Abstract
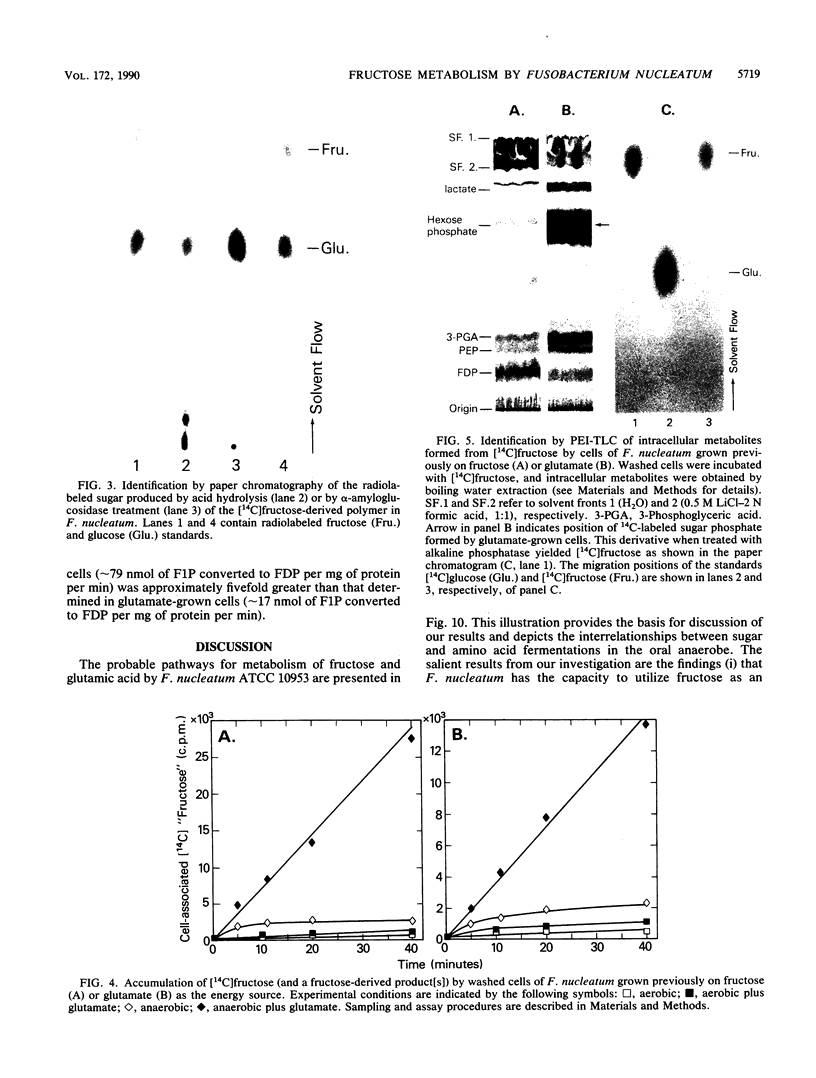
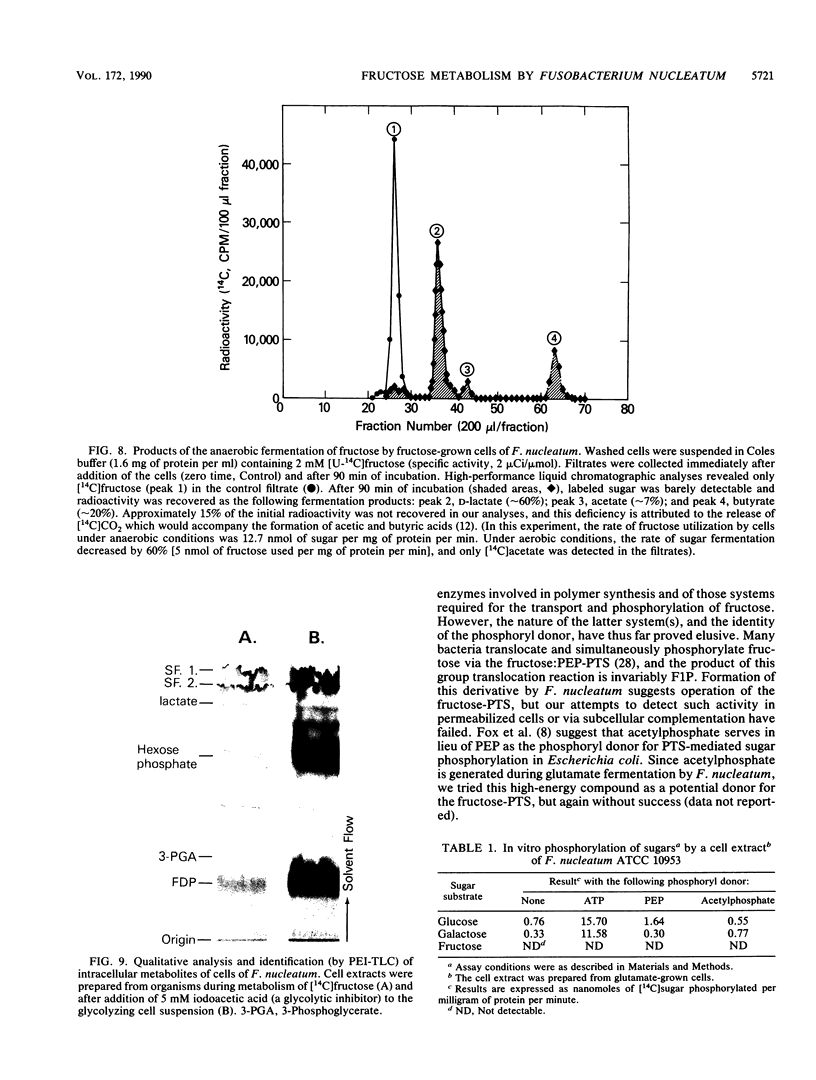
Energy for the anaerobic growth of Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953 can be derived from the fermentation of sugar (fructose) or amino acid (glutamate). During growth on fructose, the cells formed large intracellular granules which after extraction yielded glucose by either acid or enzymatic hydrolysis. The endogenous polymer was subsequently metabolized, and after overnight incubation of the cells in buffer, the glucan granules were no longer detectable by electron microscopy. Anaerobically, washed cells grown previously on fructose fermented this sugar to a mixture of lactic, acetic, and butyric acids, and little intracellular glucan was formed. Aerobically, the cells slowly metabolized fructose to acetate. Provision of glutamic acid as an additional energy (ATP) source elicited rapid synthesis of polymer by glycolyzing cells. Intracellular granules were not present in glutamate-grown cells, and under anaerobic conditions, the resting cells failed to metabolize [14C] fructose. However, the addition of glutamic acid to the suspension resulted in the rapid accumulation of sugar by the cells. Approximately 15% of the 14C-labeled material was extractable with boiling water, and by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, this phosphorylated derivative was identified as [14C]fructose-1-phosphate. The nonextractable material represented [14C]glucan polymer. Fructose-1-phosphate kinase activity in fructose-grown cells was fivefold greater than that in glutamate-grown cells. We suggest that the activity of fructose-1-phosphate kinase and the availability of ATP regulate the flow of fructose into either the glycolytic or polymer-synthesizing pathway in F. nucleatum.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken V., Högh B. T., Jensen H. B. Utilization of amino acids and peptides by Fusobacterium nucleatum. Scand J Dent Res. 1989 Feb;97(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1989.tb01429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A. Amino acid degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:23–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A., Kahn J. M., Hedrick L. Pathway of lysine degradation in Fusobacterium nucleatum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):201–207. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.201-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. W., Duerden B. I. Identification of fusobacteria in a routine diagnostic laboratory. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;59(2):171–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb03318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckel W., Barker H. A. Two pathways of glutamate fermentation by anaerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1248–1260. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1248-1260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles R. S., Jr Glucose utilization by resting cells of Fusobacterium polymorphum. Arch Oral Biol. 1977;22(2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(77)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. K., Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Phosphate transfer between acetate kinase and enzyme I of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13498–13503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., KAPSIMALIS B. Synthesis of intracellular iodophilic polysaccharide by Streptococcus mitis. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 May-Jun;8:319–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk G., von Hugo H. Phosphofructokinase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):82–87. