Abstract
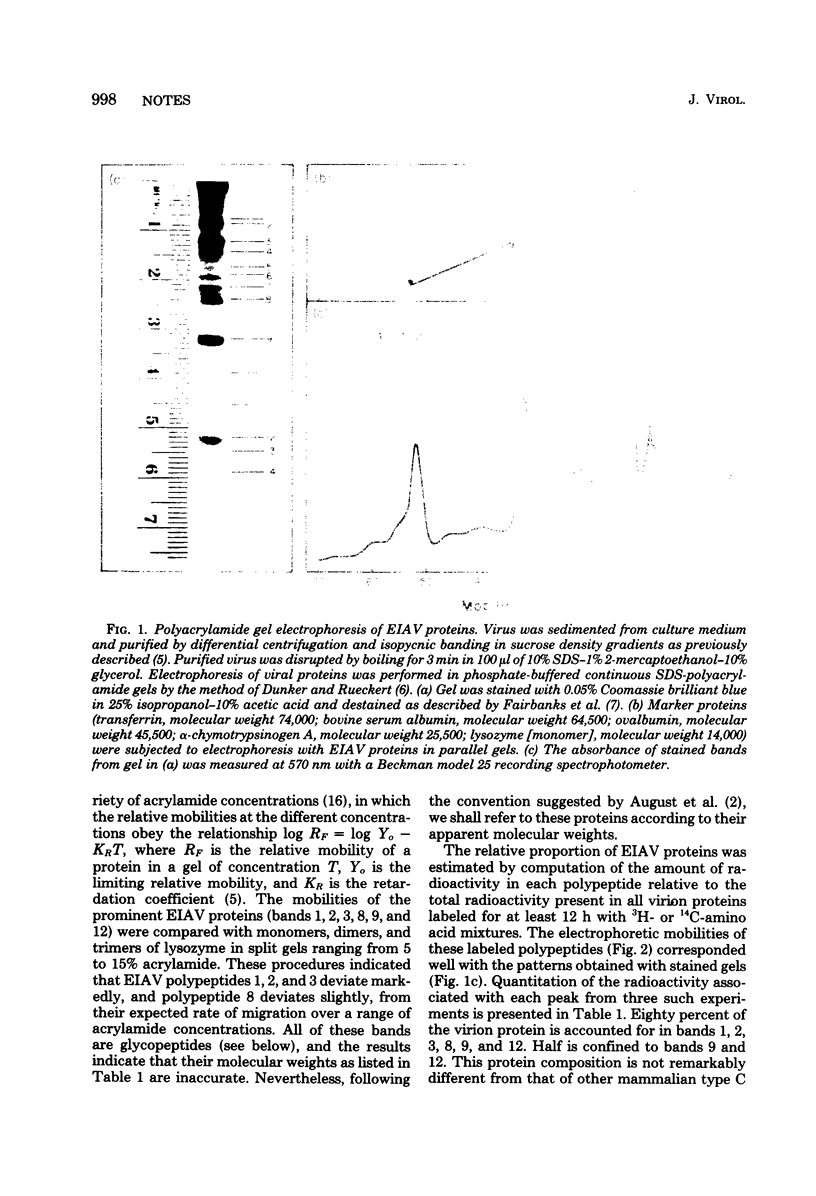
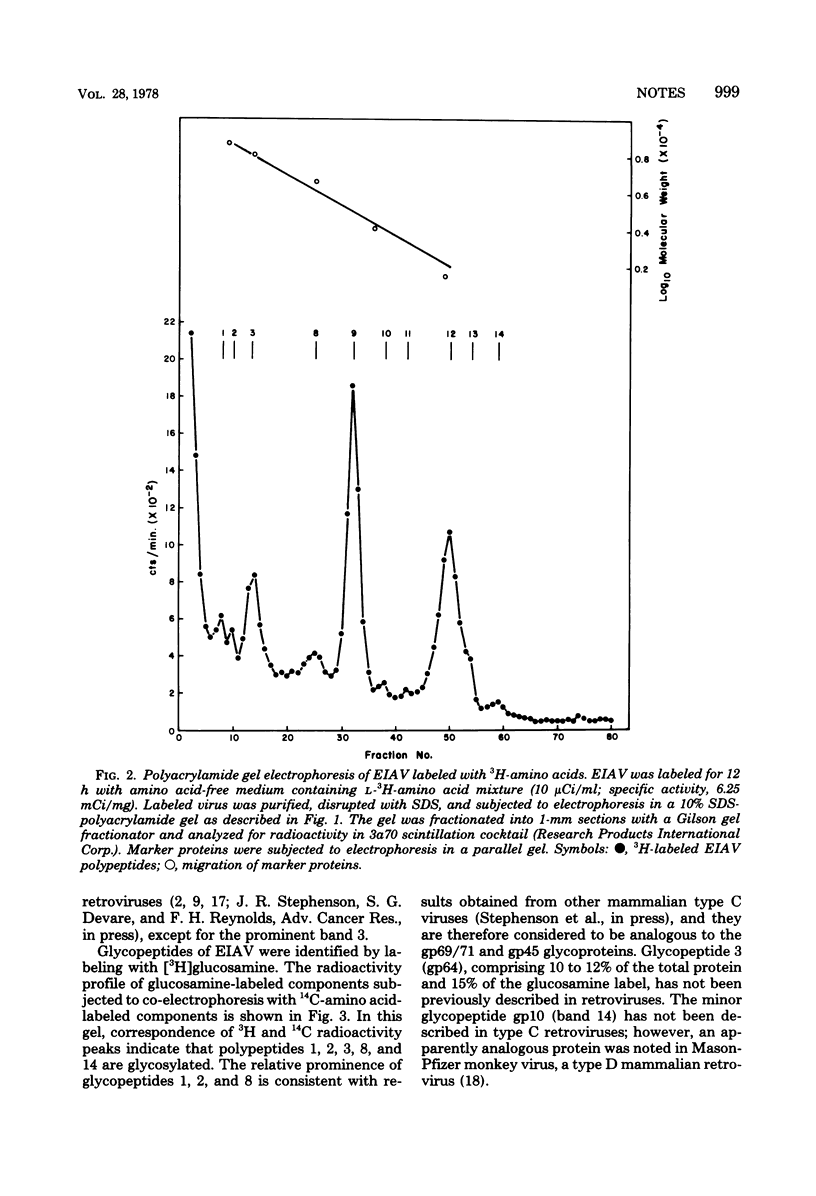
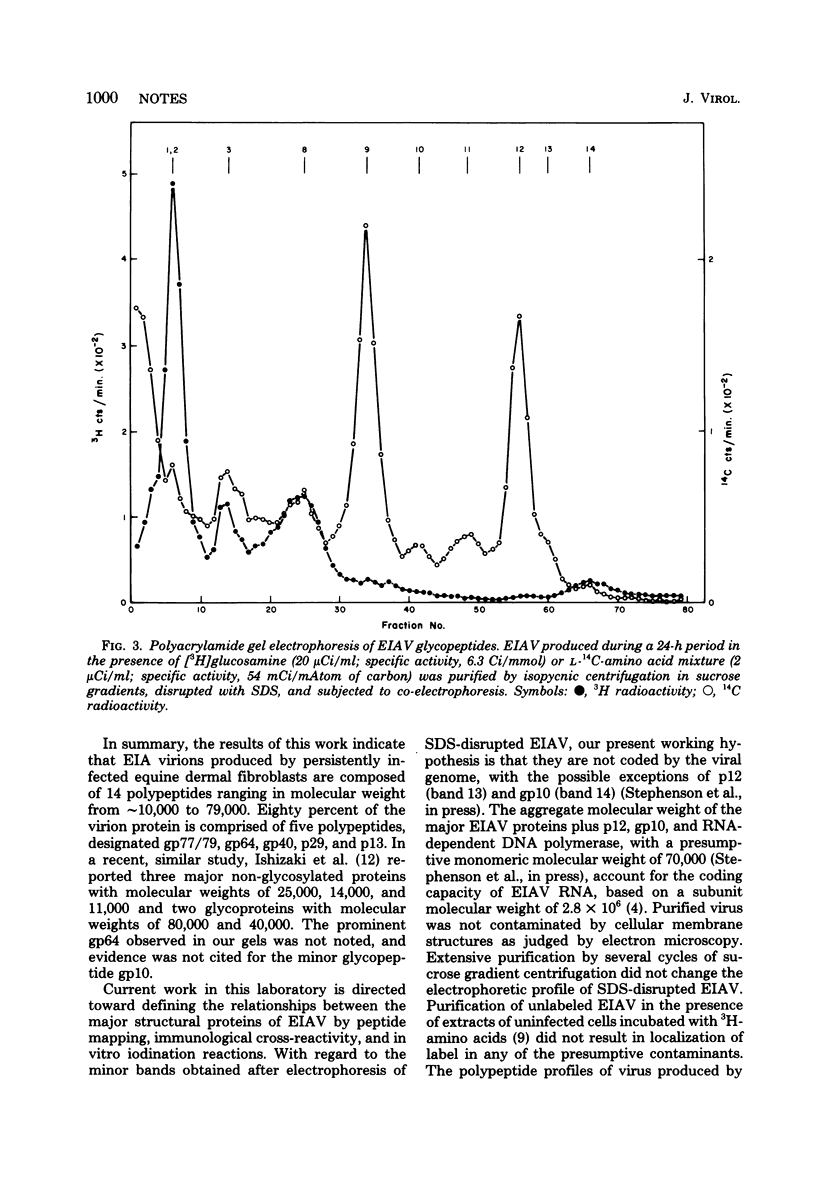
Equine infectious anemia virus was found to be comprised of fourteen polypeptides of molecular weight ranging from 10,000 to 79,000. Eighty percent of the virion protein was accounted for by five polypeptides, including two non-glycosylated components (p29 and p13) comprising one-half of the virion protein and three glycoproteins (gp77/79, gp64, and gp40).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer B. G., Crawford T. B., McGuire T. C., Frazier M. E. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase associated with equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.16-22.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- August J. T., Bolognesi D. P., Fleissner E., Gilden R. V., Nowinski R. C. A proposed nomenclature for the virion proteins of oncogenic RNA viruses. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):595–600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charman H. P., Bladen S., Gilden R. V., Coggins L. Equine infectious anemia virus: evidence favoring classification as a retravirus. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):1073–1079. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.1073-1079.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevers W. P., Archer B. G., Crawford T. B. Characterization of RNA from equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):489–497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.489-497.