Abstract
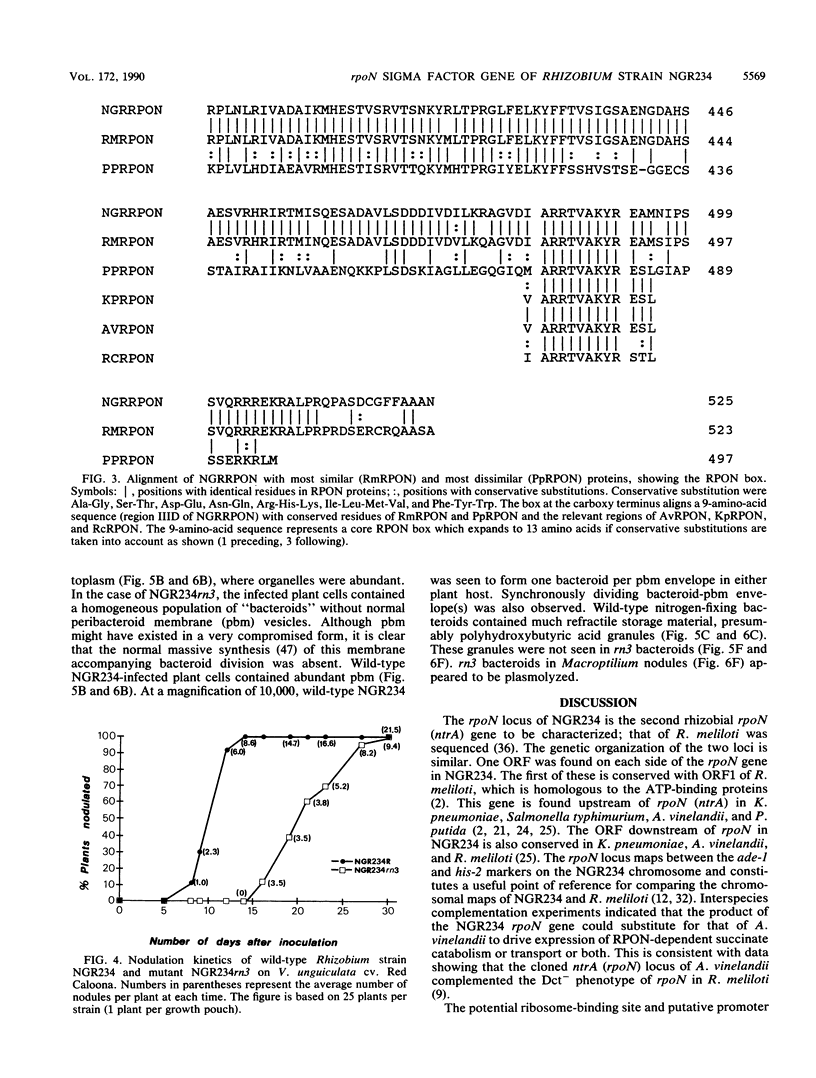
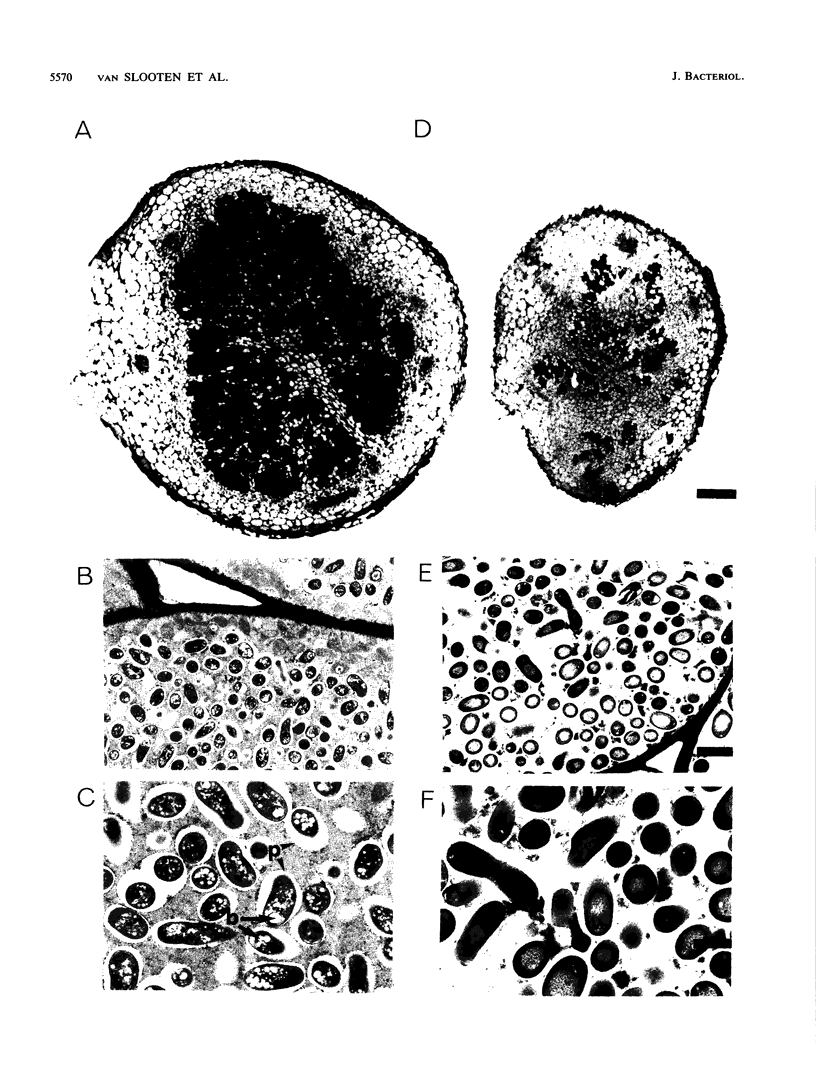
We report the nucleotide sequence of the rpoN gene from broad-host-range Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 and analyze the encoded RPON protein, a sigma factor. Comparative analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence of RPON from NGR234 with sequences from other gram-negative bacteria identified a perfectly conserved RPON box unique to RPON sigma factors. Symbiotic regulatory phenotypes were defined for a site-directed internal deletion within the coding sequence of the rpoN gene of Rhizobium strain NGR234: they included quantitative nodulation kinetics on Vigna unguiculata and microscopic analysis of the Fix- determinate nodules of V. unguiculata and Macroptilium atropurpureum. RPON was a primary coregulator of nodulation and was implicated in establishment or maintenance of the plant-synthesized peribacteroid membrane. Phenotypes of rpoN in Rhizobium strain NGR234 could be grouped as symbiosis related, rather than simply pleiotropically physiological as in free-living bacteria such as Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas putida.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aegerter E., Trachsel H. Determination of size and orientation of DNA fragments cloned in phage M13 by S1 nuclease mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):372–372. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Identification of a gene linked to Rhizobium meliloti ntrA whose product is homologous to a family to ATP-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1932–1941. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1932-1941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M. Kilo-sequencing: an ordered strategy for rapid DNA sequence data acquisition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):349–368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Turgeon B. G., Bauer W. D. Early Events in the Infection of Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr) by Rhizobium japonicum: I. LOCALIZATION OF INFECTIBLE ROOT CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cali B. M., Micca J. L., Stewart V. Genetic regulation of nitrate assimilation in Klebsiella pneumoniae M5al. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2666–2672. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2666-2672.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke T., Jording D., Kapp D., Pühler A. Identification and sequence analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti dctA gene encoding the C4-dicarboxylate carrier. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5551–5560. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5551-5560.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Kunkel B., De Vos G. F., Signer E. R. Second symbiotic megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti carrying exopolysaccharide and thiamine synthesis genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.66-72.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Oresnik I., Bottacin A. Mutants of Rhizobium meliloti defective in succinate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3396–3403. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3396-3403.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Wood J. M., Jordan D. C. Symbiotic properties of C4-dicarboxylic acid transport mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1403–1413. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1403-1413.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Alvarez-Morales A., Hennecke H. The pleiotropic nature of symbiotic regulatory mutants: Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifA gene is involved in control of nif gene expression and formation of determinate symbiosis. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1165–1173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Bang M., Ausubel F. M. Ultrastructural analysis of ineffective alfalfa nodules formed by nif::Tn5 mutants of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):367–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.367-380.