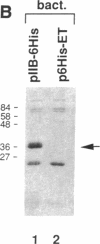
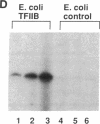
Abstract
Transcription factor TFIIB is a ubiquitous factor required for transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Previous studies have suggested that TFIIB serves as a bridge between the "TATA"-binding factor (TFIID) and RNA polymerase II during preinitiation complex assembly and, more recently, that TFIIB can be a target of acidic activators. We have purified TFIIB to homogeneity, shown that activity resides in a 33-kDa polypeptide, and obtained cDNAs encoding functional TFIIB. TFIIB contains a region with amino acid sequence similarity to a highly conserved region of prokaryotic sigma factors. This is consistent with analogous functions for these factors in promoter recognition by RNA polymerases and with similar findings for TFIID, TFIIE, and TFIIF/RAP30. Like TFIID, TFIIB contains both a large imperfect repeat that could contribute an element of symmetry to the folded protein and clusters of basic residues that could interact with acidic activator domains. These findings argue for a common origin of TFIIB, TFIID, and other general transcription factors and for the evolutionary segregation of complementary functions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Faus I., Matthes H., Chipoulet J. M., Winsor B., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Cloning of the gene encoding the yeast protein BTF1Y, which can substitute for the human TATA box-binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9803–9807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Bond M. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription system from rat liver. Purification of an essential component. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8293–8297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Masiarz F. R., Chamberlin M. J. Isolation and characterization of the Bacillus subtilis sigma 28 factor. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1560–1567. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1560-1567.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A., Sinn E., Yamamoto T., Wang J., Roy A., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Highly conserved core domain and unique N terminus with presumptive regulatory motifs in a human TATA factor (TFIID). Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):387–390. doi: 10.1038/346387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Carey M. F., Kakidani H., Roeder R. G. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Fujii H., Cromlish J. A., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Cloning and structure of a yeast gene encoding a general transcription initiation factor TFIID that binds to the TATA box. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):299–303. doi: 10.1038/341299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi N., Maguire K., Kralli A., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Weinmann R. Direct interaction between adenovirus E1A protein and the TATA box binding transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5124–5128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of general transcription factor IIE. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9304–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley S. A., Burgess R. R. Characterization of the Escherichia coli transcription factor sigma 70: localization of a region involved in the interaction with core RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7728–7734. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Ha I., Cortes P., Weis L., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: role of transcription factors IIA, IID, and IIB during formation of a transcription-competent complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6335–6347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Coleman J. E. GAL4 transcription factor is not a "zinc finger" but forms a Zn(II)2Cys6 binuclear cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Gene transcription. TFIIB or not TFIIB? Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):16–18. doi: 10.1038/351016d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Burton Z. F., Greenblatt J. Structure and associated DNA-helicase activity of a general transcription initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):410–414. doi: 10.1038/341410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumimoto H., Ohkuma Y., Yamamoto T., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: identification of general transcription factor TFIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9158–9162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Abmayr S. M., Cromlish W. A., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation by the immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]