Abstract
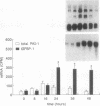
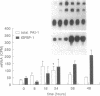
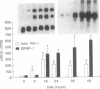
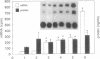
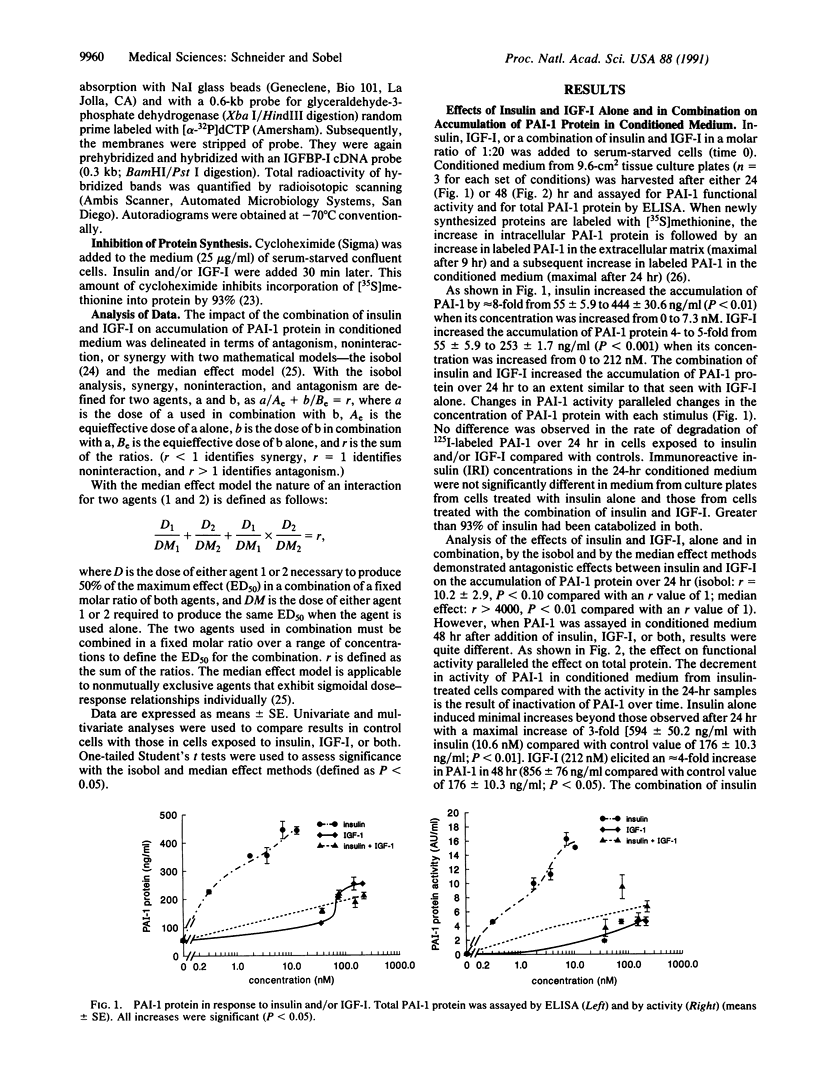
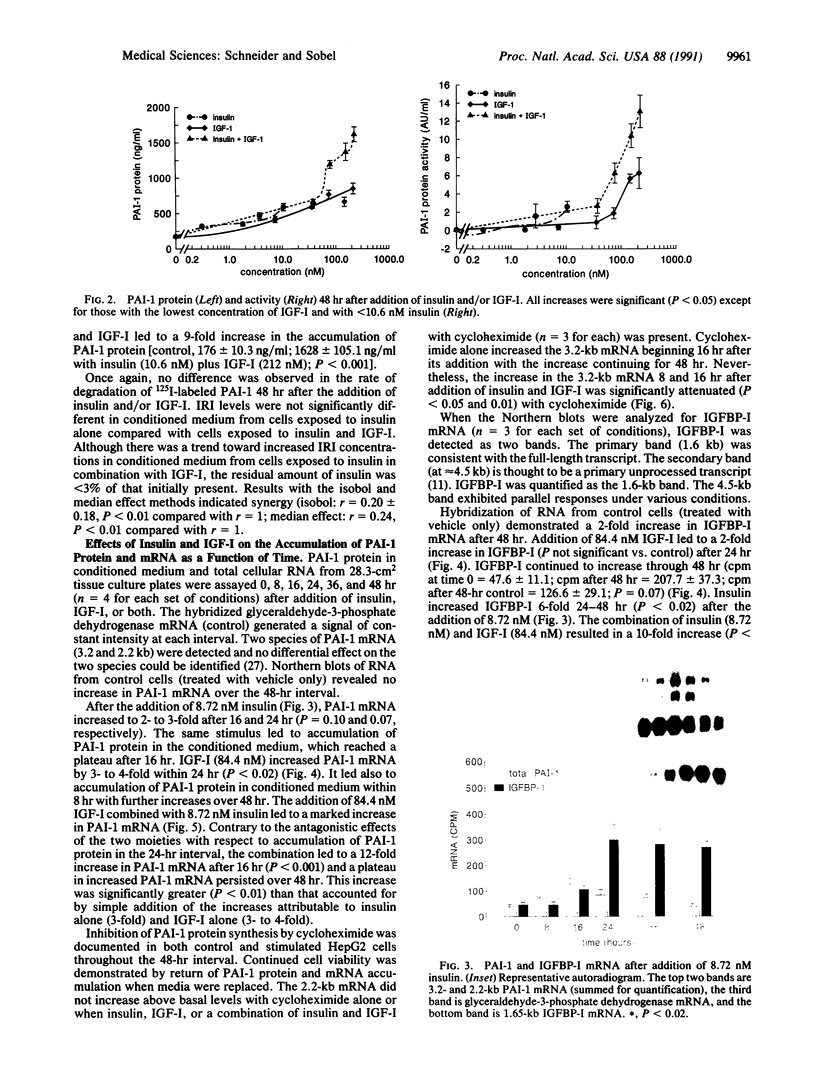
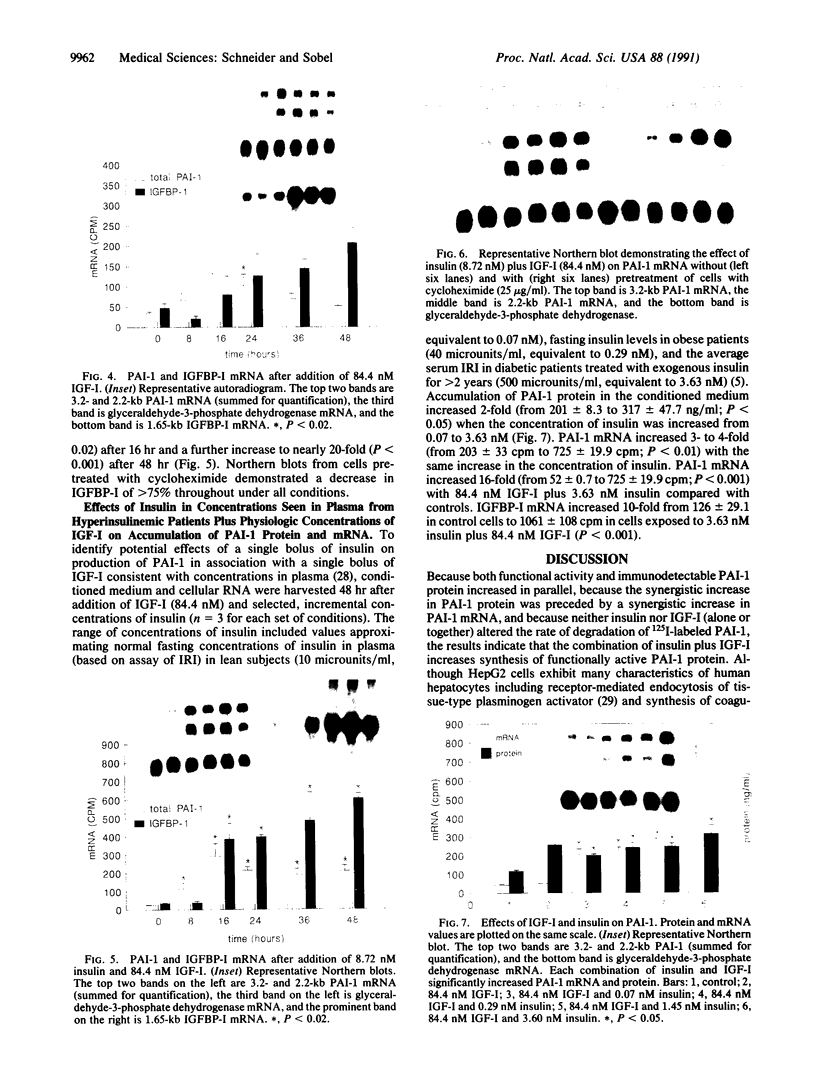
Accelerated atherosclerosis accompanying diabetes mellitus, obesity, and some types of hypertension has been associated with hyperinsulinemia, augmented plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1), or both. We hypothesized that insulin and insulin-like growth factor type I (IGF-I) can influence synthesis of PAI-1, thereby potentially attenuating fibrinolysis. In HepG2 cells used as a model system, concentrations of insulin and IGF-I consistent with those seen in plasma independently stimulated PAI-1 synthesis. Accumulation of PAI-1 protein in conditioned medium over 24 hr was stimulated more with insulin alone than with the combination. Synergistic increases were evident, however, in the accumulation of PAI-1 protein over 48 hr with a concomitant increase in PAI-1 mRNA. A 10- to 20-fold increase in IGF binding protein I mRNA was seen 16-48 hr after exposure of the HepG2 cells to insulin and IGF-I, an increase abolished by cycloheximide. The results obtained are consistent with the hypothesis that hyperinsulinemia coupled with physiologic concentrations of IGF-I may attenuate fibrinolytic activity in vivo, thereby contributing to accelerated atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi M. C., Juhan-Vague I., Kooistra T., Declerck P. J., Collen D. Insulin stimulates the synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 by the human hepatocellular cell line Hep G2. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Dec 22;60(3):491–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alessi M. C., Juhan-Vague I., Kooistra T., Declerck P. J., Collen D. Insulin stimulates the synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 by the human hepatocellular cell line Hep G2. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Dec 22;60(3):491–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum M. C. The expected effect of a combination of agents: the general solution. J Theor Biol. 1985 Jun 7;114(3):413–431. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(85)80176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. C., Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:27–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Structural and functional analysis of insulin-like growth factors. Br Med Bull. 1989 Apr;45(2):465–480. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNIE E., MARTIN F. I. Vascular disease in juvenile diabetic patients of long duration: a preliminary report. Diabetes. 1959 Sep-Oct;8:383–387. doi: 10.2337/diab.8.5.