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Kenyon A. J. Mobility of sodium dodecyl sulphate - protein complexes. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):191–197. doi: 10.1042/bj1530191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner F. The classification and nomenclature of viruses. Summary of results of meetings of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses in Madrid, September 1975. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90364-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Baringer J. R. The structural polypeptides of RNA slow viruses. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. B., McGuire T. C. Equine infectious anemia. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):143–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Ishitani R. Equine infectious anemia. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1975;19:195–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki R., Green R. W., Bolognesi D. P. The structural polypeptides of equine infections anemia virus. Intervirology. 1978;9(5):286–294. doi: 10.1159/000148946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Yoshino T., Fukanaga Y. Growth characteristics of equine infectious anemia virus in horse leukocyte cultures. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(2):252–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01250196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmquist W. A., Barnett D., Becvar C. S. Production of equine infectious anemia antigen in a persistently infected cell line. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;42(4):361–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01250717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheka H. D., Coggins L., Shively J. N., Norcross N. L. Purification and characterization of equine infectious anemia virus. Arch Virol. 1976;51(1-2):107–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01317839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Kortright K., Schlom J. Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: analysis and localization of virion proteins and glycoproteins. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1208–1219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1208-1219.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer W., Bolognesi D. P. Mammalian C-type oncornaviruses: relationships between viral structural and cell-surface antigens and their possible significance in immunological defense mechanisms. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;6:127–167. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3051-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Andrews E. P., Marchesi V. T. Human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein: a re-evaluation of the molecular weight as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Nakajima H., Ito Y. Electron microscopy of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):521–527. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.521-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]