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Gu B. H., Albright L. M., Nixon B. T. Conservation between coding and regulatory elements of Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium leguminosarum dct genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5244–5253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5244-5253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D., Gutterson N. An efficient mobilizable cosmid vector, pRK7813, and its use in a rapid method for marker exchange in Pseudomonas fluorescens strain HV37a. Gene. 1987;61(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler T., Harayama S., Ramos J. L., Timmis K. N. Involvement of Pseudomonas putida RpoN sigma factor in regulation of various metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4326–4333. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4326-4333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Gibbins J. R. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrogen-regulation gene ntrA of Klebsiella pneumoniae and comparison with conserved features in bacterial RNA polymerase sigma factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7607–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Stewart W. D. Studies on the regulation and function of the Klebsiella pneumoniae ntrA gene. Gene. 1985;35(3):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Gibbins J., Toukdarian A. The nucleotide sequence of the sigma factor gene ntrA (rpoN) of Azotobacter vinelandii: analysis of conserved sequences in NtrA proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00325701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. D., Austin S., Dixon R. A. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifLA promoter by NTRC is face-of-the-helix dependent and the activator stabilizes the interaction of sigma 54-RNA polymerase with the promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3491–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. In vivo studies on the interaction of RNA polymerase-sigma 54 with the Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti nifH promoters. The role of NifA in the formation of an open promoter complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. J., Heycke N., Trenz S. P., Ratet P., de Bruijn F. J., Schell J. Synthesis of an opine-like compound, a rhizopine, in alfalfa nodules is symbiotically regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9133–9137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Lyttleton P., Robertson J. G. C(4)-dicarboxylate transport mutants of Rhizobium trifolii form ineffective nodules on Trifolium repens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4284–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan J., Olivares J. Implication of nifA in regulation of genes located on a Rhizobium meliloti cryptic plasmid that affect nodulation efficiency. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4154–4161. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4154-4161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Parsot C., Bouvier J. Two functional domains conserved in major and alternate bacterial sigma factors. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Shiina T., Takahashi H. Multiple principal sigma factor homologs in eubacteria: identification of the "rpoD box". Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1040–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.3194753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toukdarian A., Kennedy C. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Azotobacter vinelandii: isolation of ntr and glnA genes and construction of ntr mutants. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):399–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. P., Birkenhead K., Boesten B., Manian S., O'Gara F. Genetic analysis and regulation of the Rhizobium meliloti genes controlling C4-dicarboxylic acid transport. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90473-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H., Pankhurst C. E., Kondorosi A., Broughton W. J. Morphology of root nodules and nodule-like structures formed by Rhizobium and Agrobacterium strains containing a Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):787–794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