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Lucore C. L., Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J., Sobel B. E. Induction of synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 by tissue-type plasminogen activator in human hepatic and endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Nov 30;64(3):412–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. E., Westerhausen D. R., Jr, Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Transcriptional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 mRNA in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):163–168. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Alessi M. C., Joly P., Thirion X., Vague P., Declerck P. J., Serradimigni A., Collen D. Plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in angina pectoris. Influence of plasma insulin and acute-phase response. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):362–367. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S., Schmid C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Inhibition of insulin degradation by insulin-like growth factors I and II in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Aug;121(2):279–285. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Raghow R., Sawdey M., Loskutoff D. J., Postlethwaite A. E., Kang A. H., Moses H. L. Regulation of mRNAs for type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor, fibronectin, and type I procollagen by transforming growth factor-beta. Divergent responses in lung fibroblasts and carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3111–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen B. S., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Plasminogen activator inhibitor is associated with the extracellular matrix of cultured bovine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1082–1089. doi: 10.1172/JCI113164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooistra T., Bosma P. J., Töns H. A., van den Berg A. P., Meyer P., Princen H. M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: biosynthesis and mRNA level are increased by insulin in cultured human hepatocytes. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):723–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landin K., Stigendal L., Eriksson E., Krotkiewski M., Risberg B., Tengborn L., Smith U. Abdominal obesity is associated with an impaired fibrinolytic activity and elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Metabolism. 1990 Oct;39(10):1044–1048. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Fujii S., Wun T. C., Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Regulation of the expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15845–15848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Sobel B. E. Interactions of tissue-type plasminogen activator with plasma inhibitors and their pharmacologic implications. Circulation. 1988 Mar;77(3):660–669. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.3.