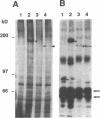
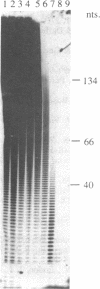
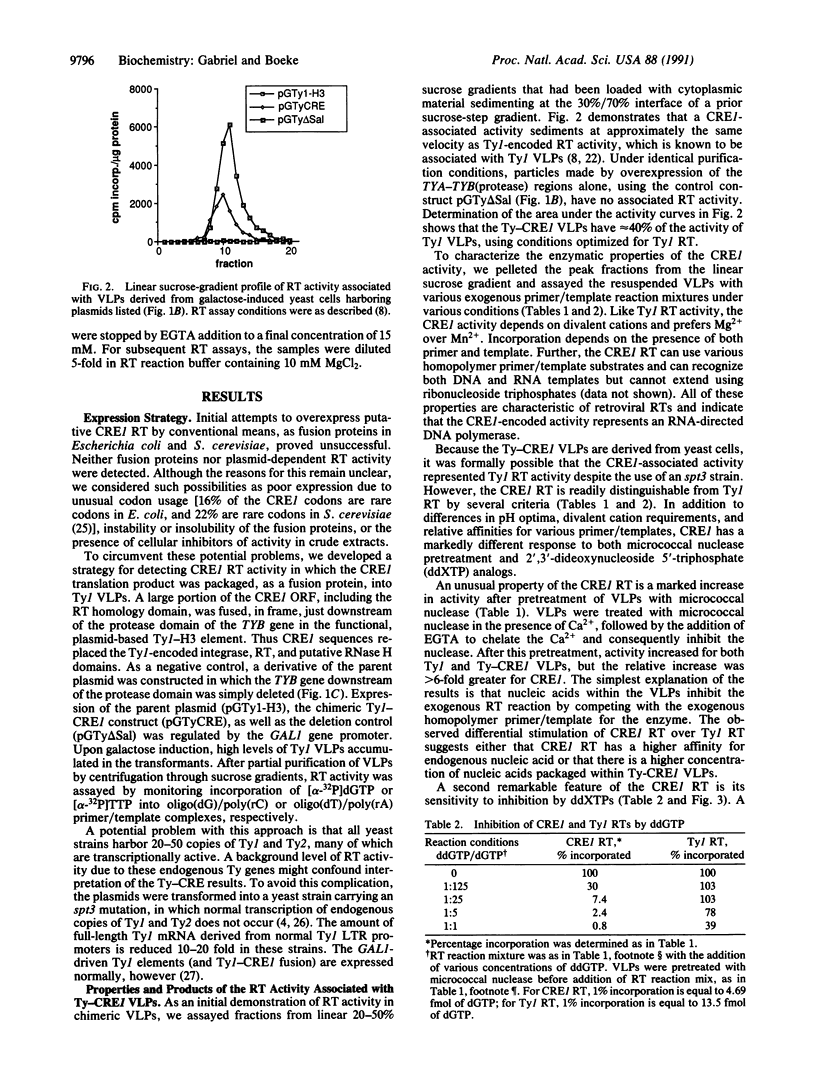
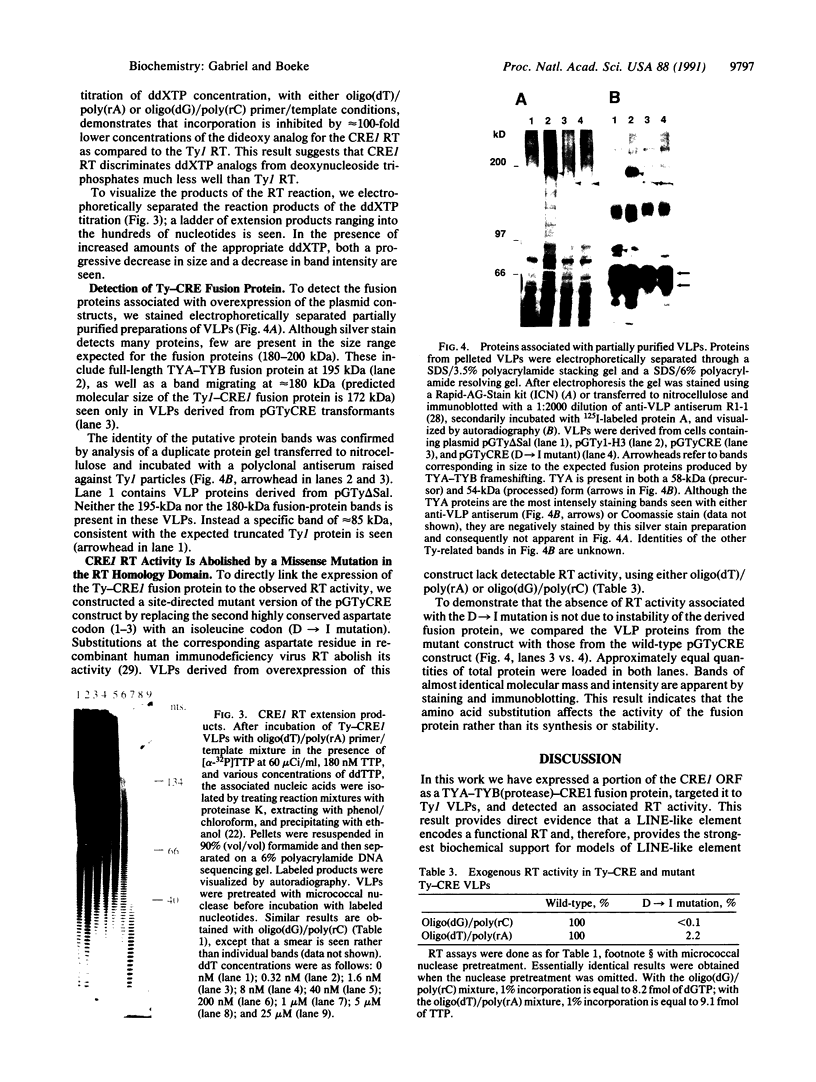
Abstract
The long interspersed nuclear element (LINE)-like elements are a distinct family of eukaryotic transposons that contain a long open reading frame with limited sequence homology to retroviral reverse transcriptases. Unlike many retrotransposons, they lack long terminal repeats. The mechanism by which LINE-like elements move within the genomes of their hosts remains speculative. We have used an unusual approach to express and detect enzymatic activities associated with Crithidia retrotransposable element 1 (CRE1), a site-specific LINE-like element found in the insect trypanosomatid Crithidia fasciculata. A chimeric gene fusing the yeast retrotransposon Ty1 and the CRE1 open reading frame is constructed and then overexpressed in yeast. Fusion proteins are packaged into virus-like particles, which can be partially purified and directly analyzed for enzymatic activity. Here we demonstrate that CRE1 encodes an RNA-directed DNA polymerase. These data provide direct biochemical evidence that this widely distributed class of retrotransposons encodes reverse transcriptase and sets the stage for a detailed understanding of the mechanisms involved in LINE-like element transposition.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. E., Dawson K. M., Gull K., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. The expression of hybrid HIV:Ty virus-like particles in yeast. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):68–70. doi: 10.1038/329068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy S., Williams S., Chang S., Richards F. F. SLACS retrotransposon from Trypanosoma brucei gambiense is similar to mammalian LINEs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):785–792. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavand M., Feitelson M., Laub O. The hepatitis B virus-associated reverse transcriptase is encoded by the viral pol gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):1019–1021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.1019-1021.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcourt M. F., Farabaugh P. J. Ribosomal frameshifting in the yeast retrotransposon Ty: tRNAs induce slippage on a 7 nucleotide minimal site. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):339–352. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90371-K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Corces V. G. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:403–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT3 gene is required for transposition and transpositional recombination of chromosomal Ty elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3575–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A. I transposable elements and I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990 Jan;6(1):16–21. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. A deletion mutation in the 5' part of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus blocks proteolytic processing of the gag and pol polyproteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.899-907.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Origins and evolutionary relationships of retroviruses. Q Rev Biol. 1989 Mar;64(1):1–30. doi: 10.1086/416128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. A specific terminal structure is required for Ty1 transposition. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):324–330. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. The DNA intermediate in yeast Ty1 element transposition copurifies with virus-like particles: cell-free Ty1 transposition. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):955–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel A., Yen T. J., Schwartz D. C., Smith C. L., Boeke J. D., Sollner-Webb B., Cleveland D. W. A rapidly rearranging retrotransposon within the miniexon gene locus of Crithidia fasciculata. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):615–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. A., Melnikov A. A., Siunov A. V., Fodor I. I., Ilyin Y. V. Authentic reverse transcriptase is coded by jockey, a mobile Drosophila element related to mammalian LINEs. