly of the [2Fe-2S] center in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):835–839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Blasio A. M., Voutilainen R., Jaffe R. B., Miller W. L. Hormonal regulation of messenger ribonucleic acids for P450scc (cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme) and P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase) in cultured human fetal adrenal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jul;65(1):170–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-1-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnanaiah W., Omdahl J. L. Isolation and characterization of pig kidney mitochondrial ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12649–12654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golos T. G., Miller W. L., Strauss J. F., 3rd Human chorionic gonadotropin and 8-bromo cyclic adenosine monophosphate promote an acute increase in cytochrome P450scc and adrenodoxin messenger RNAs in cultured human granulosa cells by a cycloheximide-insensitive mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):896–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI113149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Gutfinger T. cDNA sequence of adrenodoxin reductase. Identification of NADP-binding sites in oxidoreductases. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):479–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Jefcoate C. R. Mitochondrial cytochrome P-450scc. Mechanism of electron transport by adrenodoxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3057–3061. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambeth J. D., Seybert D. W., Kamin H. Ionic effects on adrenal steroidogenic electron transport. The role of adrenodoxin as an electron shuttle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7255–7264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Shi Y. F., Miller W. L. Cloning and sequence of the human adrenodoxin reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8516–8520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Miller W. L. Extraadrenal steroid 21-hydroxylation is not mediated by P450c21. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1497–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI114325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Vaisse C. cAMP regulates P450scc gene expression by a cycloheximide-insensitive mechanism in cultured mouse Leydig MA-10 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7775–7779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Molecular biology of steroid hormone synthesis. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):295–318. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. C., Brentano S. T., Miller W. L. Human P450scc gene transcription is induced by cyclic AMP and repressed by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and A23187 through independent cis elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6013–6023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., Picado-Leonard J., Wu D. A., Chang C. Y., Mohandas T. K., Chung B. C., Miller W. L. Assignment of the functional gene for human adrenodoxin to chromosome 11q13----qter and of adrenodoxin pseudogenes to chromosome 20cen----q13.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):52–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Sogawa K., Omura T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of human cytochrome P-450(SCC), cholesterol desmolase. J Biochem. 1987 Apr;101(4):879–887. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Voutilainen R., Kao L. C., Chung B. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin: cloning of three cDNAs and cycloheximide enhancement in JEG-3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3240–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler G. E., Kao L. C., Miller W. L., Strauss J. F., 3rd Effects of 8-bromo-cAMP on expression of endocrine functions by cultured human trophoblast cells. Regulation of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;61(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solish S. B., Picado-Leonard J., Morel Y., Kuhn R. W., Mohandas T. K., Hanukoglu I., Miller W. L. Human adrenodoxin reductase: two mRNAs encoded by a single gene on chromosome 17cen----q25 are expressed in steroidogenic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Klisak I., Miller W. L. Regional mapping of genes encoding human steroidogenic enzymes: P450scc to 15q23-q24, adrenodoxin to 11q22; adrenodoxin reductase to 17q24-q25; and P450c17 to 10q24-q25. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):359–365. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup M. R., Washington L. D. Region-specific initiation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by endogenous RNA polymerase II in preparations of cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2802–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Coordinate tropic hormone regulation of mRNAs for insulin-like growth factor II and the cholesterol side-chain-cleavage enzyme, P450scc [corrected], in human steroidogenic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Miller W. L. Developmental expression of genes for the stereoidogenic enzymes P450scc (20,22-desmolase), P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), and P450c21 (21-hydroxylase) in the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Nov;63(5):1145–1150. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-5-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Picado-Leonard J., DiBlasio A. M., Miller W. L. Hormonal and developmental regulation of adrenodoxin messenger ribonucleic acid in steroidogenic tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Feb;66(2):383–388. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen R., Tapanainen J., Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Hormonal regulation of P450scc (20,22-desmolase) and P450c17 (17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase) in cultured human granulosa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):202–207. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. R., Simpson E. R. Regulation of steroid hydroxylase gene expression is multifactorial in nature. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1989;45:533–566. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571145-6.50016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]