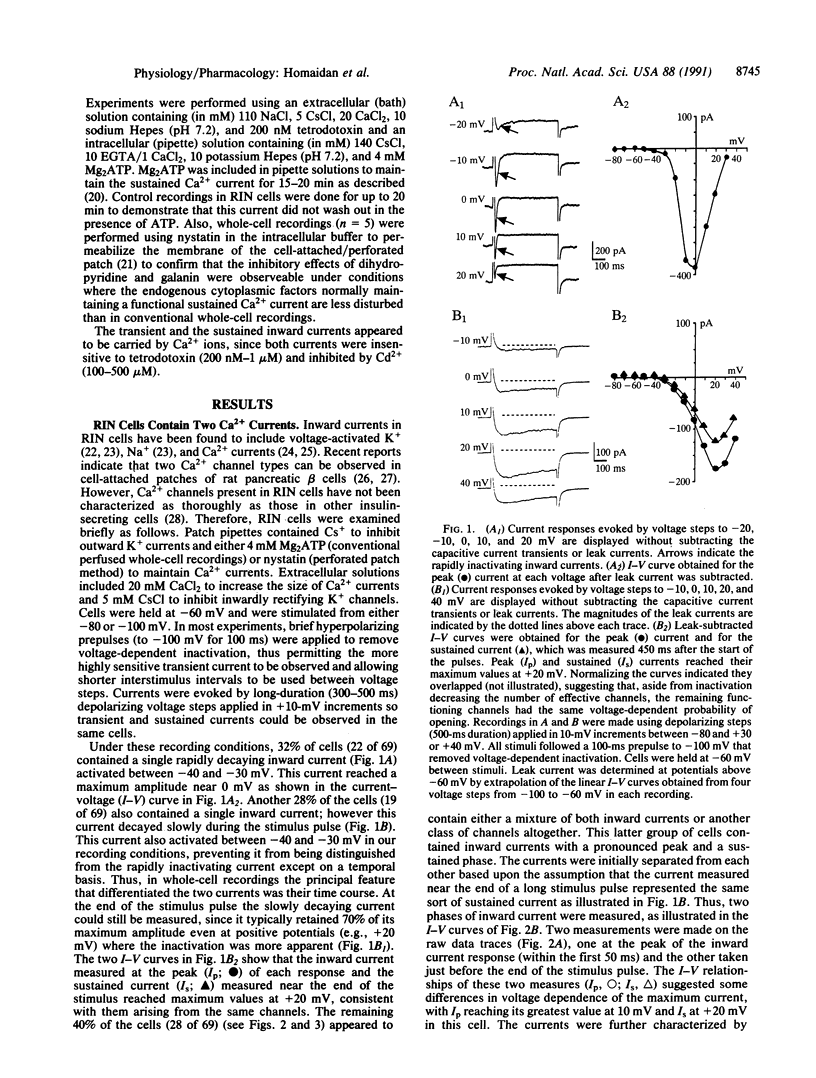
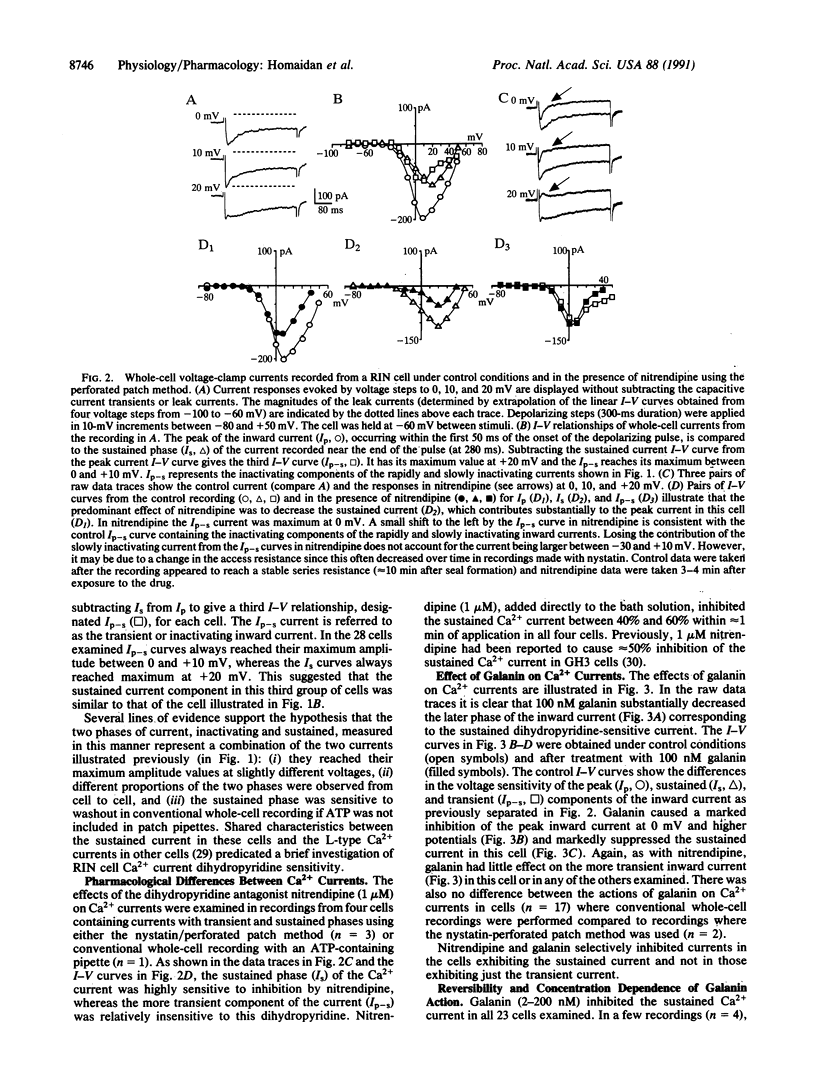
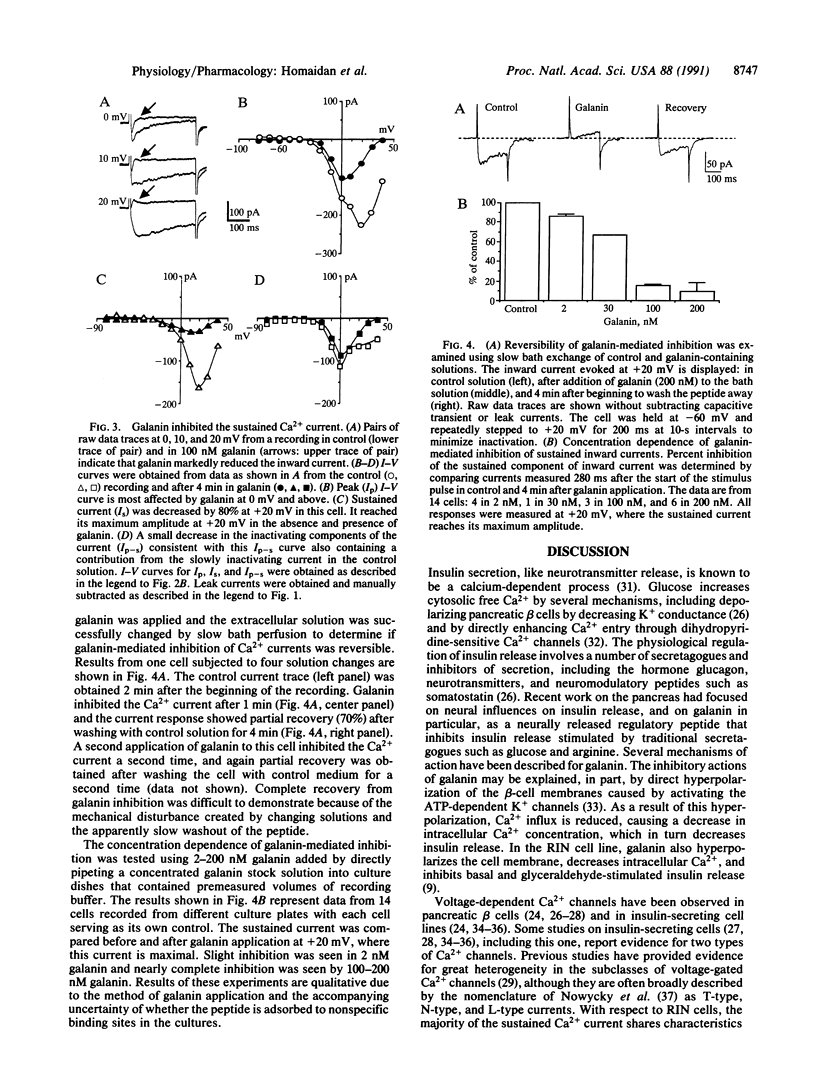
Abstract
Mechanisms of action of the neuropeptide galanin, a putative neuromodulator in the central and peripheral nervous systems, have been evaluated extensively in insulin-secreting cells isolated from pancreas and cell lines derived from pancreatic tumors. Galanin inhibits insulin secretion from these cells through several mechanisms, including activation of ATP-dependent K+ channels and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase leading to a decrease in cAMP. Here we report that galanin also inhibits a dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ current. Both electrophysiological actions by galanin would result in less Ca2+ entry, as the action to increase K+ current would hyperpolarize the cells and the decrease in voltage-gated Ca2+ current would decrease Ca2+ influx at depolarized potentials where these channels are activated. These galanin actions would directly counter the two opposing electrophysiological responses to carbohydrate stimulation in RINm5f cells, which are to inhibit K+ current and to stimulate Ca2+ current. Given that stimulation of presynaptic nerve terminals in pancreas releases galanin, these results suggest that Ca(2+)-dependent insulin release from native pancreatic beta cells may also be regulated by similar neuropeptide effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Berggren P. O., Bokvist K., Rorsman P. Does galanin inhibit insulin secretion by opening of the ATP-regulated K+ channel in the beta-cell? Peptides. 1989 Mar-Apr;10(2):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Laburthe M. Galanin receptor in the rat pancreatic beta cell line Rin m 5F. Molecular characterization by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20714–20717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Lagny-Pourmir I., Laburthe M. Mechanism of galanin-inhibited insulin release. Occurrence of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kelly R. P., Smith P. A. Two types of Ca channel in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):504–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00373633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ng J. L., Christofides N. D., Anand P., Gibson S. J., Allen Y. S., Su H. C., Tatemoto K., Morrison J. F., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Distribution of galanin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system and the responses of galanin-containing neuronal pathways to injury. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):343–354. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunning B. E., Ahren B., Veith R. C., Böttcher G., Sundler F., Taborsky G. J., Jr Galanin: a novel pancreatic neuropeptide. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):E127–E133. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.1.E127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunning B. E., Taborsky G. J., Jr Galanin release during pancreatic nerve stimulation is sufficient to influence islet function. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):E191–E198. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.1.E191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Rökaeus A., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Galanin nerve fibers in the rat gut: distribution, origin and projections. