Abstract
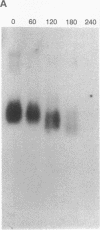
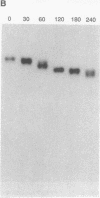
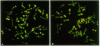
We have identified two allelic genomic cosmids from human chromosome 2, c8.1 and c29B, each containing two inverted arrays of the vertebrate telomeric repeat in a head-to-head arrangement, 5'(TTAGGG)n-(CCCTAA)m3'. Sequences flanking this telomeric repeat are characteristic of present-day human pretelomeres. BAL-31 nuclease experiments with yeast artificial chromosome clones of human telomeres and fluorescence in situ hybridization reveal that sequences flanking these inverted repeats hybridize both to band 2q13 and to different, but overlapping, subsets of human chromosome ends. We conclude that the locus cloned in cosmids c8.1 and c29B is the relic of an ancient telomere-telomere fusion and marks the point at which two ancestral ape chromosomes fused to give rise to human chromosome 2.
Full text
PDF

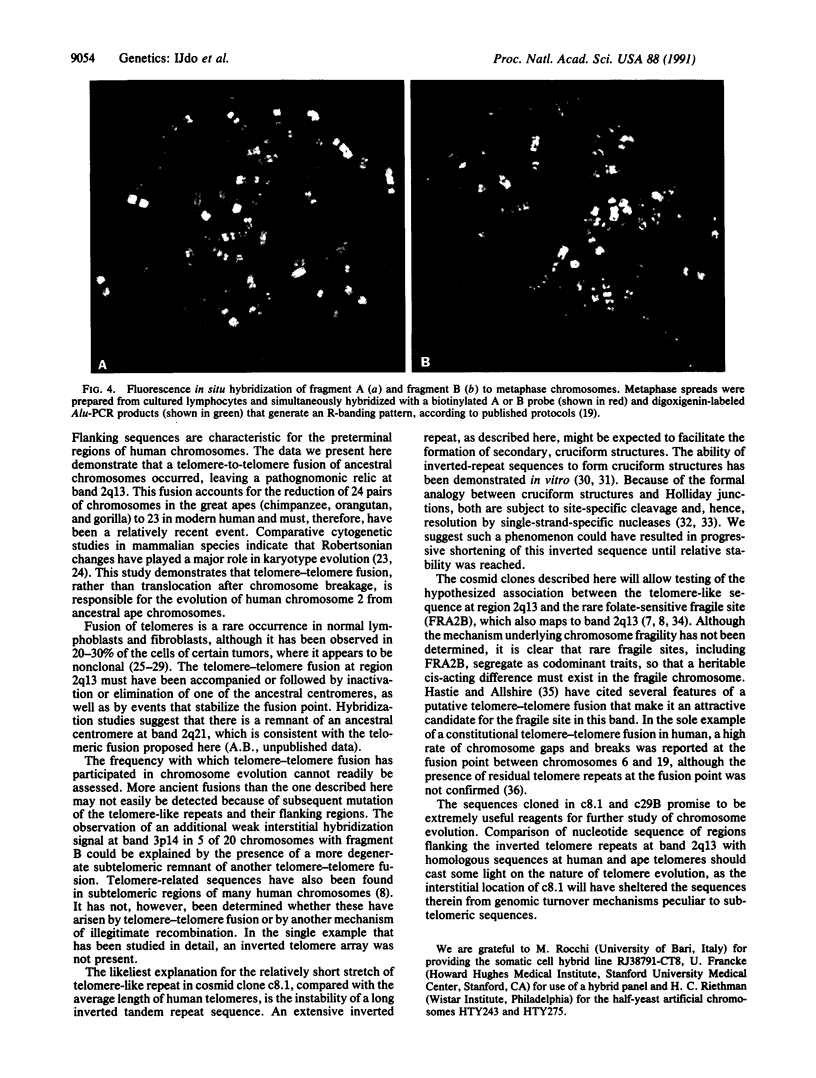

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Dempster M., Hastie N. D. Human telomeres contain at least three types of G-rich repeat distributed non-randomly. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4611–4627. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allshire R. C., Gosden J. R., Cross S. H., Cranston G., Rout D., Sugawara N., Szostak J. W., Fantes P. A., Hastie N. D. Telomeric repeat from T. thermophila cross hybridizes with human telomeres. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):656–659. doi: 10.1038/332656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Improved timing of hominoid evolution with a DNA clock. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):498–499. doi: 10.1038/314498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini A., Ward D. C. In situ hybridization banding of human chromosomes with Alu-PCR products: a simultaneous karyotype for gene mapping studies. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):770–774. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., MacKinnon P. J., Villasanté A., Spurr N., Buckle V. J., Dobson M. J. Structure and polymorphism of human telomere-associated DNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90293-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. F., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Structural and transcriptional analysis of a human subtelomeric repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):149–154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S., Lindsey J., Fantes J., McKay S., McGill N., Cooke H. The structure of a subterminal repeated sequence present on many human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6649–6657. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drets M. E., Therman E. Human telomeric 6; 19 translocation chromosome with a tendency to break at the fusion point. Chromosoma. 1983;88(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00327334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Rethoré M. O., Lejeune J. Comparaison du caryotype de l'orang-outang (Pongo pygmaeus) à celui de l'homme, du chimpanzé et du gorille. Ann Genet. 1975 Sep;18(3):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald P. H., Morris C. M. Telomeric association of chromosomes in B-cell lymphoid leukemia. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):385–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00291396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Hobom G. DNA sequences and structural homologies of the replication origins of lambdoid bacteriophages. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):621–627. doi: 10.1038/277621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Thorburn P. C., Rogers D. Meiotic and mitotic behavior of dicentric chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Feb;106(2):185–205. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Allshire R. C. Human telomeres: fusion and interstitial sites. Trends Genet. 