Abstract
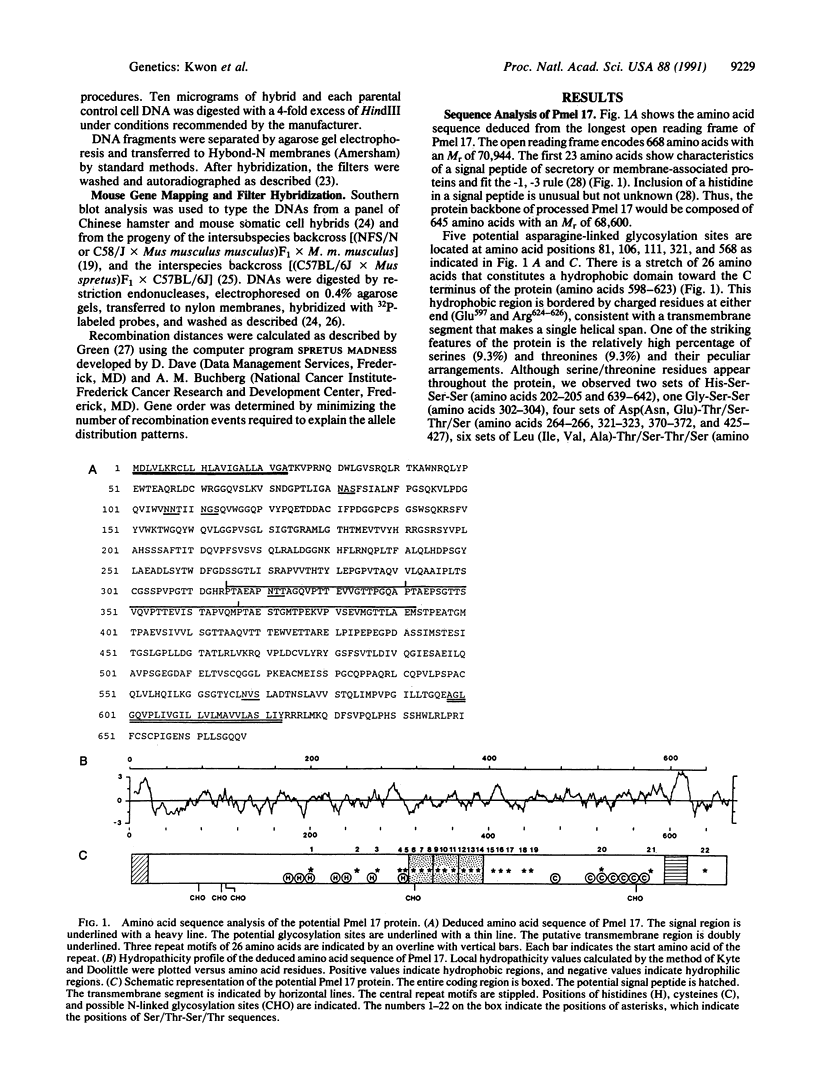
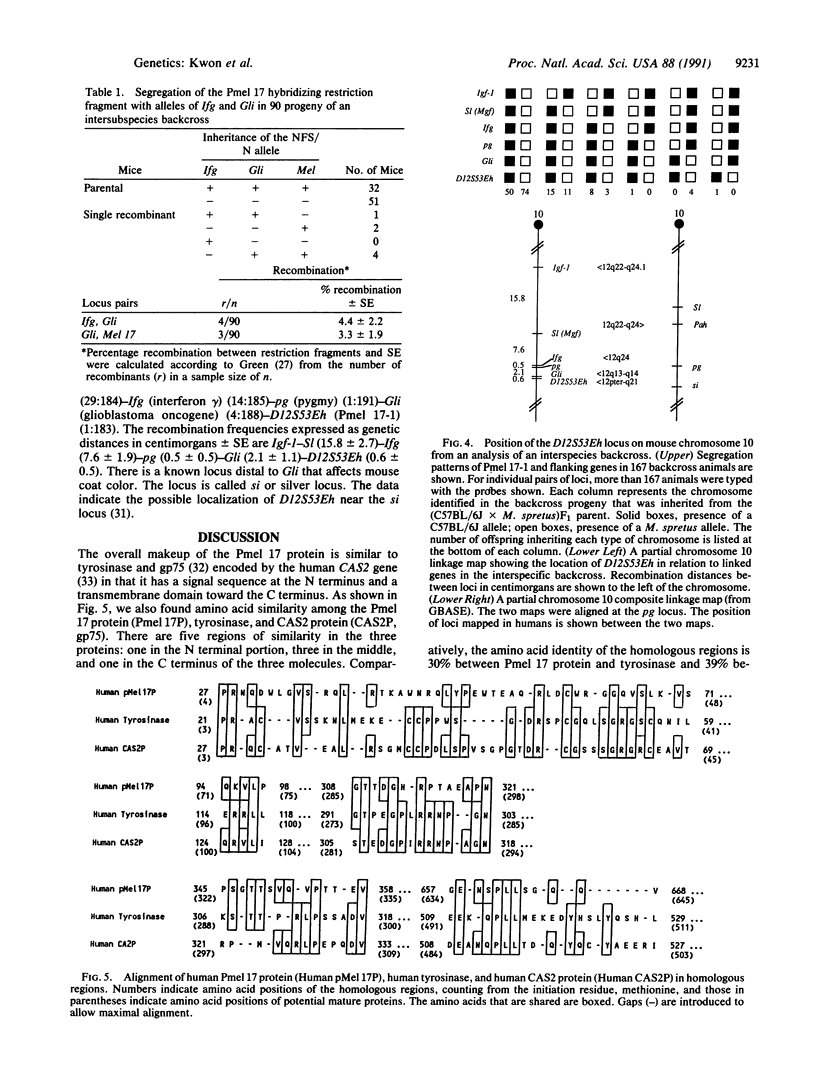
Melanocytes preferentially express an mRNA species, Pmel 17, whose protein product cross-reacts with anti-tyrosinase antibodies and whose expression correlates with the melanin content. We have now analyzed the deduced protein structure and mapped its chromosomal location in mouse and human. The amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the Pmel 17 cDNA showed that the protein is composed of 645 amino acids with a molecular weight of 68,600. The Pmel 17 protein contains a putative leader sequence and a potential membrane anchor segment, which indicates that this may be a membrane-associated protein in melanocytes. The deduced protein contains five potential N-glycosylation sites and relatively high levels of serine and threonine. Three repeats of a 26-amino acid motif appear in the middle of the molecule. The human Pmel 17 gene, designated D12S53E, maps to chromosome 12, region 12pter-q21; and the mouse homologue, designated D12S53Eh, maps to the distal region of mouse chromosome 10, a region also known to carry the coat color locus si (silver).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arheden K., Rønne M., Mandahl N., Heim S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Mitelman F. In situ hybridization localizes the human putative oncogene GLI to chromosome subbands 12q13.3-14.1. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):1–2. doi: 10.1007/BF00288260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balling R., Deutsch U., Gruss P. undulated, a mutation affecting the development of the mouse skeleton, has a point mutation in the paired box of Pax 1. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):531–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton D. E., Arquint M., Roder J., Dunn R., Francke U. The myelin-associated glycoprotein gene: mapping to human chromosome 19 and mouse chromosome 7 and expression in quivering mice. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchberg A. M., Bedigian H. G., Taylor B. A., Brownell E., Ihle J. N., Nagata S., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Localization of Evi-2 to chromosome 11: linkage to other proto-oncogene and growth factor loci using interspecific backcross mice. Oncogene Res. 1988;2(2):149–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chintamaneni C. D., Halaban R., Kobayashi Y., Witkop C. J., Jr, Kwon B. S. A single base insertion in the putative transmembrane domain of the tyrosinase gene as a cause for tyrosinase-negative oculocutaneous albinism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5272–5276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chintamaneni C. D., Ramsay M., Colman M. A., Fox M. F., Pickard R. T., Kwon B. S. Mapping the human CAS2 gene, the homologue of the mouse brown (b) locus, to human chromosome 9p22-pter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 15;178(1):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91803-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danciger M., Bowes C., Kozak C. A., LaVail M. M., Farber D. B. Fine mapping of a putative rd cDNA and its co-segregation with rd expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 Aug;31(8):1427–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Yang-Feng T. L., Brissenden J. E., Ullrich A. Chromosomal mapping of genes involved in growth control. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):855–866. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Halden N. F., Buckler C. E., Kozak C. A. Genetic mapping of the mouse c-fms proto-oncogene to chromosome 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1055–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1055-1056.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Siracusa L. D., Gilbert D. J., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Chada K., Silan C. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. A genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 10: localization of eighteen molecular markers using a single interspecific backcross. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):855–866. