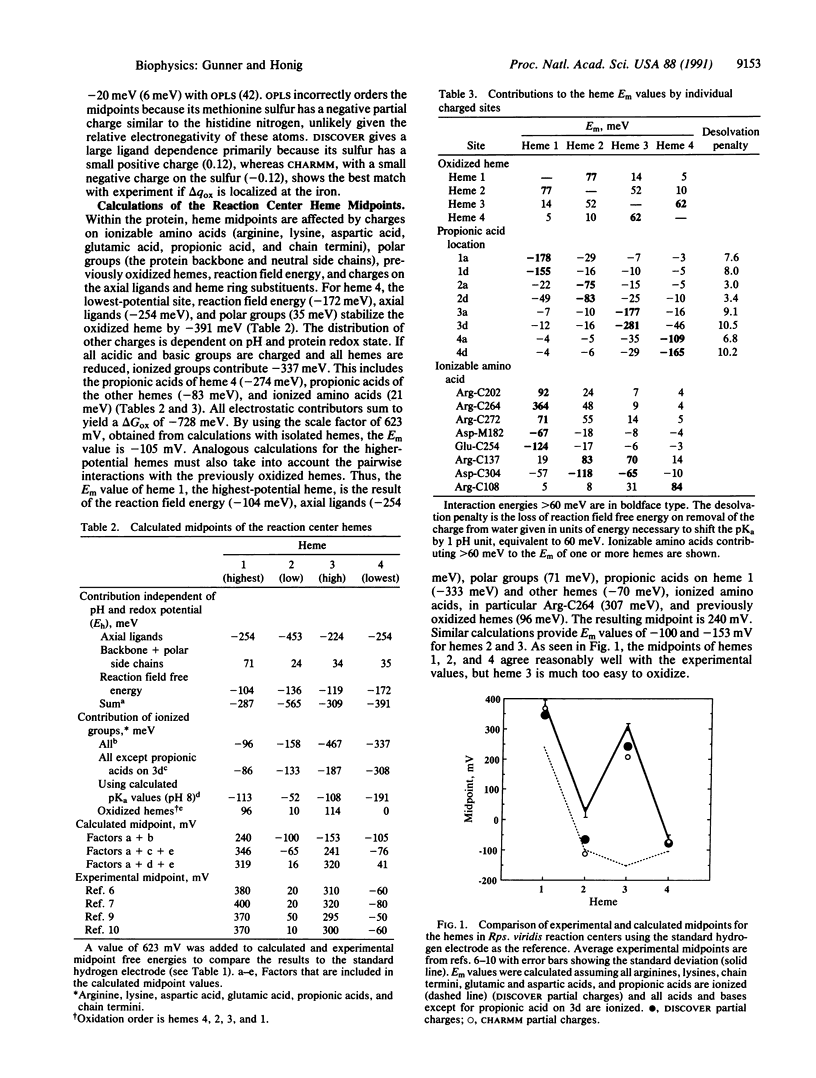
Abstract
The photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas viridis has four hemes in a linear arrangement with alternating high- and low-potential sites. Their midpoints are -60, 20, 310, and 380 mV [Dracheva, S. M., Drachev, L. A., Konstantinov, A. A., Semenov, A. Y., Skulachev, V. P., Arutjunjan, A. M., Shuvalov, V. A. & Zaberezhnaya, S. M. (1988) Eur. J. Biochem. 171, 253-264]. Electrostatic calculations reproduce the 440-mV midpoint spread and assignments of high- and low-potential hemes. When calculations on model compounds to connect the theoretical midpoints to the standard hydrogen electrode are used, the absolute electrochemical midpoints for the reaction center hemes are also in good agreement with experiment. The free energy of oxidation is found to be dependent on pairwise interactions with charged amino acids, heme propionic acids, previously oxidized hemes, and axial ligands and on the reaction field induced by heme oxidation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashford D., Karplus M. pKa's of ionizable groups in proteins: atomic detail from a continuum electrostatic model. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10219–10225. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg A. K., Warshel A. Control of the redox potential of cytochrome c and microscopic dielectric effects in proteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1675–1681. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Michel H. Nobel lecture. The photosynthetic reaction centre from the purple bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2149–2170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracheva S. M., Drachev L. A., Konstantinov A. A., Semenov AYu, Skulachev V. P., Arutjunjan A. M., Shuvalov V. A., Zaberezhnaya S. M. Electrogenic steps in the redox reactions catalyzed by photosynthetic reaction-centre complex from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):253–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. H. Energetics of charge-charge interactions in proteins. Proteins. 1988;3(1):32–52. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. H. The dielectric constant of a folded protein. Biopolymers. 1986 Nov;25(11):2097–2119. doi: 10.1002/bip.360251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. Calculation of the total electrostatic energy of a macromolecular system: solvation energies, binding energies, and conformational analysis. Proteins. 1988;4(1):7–18. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Rashin A., Fine R., Honig B. On the calculation of electrostatic interactions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):503–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler A. T., Moult J. Computer simulation of the solvent structure around biological macromolecules. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):222–226. doi: 10.1038/272222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury H. A., Cronin J. R., Fanger M. W., Hettinger T. P., Murphy A. J., Myer Y. P., Vinogradov S. N. Complex formation between methionine and a heme peptide from cytochrome c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1658–1664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassner R. J. A theoretical model for the effects of local nonpolar heme environments on the redox potentials in cytochromes. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Apr 18;95(8):2674–2677. doi: 10.1021/ja00789a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassner R. J. Effects of nonpolar environments on the redox potentials of heme complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2263–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper I., Hagstrom R., Fine R., Sharp K., Honig B. Focusing of electric fields in the active site of Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase: effects of ionic strength and amino-acid modification. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):47–59. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Kamen M. D. New perspectives on c-type cytochromes. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:105–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60469-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R. Control of redox properties of cytochrome c by special electrostatic interactions. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Pettigrew G. W., Rogers N. K. Factors influencing redox potentials of electron transfer proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):4998–4999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.4998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Structural basis for the variation in redox potential of cytochromes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80793-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock M. L., Rongey S. H., Feher G., Okamura M. Y. Pathway of proton transfer in bacterial reaction centers: replacement of glutamic acid 212 in the L subunit by glutamine inhibits quinone (secondary acceptor) turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parson W. W., Chu Z. T., Warshel A. Electrostatic control of charge separation in bacterial photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 26;1017(3):251–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C. Electrostatic influence on energetics of electron transfer reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3082–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers N. K., Moore G. R., Sternberg M. J. Electrostatic interactions in globular proteins: calculation of the pH dependence of the redox potential of cytochrome c551. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):613–616. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90248-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Honig B. Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules: theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:301–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman K., Yang A. S., Honig B., Fletterick R. Electrical potentials in trypsin isozymes. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):9918–9926. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E. Haem exposure as the determinate of oxidation-reduction potential of haem proteins. Nature. 1978 Sep 7;275(5675):73–74. doi: 10.1038/275073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Roxby R. Interpretation of protein titration curves. Application to lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1972 May 23;11(11):2192–2198. doi: 10.1021/bi00761a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollin G., Hanson L. K., Caffrey M., Meyer T. E., Cusanovich M. A. Redox pathways in electron-transfer proteins: correlations between reactivities, solvent exposure, and unpaired-spin-density distributions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3693–3697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warme P. K., Hager L. P. Heme sulfuric anhydrides. II. Properties of heme models prepared from mesoheme sulfuric anhydrides. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1606–1614. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


