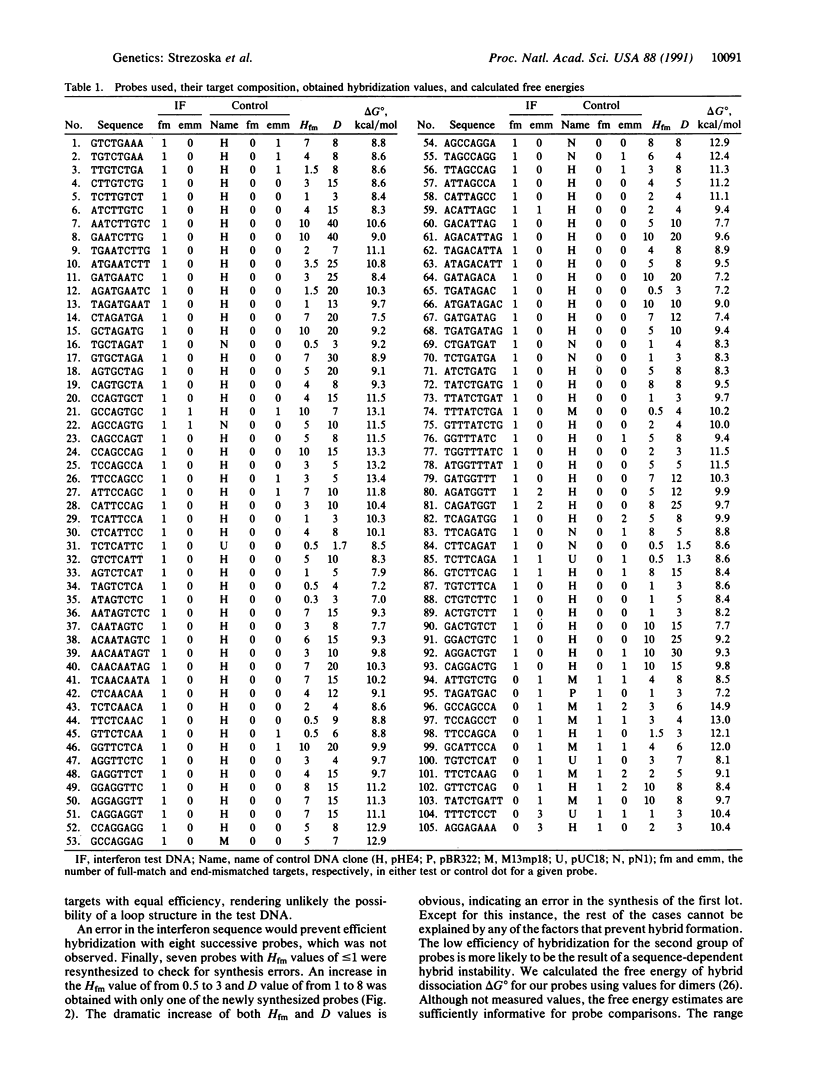
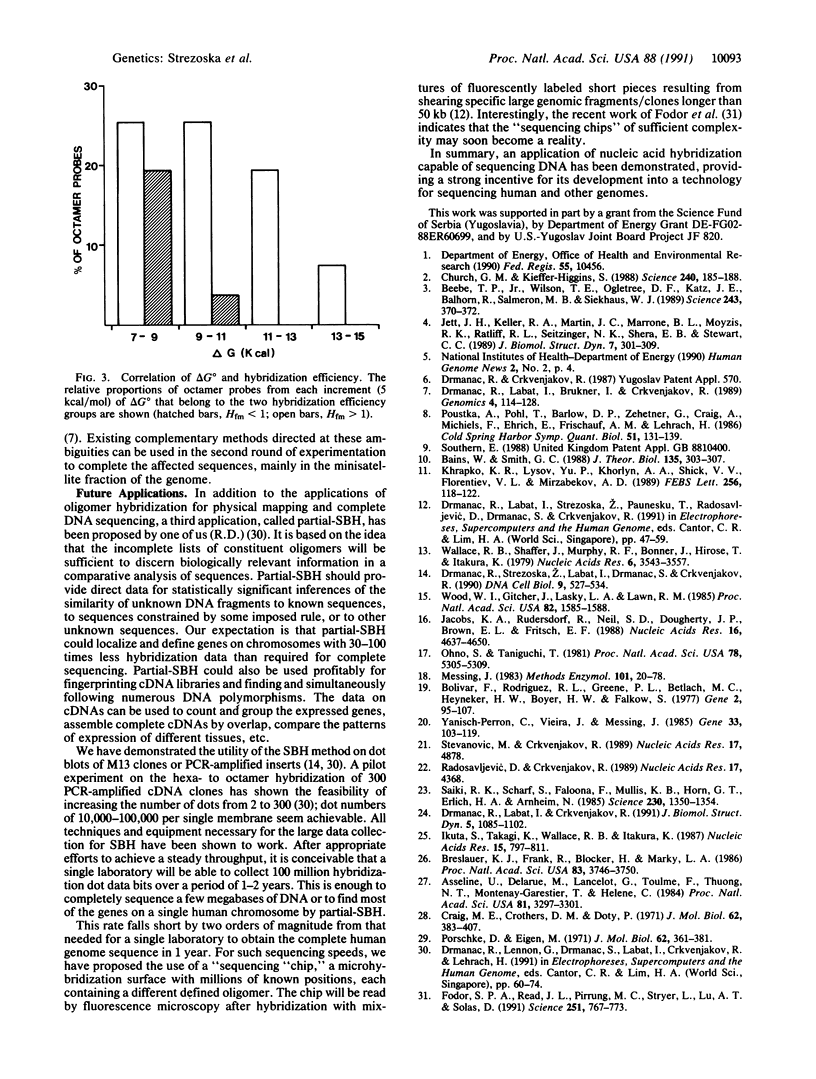
Abstract
Determination of the sequences of human and other complex genomes requires much faster and less expensive sequencing processes than the methods in use today. Sequencing by hybridization is potentially such a process. In this paper we present hybridization data sufficient to accurately read a known sequence of 100 base pairs. In independent reactions, octamer and nonamer oligonucleotides derived from the sequence hybridized more strongly to this DNA than to controls. The 93 consecutive overlapping probes were derived from a 100-base-pair segment of test DNA and additional probes were generated by incorporation of a noncomplementary base at one of the ends of 12 of the basic probes. These 12 additional probes also had a full-match target in one of the control DNAs. The test and one of five control DNAs spotted on nylon filters were hybridized with 83 octamers and 22 nonamers under low-temperature conditions. A stronger signal in DNA containing a full-match target compared to DNA with only mismatched targets was obtained with all 105 probes. In 3 cases (2.9%), the difference of signals was not significant (less than 2-fold) due to inefficient hybridization and the consequently higher influence of background. The hybridization pattern obtained enabled us to resequence the 100 base pairs by applying an algorithm that tolerates an error rate much higher than was observed in the experiment. With this result, the technological components of large-scale DNA sequencing using the sequencing by hybridization method are in place.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asseline U., Delarue M., Lancelot G., Toulmé F., Thuong N. T., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Nucleic acid-binding molecules with high affinity and base sequence specificity: intercalating agents covalently linked to oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3297–3301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bains W., Smith G. C. A novel method for nucleic acid sequence determination. J Theor Biol. 1988 Dec 7;135(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe T. P., Jr, Wilson T. E., Ogletree D. F., Katz J. E., Balhorn R., Salmeron M. B., Siekhaus W. J. Direct observation of native DNA structures with the scanning tunneling microscope. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):370–372. doi: 10.1126/science.2911747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Kieffer-Higgins S. Multiplex DNA sequencing. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):185–188. doi: 10.1126/science.3353714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig M. E., Crothers D. M., Doty P. Relaxation kinetics of dimer formation by self complementary oligonucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):383–401. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Labat I., Brukner I., Crkvenjakov R. Sequencing of megabase plus DNA by hybridization: theory of the method. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):114–128. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Labat I., Crkvenjakov R. An algorithm for the DNA sequence generation from k-tuple word contents of the minimal number of random fragments. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Apr;8(5):1085–1102. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Strezoska Z., Labat I., Drmanac S., Crkvenjakov R. Reliable hybridization of oligonucleotides as short as six nucleotides. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;9(7):527–534. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Read J. L., Pirrung M. C., Stryer L., Lu A. T., Solas D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):767–773. doi: 10.1126/science.1990438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta S., Takagi K., Wallace R. B., Itakura K. Dissociation kinetics of 19 base paired oligonucleotide-DNA duplexes containing different single mismatched base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):797–811. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs K. A., Rudersdorf R., Neill S. D., Dougherty J. P., Brown E. L., Fritsch E. F. The thermal stability of oligonucleotide duplexes is sequence independent in tetraalkylammonium salt solutions: application to identifying recombinant DNA clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4637–4650. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett J. H., Keller R. A., Martin J. C., Marrone B. L., Moyzis R. K., Ratliff R. L., Seitzinger N. K., Shera E. B., Stewart C. C. High-speed DNA sequencing: an approach based upon fluorescence detection of single molecules. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Oct;7(2):301–309. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10507773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khrapko K. R., Lysov YuP, Khorlyn A. A., Shick V. V., Florentiev V. L., Mirzabekov A. D. An oligonucleotide hybridization approach to DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 9;256(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81730-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Structure of a chromosomal gene for human interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T., Barlow D. P., Zehetner G., Craig A., Michiels F., Ehrich E., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Molecular approaches to mammalian genetics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):131–139. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pörschke D., Eigen M. Co-operative non-enzymic base recognition. 3. Kinetics of the helix-coil transition of the oligoribouridylic--oligoriboadenylic acid system and of oligoriboadenylic acid alone at acidic pH. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):361–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radosavljević D., Crkvenjakov R. Genomic sequence of rat beta-globin major gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4368–4368. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović M., Crkvenjakov R. Genomic sequence of rat beta-globin minor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4878–4878. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