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J. A follow-up study of vascular disease in growth-hormone-deficient dwarfs with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 1;298(22):1217–1222. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806012982202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owensby D. A., Sobel B. E., Schwartz A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of tissue-type plasminogen activator by the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10587–10594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan W. H., Cedres L. B., Liu K., Dyer A., Schoenberger J. A., Shekelle R. B., Stamler R., Smith D., Collette P., Stamler J. Relationship of clinical diabetes and asymptomatic hyperglycemia to risk of coronary heart disease mortality in men and women. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Mar;123(3):504–516. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek H., Veerman H., Lambers H., Diergaarde P., Verweij C. L., van Zonneveld A. J., van Mourik J. A. Endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI): a new member of the Serpin gene family. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2539–2544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. R., Rosenfeld R. G., Baker B. K., Liu F., Hintz R. L. Serum somatomedin levels in adults with chronic renal failure: the importance of measuring insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-II in acid-chromatographed uremic serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Nov;63(5):1186–1192. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-5-1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen S. M., Heding L. G., Parbst E., Volund A. Serum IRI in insulin-treated diabetics during a 24-hour period. Diabetologia. 1975 Apr;11(2):151–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00429840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Pekonen F. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1990 Jul;123(1):7–13. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1230007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swislocki A. L., Hoffman B. B., Reaven G. M. Insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in patients with hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Jun;2(6 Pt 1):419–423. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.6.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vague P., Juhan-Vague I., Aillaud M. F., Badier C., Viard R., Alessi M. C., Collen D. Correlation between blood fibrinolytic activity, plasminogen activator inhibitor level, plasma insulin level, and relative body weight in normal and obese subjects. Metabolism. 1986 Mar;35(3):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. K., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Pfeifer M. A., Porte D., Jr Pathophysiology of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1984 Sep-Oct;7(5):491–502. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.5.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]