Abstract
A novel reduced nicotinamide-dependent disulfide reductase, the 2,2'-dithiodiethanesulfonate [(S-CoM)2] reductase (CoMDSR) of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum was purified 405-fold to electrophoretic homogeneity. Both NADPH and NADH functioned as electron donors, although rates with NADPH were three times higher. Reduced factor F420, the deazaflavin electron carrier characteristic of methanogenic bacteria, was not a substrate for the enzyme. The enzyme was most active with (S-CoM)2 but could also reduce L-cystine at 23% the (S-CoM)2 rate. Results of sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicated that the enzyme was monomeric with an Mr of about 64,000; spectral analysis showed that it was a flavoprotein with an estimated composition of one molecule of flavin per polypeptide. Maximal activity occurred at 64 degrees C, and the pH optimum was 8.5. The apparent Km for both NADPH and (S-CoM)2 was 80 microM. The enzyme was completely inactivated by oxygen in crude cell extracts but was oxygen stable in the homogeneous state. The low activity of the CoMDSR in cell extracts as well as its relatively low rate of reducing CoM-S-S-HTP (the heterodisulfide of the two thiol cofactors involved in the last step of methanogenesis) make it unlikely that it plays a role in the methylreductase system. It may be involved in the redox balance of the cell, such as the NADPH-dependent bis-gamma-glutamylcystine reductase with which it shows physical similarity in another archaebacterium, Halobacterium halobium (A. R. Sundquist and R. C. Fahey, J. Bacteriol. 170:3459-3467, 1988). The CoMDSR might also be involved in regenerating the coenzyme M trapped as its homodisulfide, a nonutilizable form of the cofactor.
Full text
PDF


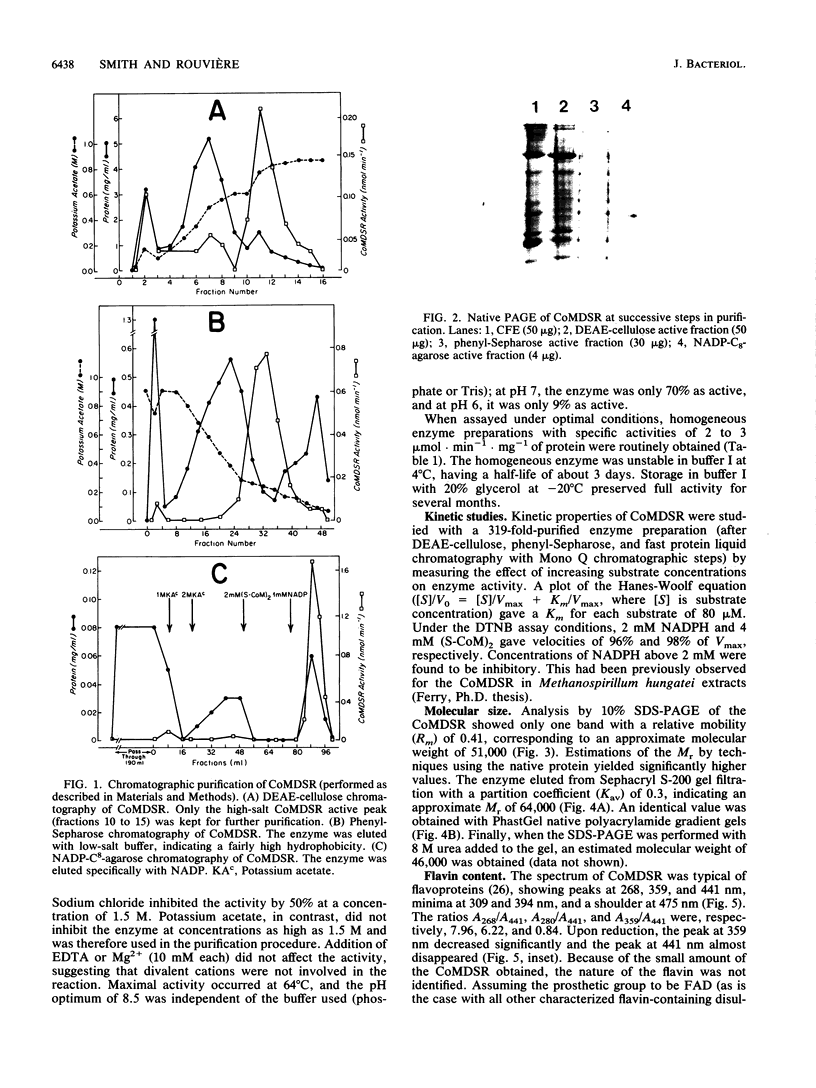
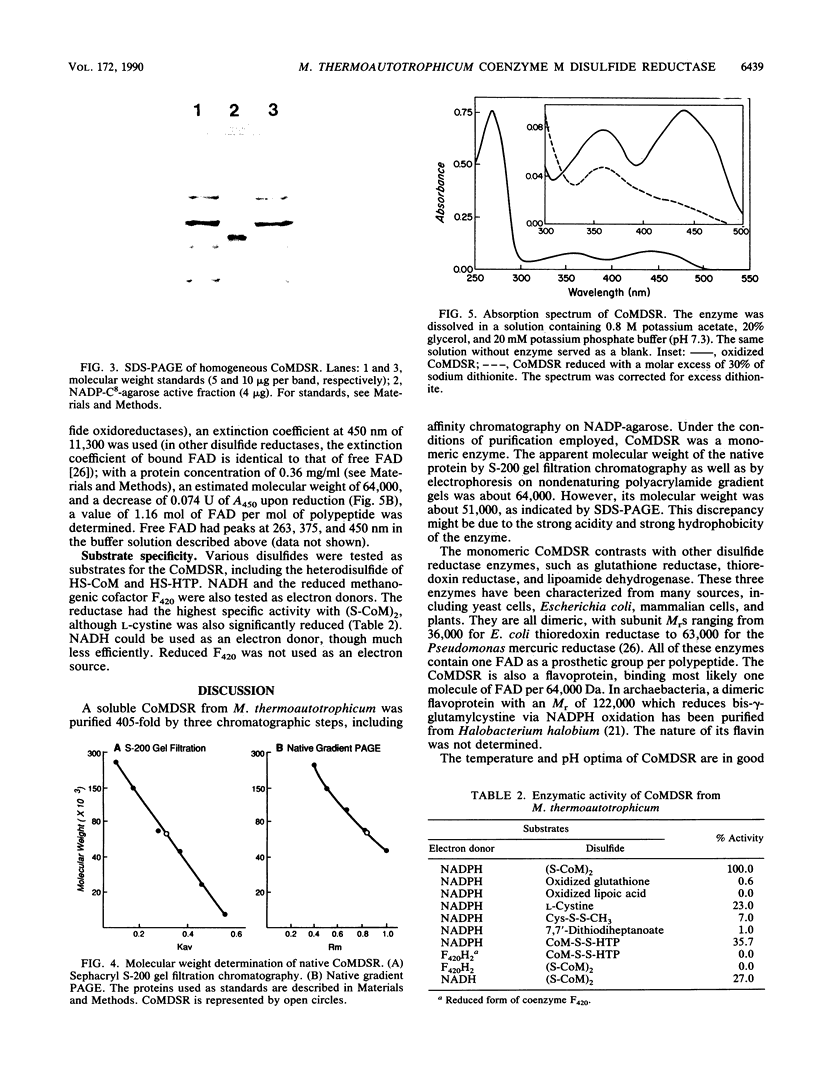


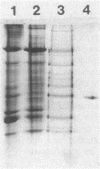
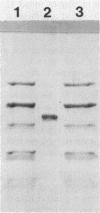
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. Transport of coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid) in Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):264–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.264-273.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobik T. A., Olson K. D., Noll K. M., Wolfe R. S. Evidence that the heterodisulfide of coenzyme M and 7-mercaptoheptanoylthreonine phosphate is a product of the methylreductase reaction in Methanobacterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):455–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobik T. A., Wolfe R. S. An unusual thiol-driven fumarate reductase in Methanobacterium with the production of the heterodisulfide of coenzyme M and N-(7-mercaptoheptanoyl)threonine-O3-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18714–18718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybas M., Konisky J. Transport of coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid) and methylcoenzyme M [(2-methylthio)ethanesulfonic acid] in Methanococcus voltae: identification of specific and general uptake systems. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5866–5871. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5866-5871.