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2489–2495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubczak J. L., Burke W. D., Eickbush T. H. Retrotransposable elements R1 and R2 interrupt the rRNA genes of most insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3295–3299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S., Heidmann T. An indicator gene for detection of germline retrotransposition in transgenic Drosophila demonstrates RNA-mediated transposition of the LINE I element. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1927–1937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Blaug G., Hansen M., Barklis E. Assembly of gag-beta-galactosidase proteins into retrovirus particles. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2265–2279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2265-2279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Fulton S. M., Dobson M. J., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. A retrovirus-like strategy for expression of a fusion protein encoded by yeast transposon Ty1. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):243–246. doi: 10.1038/313243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Malim M. H., Gull K., Tuite M. F., McCready S., Dibbayawan T., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Reverse transcriptase activity and Ty RNA are associated with virus-like particles in yeast. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):583–586. doi: 10.1038/318583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse B., Rotherg P. G., South V. J., Spandorfer J. M., Astrin S. M. Insertional mutagenesis of the myc locus by a LINE-1 sequence in a human breast carcinoma. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):87–90. doi: 10.1038/333087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsoulis G., Boeke J. D. New antiviral strategy using capsid-nuclease fusion proteins. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):632–635. doi: 10.1038/352632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offensperger W. B., Walter E., Offensperger S., Zeschnigk C., Blum H. E., Gerok W. Duck hepatitis B virus: DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase activities of replicative complexes isolated from liver and their inhibition in vitro. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90618-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A., Finnegan D. J., Bucheton A. Evidence for retrotransposition of the I factor, a LINE element of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4907–4910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Zentgraf H., Schaller H., Bosch V. The duck hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase is tightly associated with the viral core structure and unable to switch to an exogenous template. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Cowe E., Higgins D. G., Shields D. C., Wolfe K. H., Wright F. Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable within-species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8207–8211. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weldon R. A., Jr, Erdie C. R., Oliver M. G., Wills J. W. Incorporation of chimeric gag protein into retroviral particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4169–4179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4169-4179.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Durbin K. J., Fink G. R. The SPT3 gene is required for normal transcription of Ty elements in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Boeke J. D. Inhibition of Ty1 transposition by mating pheromones in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2736–2743. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngren S. D., Boeke J. D., Sanders N. J., Garfinkel D. J. Functional organization of the retrotransposon Ty from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Ty protease is required for transposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1421–1431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]