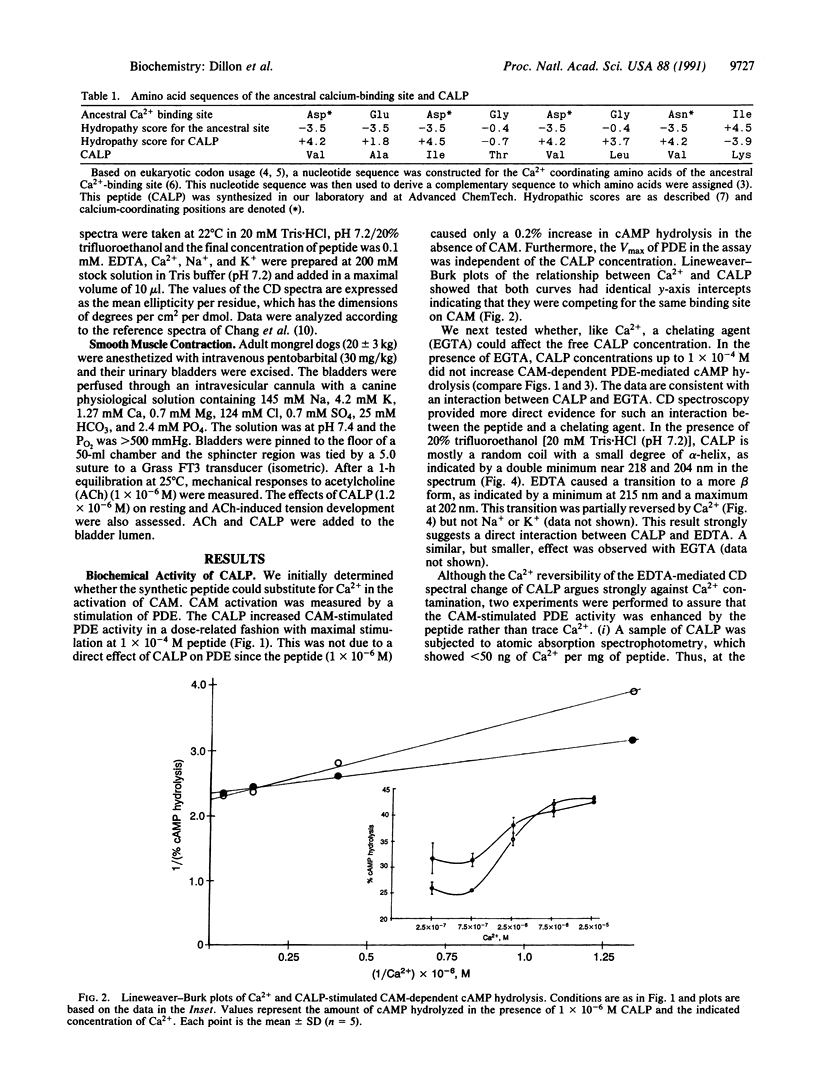
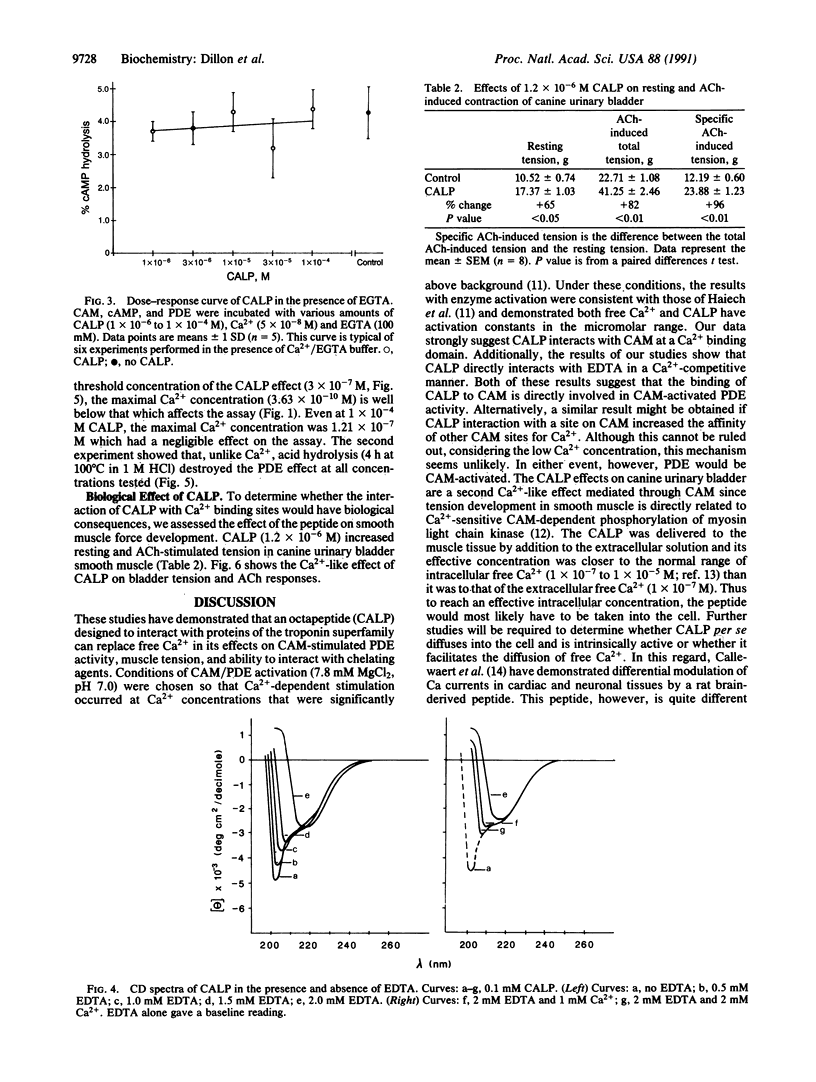
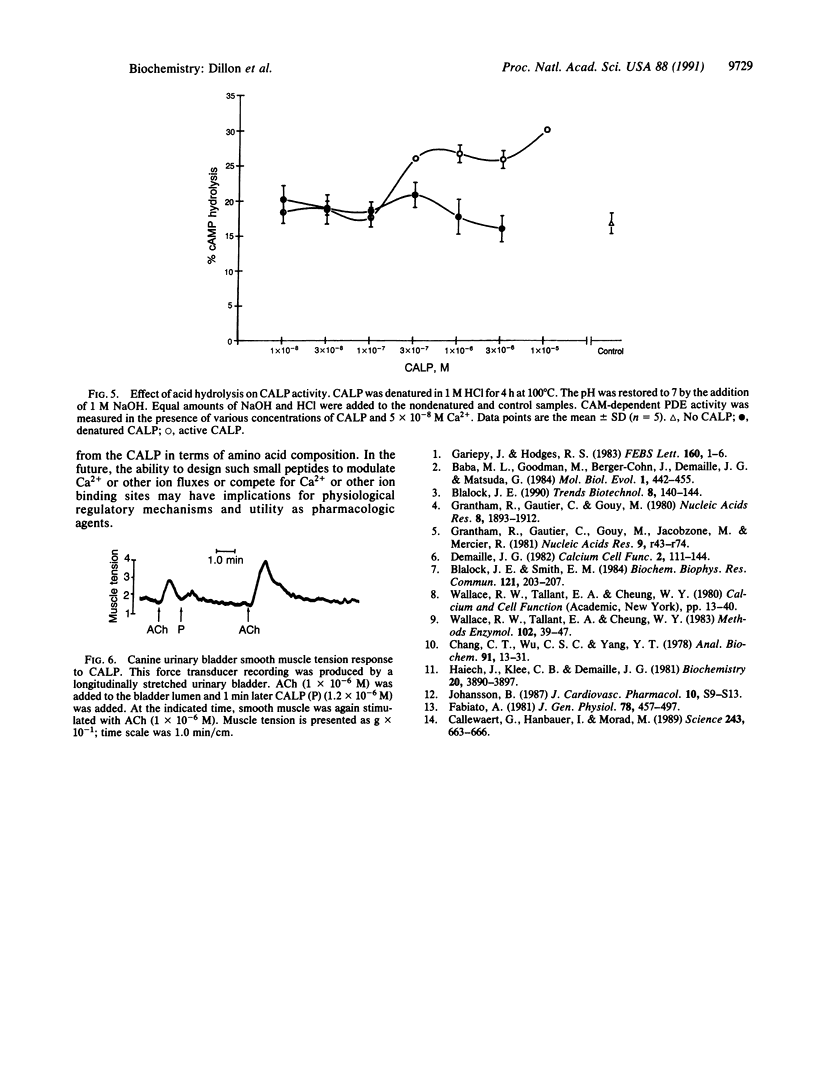
Abstract
Proteins of the troponin superfamily use homologous amino acid sequences as binding sites for Ca2+ and seem to have evolved from an ancestral Ca2+ binding site. We have utilized this ancestral sequence to construct a peptide (Ca(2+)-like peptide) with inverted hydropathy to the calcium-coordinating region of this protein. This synthetic peptide acted like Ca2+ in that (i) it increased the calmodulin-dependent hydrolysis of cAMP by phosphodiesterase, (ii) it interacted with EDTA, and (iii) it enhanced contraction of urinary bladder smooth muscle in vitro. Unlike Ca2+, the peptide's effects were destroyed by acid hydrolysis. These findings demonstrate the synthesis of a peptide that can substitute for Ca2+ and may have considerable utility for the study of Ca(2+)-regulated pathways and possible therapeutic value as a pharmacologic agent.