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01868430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J. Voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Oxford G. S. Modulation of calcium channels by norepinephrine in internally dialyzed avian sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):743–763. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen K. Effects of galanin on the release of insulin, glucagon and somatostatin from the isolated, perfused dog pancreas. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Sep;119(1):91–98. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1190091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiriart M., Matteson D. R. Na channels and two types of Ca channels in rat pancreatic B cells identified with the reverse hemolytic plaque assay. J Gen Physiol. 1988 May;91(5):617–639. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keahey H. H., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Kunze D. L. Catecholamine modulation of calcium currents in clonal pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):C1171–C1176. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.6.C1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu M., Yokokawa N., Takeda T., Nagasawa Y., Aizawa T., Yamada T. Pharmacological characterization of the voltage-dependent calcium channel of pancreatic B-cell. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2008–2014. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka L. M., McKeon T. W., Parsons R. L. Galanin-induced hyperpolarization and decreased membrane excitability of neurones in mudpuppy cardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:107–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagny-Pourmir I., Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Tatemoto K., Laburthe M. Characterization of galanin receptors in the insulin-secreting cell line Rin m 5F: evidence for coupling with a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanosine triphosphate regulatory protein. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2635–2641. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Fahrenkrug J., Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Distribution of galanin-like immunoreactivity in the gastro-intestinal tract of several mammalian species. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(2):253–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00218003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A. Functional comparison of neurotransmitter receptor subtypes in mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):513–565. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Suppression of insulin release by galanin and somatostatin is mediated by a G-protein. An effect involving repolarization and reduction in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):973–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottlecz A., Snyder G. D., McCann S. M. Regulatory role of galanin in control of hypothalamic-anterior pituitary function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9861–9865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan A. S., Aguilar-Bryan L., Nelson D. A., Yaney G. C., Hsu W. H., Kunze D. L., Boyd A. E., 3rd Ion channels and insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):340–363. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O. Voltage-activated Na+ currents and their suppression by phorbol ester in clonal insulin-producing RINm5F cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):C912–C919. