Abstract
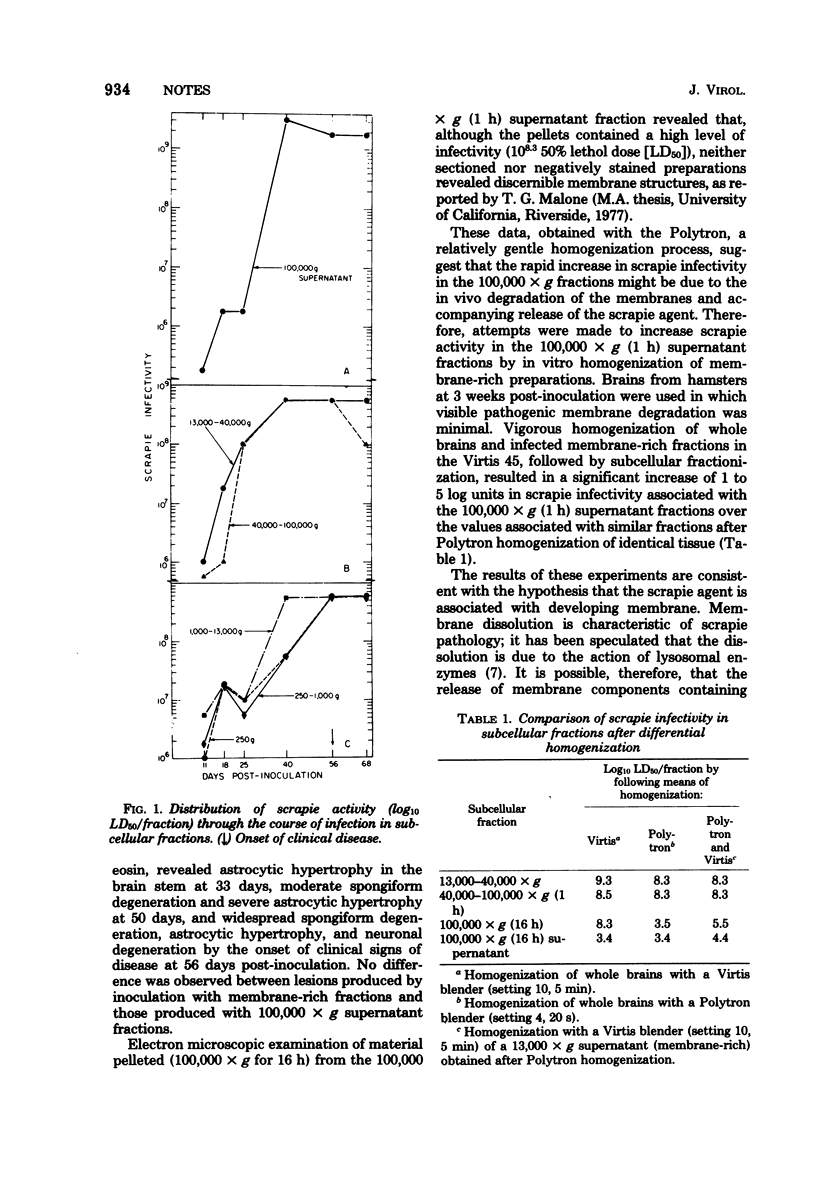
Determinations of scrapie activity in subcellular fractions from infected hamster brains through the asymptomatic and symptomatic course of infection revealed the presence of substantial amounts of scrapie infectivity in the 100,000 X g supernatant fractions, indicating that association with physically discernible membrane structures is not necessary for the transmission of the scrapie agent. An increase of scrapie infectivity in the 100,000 X g supernatant fractions after vigorous homogenization of infected membrane-rich fractions suggests that the agent is identical in membrane-rich and 100,000 X g supernatant fractions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke M. C., Millson G. C. The membrane location of scrapie infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):441–445. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. A., Hunter G. D. Nature of the scrapie agent. Nature. 1967 Sep 2;215(5105):1041–1043. doi: 10.1038/2151041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER G. D., MILLSON G. C., MEEK G. THE INTRACELLULAR LOCATION OF THE AGENT OF MOUSE SCRAPIE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:319–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. D., Kimberlin R. H., Millson G. C., Gibbons R. A. An experimental examination of the scrapie agent in cell membrane mixtures. I. Stability and physicochemical properties of the scrapie agent. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Jan;81(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. D., Millson G. C. Attempts to release the scrapie agent from tissue debris. J Comp Pathol. 1967 Jul;77(3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(67)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Marsh R. F. Comparison of scrapie and transmissible mink encephalopathy in hamsters. I. Biochemical studies of brain during development of disease. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):97–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. F., Sipe J. C., Morse S. S., Hanson R. P. Transmissible mink encephalopathy. Reduced spongiform degeneration in aged mink of the Chediak-Higashi genotype. Lab Invest. 1976 Apr;34(4):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millson G. C., Hunter G. D., Kimberlin R. H. An experimental examination of the scrapie agent in cell membrane mixtures. II. The association of scrapie activity with membrane fractions. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Apr;81(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould D. L., Smith W., Dawson A. M. Centrifugation studies on the infectivities of cellular fractions derived from mouse brain infected with scrapie (Suffolk strain). J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jul;40(1):71–79. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semancik J. S., Marsh R. F., Geelen J. L., Hanson R. P. Properties of the scrapie agent-endomembrane complex from hamster brain. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.693-700.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siakotos A. N., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Traub R. D., Bucana C. Partial purification of the scrapie agent from mouse brain by pressure disruption and zonal centrifugation in sucrose-sodium chloride gradients. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