Full text
PDF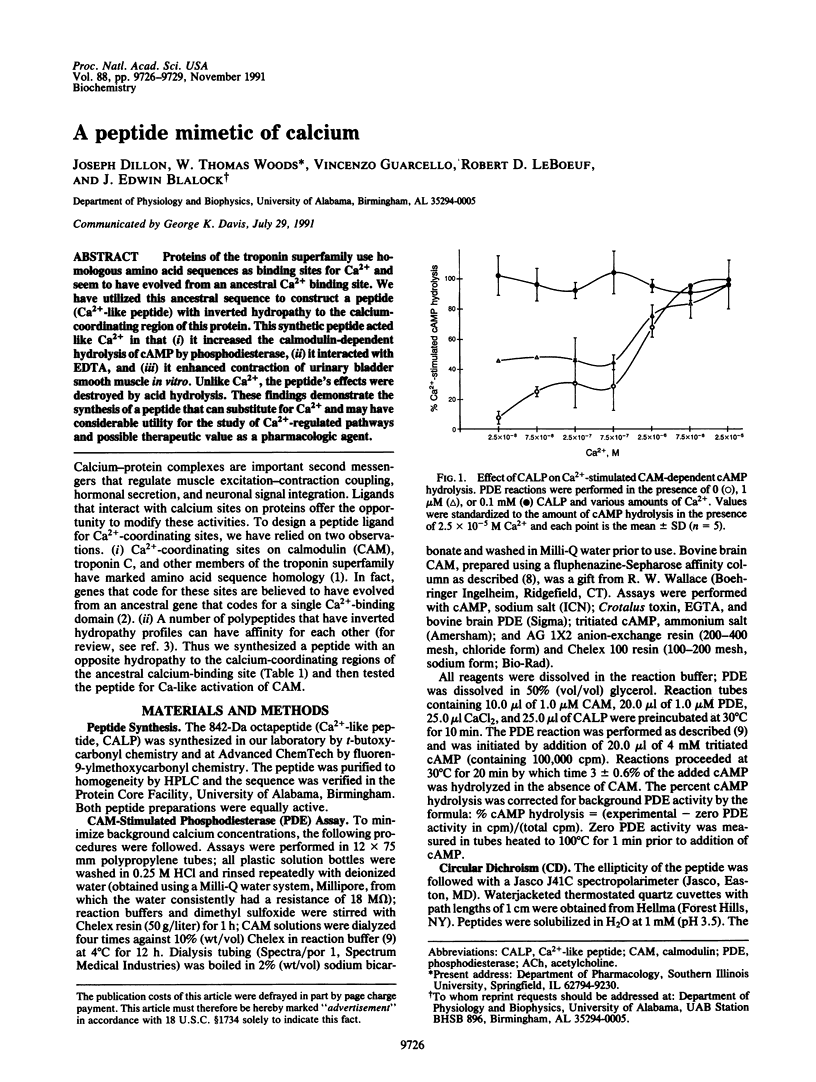
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba M. L., Goodman M., Berger-Cohn J., Demaille J. G., Matsuda G. The early adaptive evolution of calmodulin. Mol Biol Evol. 1984 Nov;1(6):442–455. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E. Complementarity of peptides specified by 'sense' and 'antisense' strands of DNA. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Jun;8(6):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90159-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Smith E. M. Hydropathic anti-complementarity of amino acids based on the genetic code. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 31;121(1):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90707-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert G., Hanbauer I., Morad M. Modulation of calcium channels in cardiac and neuronal cells by an endogenous peptide. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):663–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2536955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Wu C. S., Yang J. T. Circular dichroic analysis of protein conformation: inclusion of the beta-turns. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90812-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):457–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Hodges R. S. Primary sequence analysis and folding behavior of EF hands in relation to the mechanism of action of troponin C and calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80924-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M. Codon frequencies in 119 individual genes confirm consistent choices of degenerate bases according to genome type. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1893–1912. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haiech J., Klee C. B., Demaille J. G. Effects of cations on affinity of calmodulin for calcium: ordered binding of calcium ions allows the specific activation of calmodulin-stimulated enzymes. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3890–3897. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. Calcium and regulation of contraction: a short review. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987;10 (Suppl 1):S9–13. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198710001-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Assay of calmodulin by Ca2+-dependent phosphodiesterase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:39–47. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


