Abstract
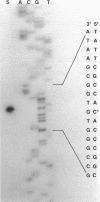
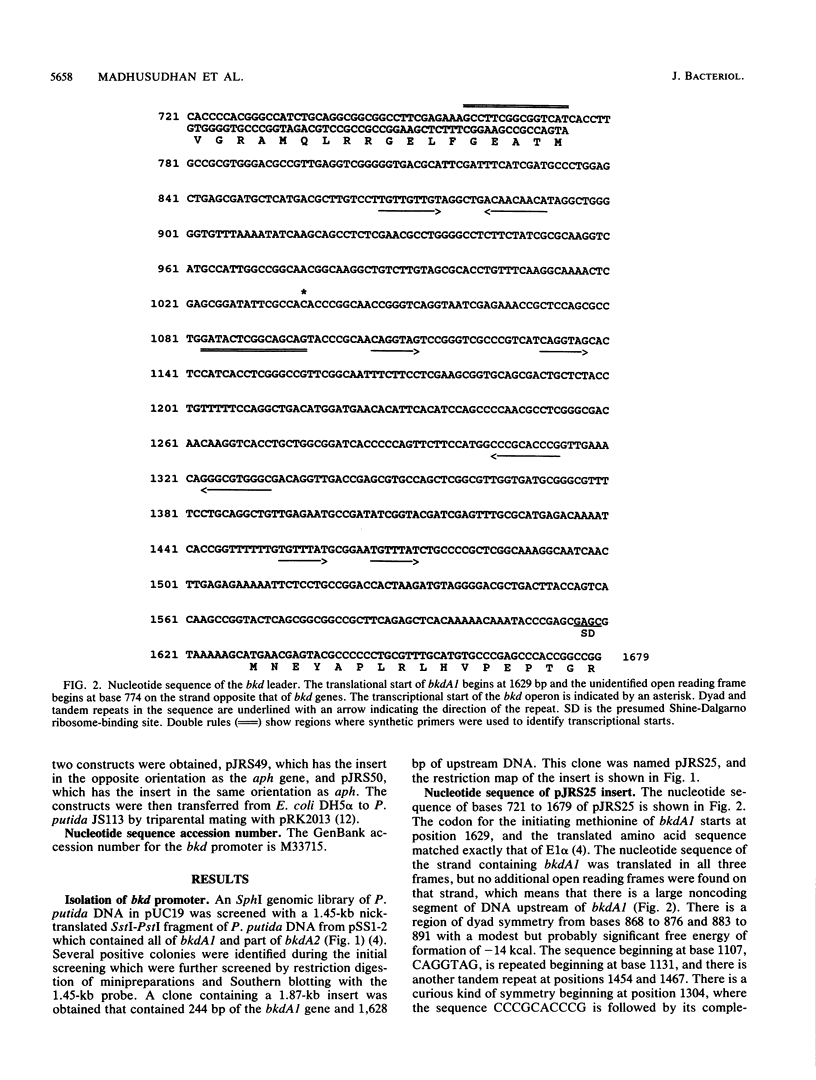
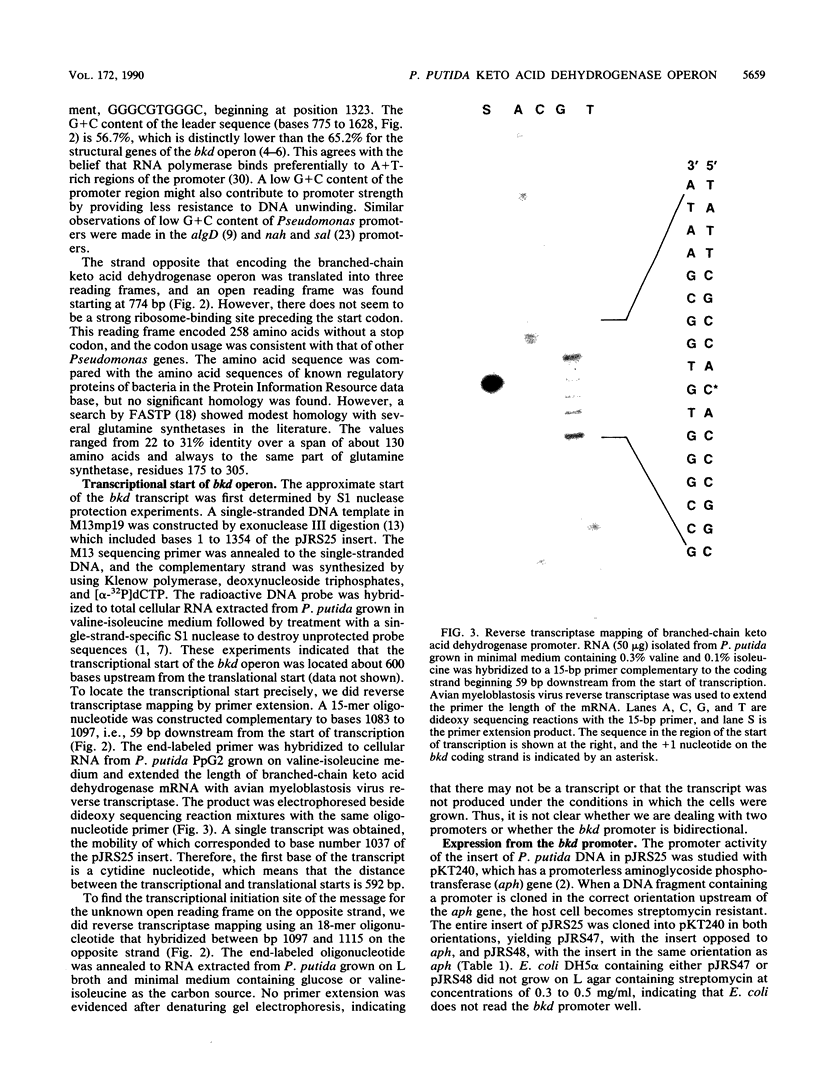
Branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase is a multienzyme complex produced by Pseudomonas putida when it is grown in a minimal medium containing branched-chain amino acids. A 1.87-kilobase (kb) DNA fragment was cloned and sequenced which contained 0.24 kb of the E1 alpha structural gene and 1.6 kb of upstream DNA. There were 854 base pairs (bp) of noncoding DNA upstream of bkdA1, the first gene of the bkd operon, and 592 bp between the transcriptional and translational starts. The G + C content of the noncoding region was 56.7% compared with 65.2% for all the structural genes of the operon. A partial open reading frame was found on the strand opposite that of the bkd operon beginning at base 774. When the bkd promoter was cloned into the promoter probe vector pKT240, streptomycin resistance was obtained in P. putida but not Escherichia coli with the promoter in both orientations, which indicates either that the bkd promoter is bidirectional or that there are two promoters in this region. A series of ordered deletions on both sides of the proposed site of the start of transcription revealed that almost 700 bp upstream of the start of translation were required for expression. Streptomycin resistance was also obtained in an rpoN mutant of P. putida KT2440 containing constructs with the intact bkd promoter, indicating that the bkd operon does not require the rpoN sigma factor for expression. Another construct containing the bkd promoter, bkdA1, and bkdA2 in pKT240 was used to transform P. putida JS113, a mutant which was unable to produce the E1 subunits of the branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase. In this case, very high inducible expression of the bkd operon was obtained.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldea M., Claverie-Martín F., Díaz-Torres M. R., Kushner S. R. Transcript mapping using [35S]DNA probes, trichloroacetate solvent and dideoxy sequencing ladders: a rapid method for identification of transcriptional start points. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M. M., Amann E., Lurz R., Rückert B., Bagdasarian M. Activity of the hybrid trp-lac (tac) promoter of Escherichia coli in Pseudomonas putida. Construction of broad-host-range, controlled-expression vectors. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Oster T., Branlant G. Nucleotide sequence determination of the DNA region coding for Bacillus stearothermophilus glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and of the flanking DNA regions required for its expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Idriss J. M., Sokatch J. R. Similarity of the E1 subunits of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida to the corresponding subunits of mammalian branched-chain-oxoacid and pyruvate dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 15;176(2):311–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the transacylase components of branched chain oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida, and the pyruvate and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):165–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Sequence analysis of the lpdV gene for lipoamide dehydrogenase of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):61–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Mapping of gene transcripts by nuclease protection assays and cDNA primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:611–632. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional regulation of the algD gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4567–4581. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. The xylABC promoter from the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid is activated by nitrogen regulatory genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00330393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Raibaud O. Expression of the Escherichia coli malPQ operon remains unaffected after drastic alteration of its promoter. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1221–1227. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1221-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Allison S. L., Phillips A. T. Identification of multiple repressor recognition sites in the hut system of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4189–4195. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4189-4195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H., Aramaki H., Yamaguchi E., Takeuchi K., Horiuchi T., Gunsalus I. C. camR, a negative regulator locus of the cytochrome P-450cam hydroxylase operon. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1089–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1089-1095.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler T., Harayama S., Ramos J. L., Timmis K. N. Involvement of Pseudomonas putida RpoN sigma factor in regulation of various metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4326–4333. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4326-4333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., Marshall V. D., Sokatch J. R., Unger L. Common enzymes of branched-chain amino acid catabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):198–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.198-204.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCully V., Burns G., Sokatch J. R. Resolution of branched-chain oxo acid dehydrogenase complex of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):737–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2330737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. T., Mulfinger L. M. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa during induction and carbon catabolite repression of histidase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1286–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1286-1292.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A. Homology between nucleotide sequences of promoter regions of nah and sal operons of NAH7 plasmid of Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):369–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Williams D. L. Apolipoprotein II messenger RNA. Transcriptional and splicing heterogeneity yields six 5'-untranslated leader sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9929–9935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokatch J. R., McCully V., Gebrosky J., Sokatch D. J. Isolation of a specific lipoamide dehydrogenase for a branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.639-646.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokatch J. R., McCully V., Roberts C. M. Purification of a branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.647-652.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes P. J., Burns G., Menard J., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Molecular cloning of genes encoding branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1619–1625. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1619-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes P. J., Menard J., McCully V., Sokatch J. R. Conjugative mapping of pyruvate, 2-ketoglutarate, and branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase genes in Pseudomonas putida mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.203-208.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider H. J., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. A relationship between DNA helix stability and recognition sites for RNA polymerase. Science. 1979 Aug 3;205(4405):508–511. doi: 10.1126/science.377494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., Olsen R. H., Ballou D. P. Cloning, expression, and regulation of the Pseudomonas cepacia protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5907–5914. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5907-5914.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]