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirich L. D., Vogels G. D., Wolfe R. S. Proposed structure for coenzyme F420 from Methanobacterium. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4583–4593. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellefson W. L., Wolfe R. S. Component C of the methylreductase system of Methanobacterium. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4259–4262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellefson W. L., Wolfe R. S. Role of component C in the methylreductase system of Methanobacterium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8388–8389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellermann J., Hedderich R., Böcher R., Thauer R. K. The final step in methane formation. Investigations with highly purified methyl-CoM reductase (component C) from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum (strain Marburg). Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):669–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Tandon S. M., Wolfe R. S. A procedure for anaerobic column chromatography employing an anaerobic Freter-type chamber. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 15;101(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNITZ M. Crystalline inorganic pyrophosphatase isolated from baker's yeast. J Gen Physiol. 1952 Jan;35(3):423–450. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll K. M., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Tanner R. S., Wolfe R. S. Structure of component B (7-mercaptoheptanoylthreonine phosphate) of the methylcoenzyme M methylreductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4238–4242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière P. E., Wolfe R. S. Novel biochemistry of methanogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7913–7916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist A. R., Fahey R. C. The novel disulfide reductase bis-gamma-glutamylcystine reductase and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase from Halobacterium halobium: purification by immobilized-metal-ion affinity chromatography and properties of the enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3459–3467. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3459-3467.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. A simplified assay for coenzyme M (HSCH2CH2SO3). Resolution of methylcobalamin-coenzyme M methyltransferase and use of sodium borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4886–4890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENKATARAMAN R., REITHEL F. J. Carbohydrates of the sapotaceae. I. The origin of lactose in A. sapota. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Jun;75(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90444-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meijden P., van der Lest C., van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Reductive activation of methanol: 5-hydroxybenzimidazolylcobamide methyltransferase of Methanosarcina barkeri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):760–766. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]