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T. Pathogenicity of anaerobic gram-negative rods: possible mechanisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6(2):189–199. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKINS H. C., BARKER H. A. Fermentative processes of the fusiform bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):101–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.101-114.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOE H., THEILADE E., JENSEN S. B. EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVITIS IN MAN. J Periodontol. 1965 May-Jun;36:177–187. doi: 10.1902/jop.1965.36.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Gibbons R. J. Amino acid fermentation by Fusobacterium nucleatum. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Feb;13(2):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Oxygen sensitivity of various anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):723–727. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.723-727.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Good I. J., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of experimental gingivitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):651–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.651-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkinen K. K., Hurttia H., Mäkinen P. L., Paunio K. Effects on oral health of mouthrinses containing xylitol, sodium cyclamate and sucrose sweeteners in the absence of oral hygiene. II. Relative composition of free amino acids in human crevicular fluid. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1984;80(1):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):232–269. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.232-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J. Bacterial glycogen synthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:419–458. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robrish S. A., Oliver C., Thompson J. Amino acid-dependent transport of sugars by Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3891–3897. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3891-3897.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. L., Kleinberg I. The free amino acids in human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1983;28(9):873–878. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(83)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. E., Buckner B. A. Butyrate and propionate: important components of toxic dental plaque extracts. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):458–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.458-463.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Jan-Feb;85(2):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):465–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.465-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Torchia D. A. Use of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 14C fluorography in studies of glycolysis and regulation of pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.791-800.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Ratliff D., Muller D., Mandell R., Socransky S. S. Medium for selective isolation of Fusobacterium nucleatum from human periodontal pockets. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):844–849. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.844-849.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Neuhaus F., Hussels H. A biochemical study of fusiform anaerobes. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1971;157(1):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02121286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]