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.6.C912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala S., Matteson D. R. Single-channel recordings of two types of calcium channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):567–571. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82400-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Evidence for two calcium currents in insulin-secreting cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):401–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00587719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnuerer E. M., McDonald T. J., Dupre J. Inhibition of insulin release by galanin and gastrin-releasing peptide in the anaesthetized rat. Regul Pept. 1987 Sep;18(5-6):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(87)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Yada T., Russo L. L., Bliss C. R., Cormont M., Monge L., Van Obberghen E. Galanin can inhibit insulin release by a mechanism other than membrane hyperpolarization or inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7302–7309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestre R. A., Miralles P., Monge L., Moreno P., Villanueva M. L., Marco J. Effects of galanin on hormone secretion from the in situ perfused rat pancreas and on glucose production in rat hepatocytes in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Jul;121(1):378–383. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-1-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simasko S. M., Weiland G. A., Oswald R. E. Pharmacological characterization of two calcium currents in GH3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):E328–E336. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.3.E328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Rorsman P., Ashcroft F. M. Modulation of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels by glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):550–553. doi: 10.1038/342550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldani G., Mengozzi G., Della Longa A., Intorre L., Martelli F., Brown D. R. An analysis of the effects of galanin on gastric acid secretion and plasma levels of gastrin in the dog. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 23;154(3):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Palmer J. M., Winkelmann C. K., Wood J. D. Mechanism of action of galanin on myenteric neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Sep;60(3):966–979. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.3.966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco J. M., Petersen J. U., Petersen O. H. Single-channel Ba2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells are activated by glyceraldehyde stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau W. M., Dorsett J. A., Youther M. L. Evidence for galanin as an inhibitory neuropeptide on myenteric cholinergic neurons in the guinea pig small intestine. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 23;72(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J. R., Fosset M., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Lazdunski M. Galanin inhibits dopamine secretion and activates a potassium channel in pheochromocytoma cells. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 17;485(1):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90685-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels that are blocked by hypoglycemia-inducing sulfonylureas in insulin-secreting cells are activated by galanin, a hyperglycemia-inducing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1312–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