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Ruppert J. M., Bigner S. H., Vogelstein B. The GLI gene is a member of the Kruppel family of zinc finger proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):371–374. doi: 10.1038/332371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Peyser M., Krall M., Mariano T. M., Kumar C. S., Pestka S., Mock B. A. Molecular genetic markers spanning mouse chromosome 10. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):519–524. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90039-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Halaban R., Kim G. S., Usack L., Pomerantz S., Haq A. K. A melanocyte-specific complementary DNA clone whose expression is inducible by melanotropin and isobutylmethyl xanthine. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Dec;4(6):339–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Haq A. K., Pomerantz S. H., Halaban R. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for human tyrosinase that maps at the mouse c-albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7473–7477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner A. M., Pawelek J. Dopachrome conversion: a possible control point in melanin biosynthesis. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Aug;75(2):192–195. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12522650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner A., Pawelek J. Mammalian tyrosinase catalyzes three reactions in the biosynthesis of melanin. Science. 1982 Sep 17;217(4565):1163–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.6810464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Law M. L., Morse H. G., Kao F. T., Rabin M., Ruddle F. H., Woo S. L. Regional mapping of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene and the phenylketonuria locus in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6221–6225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Efficient mapping of protein antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7013–7017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton C. C., Byers M. G., Nakai H., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. Human genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II and epidermal growth factor are located on 12q22----q24.1, 11p15, and 4q25----q27, respectively. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(4):245–249. doi: 10.1159/000132237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H. Maps of linkage and synteny homologies between mouse and man. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H. The tyrosine hydroxylase activity of mammalian tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Chalupny J., Whitney J. A., Hammond C., Amrein K. E., Kavathas P., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. Short related sequences in the cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 mediate binding to the amino-terminal domain of the p56lck tyrosine protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1853–1862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K. M., Giebel L. B., King R. A. Detection of mutations in the tyrosinase gene in a patient with type IA oculocutaneous albinism. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 14;322(24):1724–1728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006143222407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y., Takeda A., Okinaga S., Tagami H., Shibahara S. Human oculocutaneous albinism caused by single base insertion in the tyrosinase gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):990–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayasaradhi S., Bouchard B., Houghton A. N. The melanoma antigen gp75 is the human homologue of the mouse b (brown) locus gene product. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1375–1380. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., DeGennaro L. J., Francke U. Genes for synapsin I, a neuronal phosphoprotein, map to conserved regions of human and murine X chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8679–8683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