1989 Oct;5(10):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Goodman M., Xu P., Chan K., Slightom J. L. Primate eta-globin DNA sequences and man's place among the great apes. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):234–238. doi: 10.1038/319234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G., Müller-Brechlin R., Szücs S. Telomeric association in two human renal tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Oct;28(2):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Kemper B. Cruciform-resolvase interactions in supercoiled DNA. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandahl N., Heim S., Arheden K., Rydholm A., Willén H., Mitelman F. Rings, dicentrics, and telomeric association in histiocytomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jan;30(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandahl N., Heim S., Kristoffersson U., Mitelman F., Röser B., Rydholm A., Willén H. Telomeric association in a malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Hum Genet. 1985;71(4):321–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00388457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R., Jarzabek V., Jaffe J. P., Hecht B. K., Hecht F., Sandberg A. A. Telomeric fusion in pre-T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):260–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00401240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethman H. C., Moyzis R. K., Meyne J., Burke D. T., Olson M. V. Cloning human telomeric DNA fragments into Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a yeast-artificial-chromosome vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6240–6244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Mattei J. F. Report of the committee on cytogenetic markers. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):316–324. doi: 10.1159/000132482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward O. G., Wurster-Hill D. H., Ratty F. J., Song Y. Comparative cytogenetics of Chinese and Japanese raccoon dogs, Nyctereutes procyonoides. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;45(3-4):177–186. doi: 10.1159/000132451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. A., Germino G. G., Krishna S., Buckle V. J., Reeders S. T. Telomere-related sequences at interstitial sites in the human genome. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):699–704. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90257-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienberg J., Jauch A., Stanyon R., Cremer T. Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Higgs D. R., Rack K. A., Buckle V. J., Spurr N. K., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Ceccherini I., Brown W. R., Harris P. C. Stable length polymorphism of up to 260 kb at the tip of the short arm of human chromosome 16. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90243-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. L., Müller U. R. Effects of palindrome size and sequence on genetic stability in the bacteriophage phi X174 genome. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90401-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster-Hill D. H., Ward O. G., Davis B. H., Park J. P., Moyzis R. K., Meyne J. Fragile sites, telomeric DNA sequences, B chromosomes, and DNA content in raccoon dogs, Nyctereutes procyonoides, with comparative notes on foxes, coyote, wolf, and raccoon. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;49(4):278–281. doi: 10.1159/000132677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Prakash O. The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science. 1982 Mar 19;215(4539):1525–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.7063861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T., Shiue L., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Naylor S. L., Killery A. M., Varmus H. E. Structure and variability of human chromosome ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):518–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]