Abstract
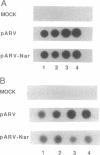
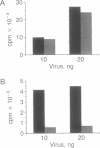
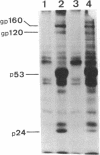
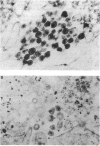
In an effort to understand the contribution of the primer-binding site (PBS) region to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication, we have constructed a mutant HIV proviral DNA with an alteration in the 5' end of the PBS. The PBS mutant proviral DNA was characterized by transfection of the viral DNA into CD4+ and non-CD4+ target cells. The results indicate that mutation in the PBS reduced the level of viral particles released into the medium of transfected cells in comparison to wild-type proviral DNA. The viral particles were noninfectious upon transmission to established CD4+ cell lines and phytohemagglutinin-stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes. Electron microscopic analysis of the transfected cells revealed no abnormalities in the structure of the virion directed by the mutant proviral DNA. Also, the protein and RNA contents of the mutant virions were similar to the wild type. The quantitation of intracellular viral structural protein in the transfected cells, however, indicated that the PBS mutation may have an effect on the assembly of viral particles in addition to completely abolishing reverse transcription of viral RNA into DNA. These results provide evidence that the PBS region of the viral genome has multiple functions in HIV-1 replication.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barat C., Le Grice S. F., Darlix J. L. Interaction of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with a synthetic form of its replication primer, tRNA(Lys,3). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):751–757. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barat C., Lullien V., Schatz O., Keith G., Nugeyre M. T., Grüninger-Leitch F., Barré-Sinoussi F., LeGrice S. F., Darlix J. L. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase specifically interacts with the anticodon domain of its cognate primer tRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3279–3285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Levy J. A. Altered host range of HIV-1 after passage through various human cell types. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):288–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90494-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Soskey L., Leis J. A retroviral RNA secondary structure required for efficient initiation of reverse transcription. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3622–3630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3622-3630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Zuker M., Spahr P. F. Structure-function relationship of Rous sarcoma virus leader RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5183–5196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Ish-Horowicz D. The origin of extrachromosomal circular copia elements. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R. Assembly and morphology of HIV: potential effect of structure on viral function. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):617–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick R. J., Nigida S. M., Jr, Bess J. W., Jr, Arthur L. O., Henderson L. E., Rein A. Noninfectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants deficient in genomic RNA. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3207–3211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3207-3211.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., de Wolf F., Paul D. A., Epstein L. G., Lange J. M., Krone W. J., Speelman H., Wolters E. C., Van der Noordaa J., Oleske J. M. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus antigen (HIV-Ag) in serum and cerebrospinal fluid during acute and chronic infection. Lancet. 1986 Jul 26;2(8500):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Role of capsid precursor processing and myristoylation in morphogenesis and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Development of antiviral drugs for the treatment of AIDS: strategies and prospects. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):311–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Retroviral recombination and reverse transcription. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1227–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1700865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanaraman V. S., Pal R., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. A unique human immunodeficiency virus culture secreting soluble gp160. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Oct;4(5):319–329. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Ando Y., Shiba T. Unusual priming mechanism of RNA-directed DNA synthesis in copia retrovirus-like particles of Drosophila. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):824–826. doi: 10.1038/323824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Dixon R. A., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Active human immunodeficiency virus protease is required for viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4686–4690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C., Dina D., Luciw P. A. AIDS retrovirus (ARV-2) clone replicates in transfected human and animal fibroblasts. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):998–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.3010461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh T. P., Sievert L. L., Scott R. W. Evidence for a stem cell-specific repressor of Moloney murine leukemia virus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4045–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murti K. G., Bondurant M., Tereba A. Secondary structural features in the 70S RNAs of Moloney murine leukemia and Rous sarcoma viruses as observed by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.411-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. C., Swanstrom R. A new pathway in the generation of defective retrovirus DNA. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.779-789.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Sporborg C., Harrison A., Martin M. L., Feorino P. Morphology and immunoelectron microscopy of AIDS virus. Arch Virol. 1985;85(3-4):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01314230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Housset V., de Billy G., Cornille F., Prats H., Roques B., Darlix J. L. Viral RNA annealing activities of the nucleocapsid protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus are zinc independent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3533–3541. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Sarih L., Gabus C., Litvak S., Keith G., Darlix J. L. Small finger protein of avian and murine retroviruses has nucleic acid annealing activity and positions the replication primer tRNA onto genomic RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1777–1783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Park J., Morrow C. D. Deletions in the tRNA(Lys) primer-binding site of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 identify essential regions for reverse transcription. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4555–4564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4555-4564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K. A potential primer for reverse transcription of mdg3, a Drosophila copia-like element, is a leucine tRNA lacking its 3' terminal 5 bases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4370–4370. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer R., Tautz D. Minimal homology requirements for PCR primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6749–6749. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Anand R., York D., Ranganathan P., Feorino P., Schochetman G., Curran J., Kalyanaraman V. S., Luciw P. A., Sanchez-Pescador R. Molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus from Zaire: nucleotide sequence analysis identifies conserved and variable domains in the envelope gene. Gene. 1987;52(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Goldsmith C. S., York D., Anand R., Luciw P., Schochetman G., Palmer E., Bohan C. Studies on human immunodeficiency virus-induced cytopathic effects: use of human rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells. Arch Virol. 1988;99(1-2):21–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01311020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., York D., Jannoun-Nasr R., Kalyanaraman S., Swan D., Benson J., Bohan C., Luciw P. A., Schnoll S., Robinson R. A. Generation of hybrid human immunodeficiency virus by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford J., Queen C. Cell-type specific expression of a transfected immunoglobulin gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):77–79. doi: 10.1038/306077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnav Y. N., Wong-Staal F. The biochemistry of AIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:577–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velpandi A., Monken C. E., Srinivasan A. Development of RD-tat cell lines: use in HIV recombination studies. J Virol Methods. 1990 Sep;29(3):291–302. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90056-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velpandi A., Nagashunmugam T., Murthy S., Cartas M., Monken C., Srinivasan A. Generation of hybrid human immunodeficiency virus utilizing the cotransfection method and analysis of cellular tropism. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4847–4852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4847-4852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]