Abstract
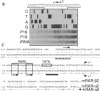
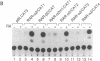
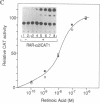
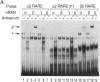
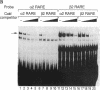
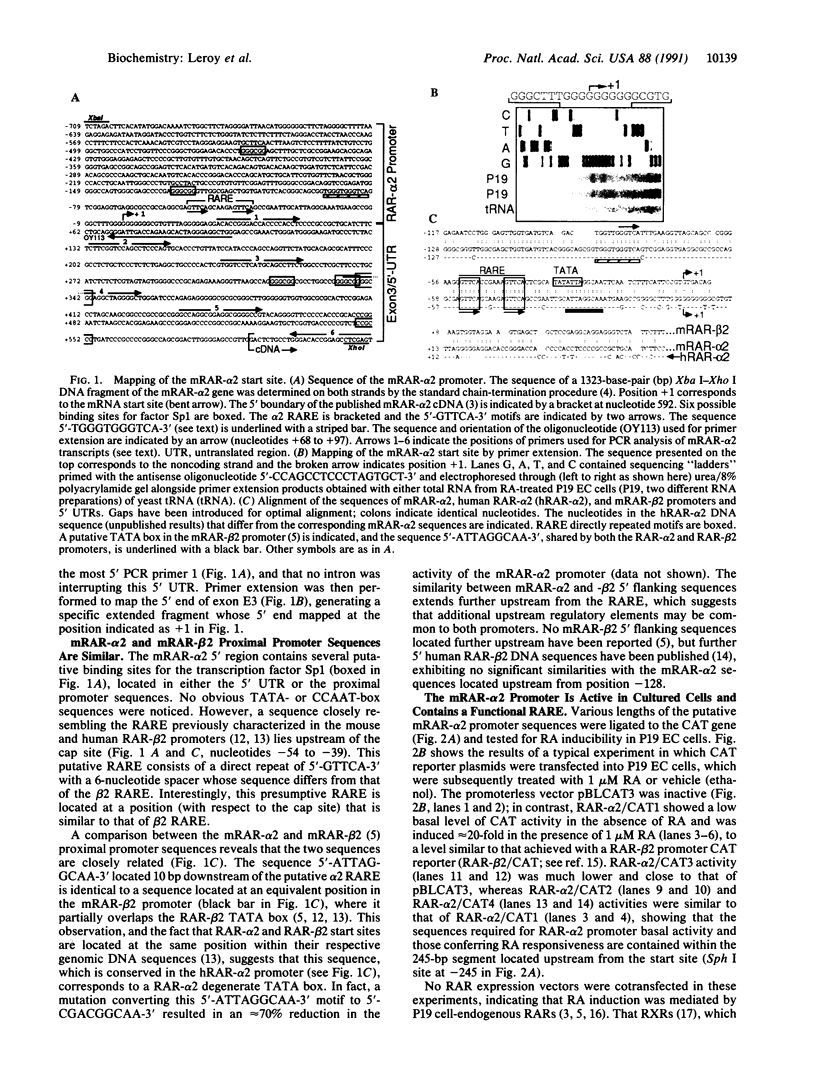
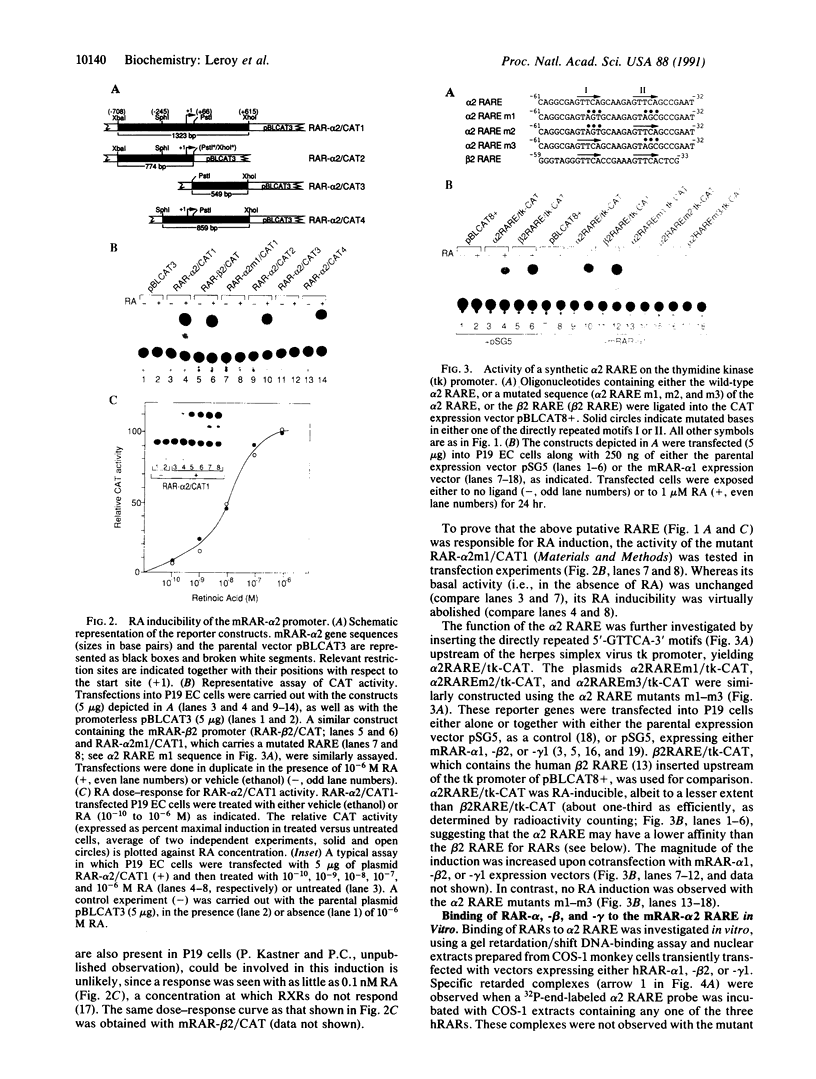
We have characterized the promoter of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha 2 (mRAR-alpha 2) isoform. This promoter contains a retinoic acid response element (RARE) that closely resembles the RARE that is present in the RAR-beta 2 promoter. Moreover, RAR-alpha 2 and RAR-beta 2 proximal promoter sequences are similar to each other and generate transcripts whose respective start sites are located at similar positions. The RAR-alpha 2 RARE consists of two directly repeated 5'-GTTCA-3' motifs to which all three RARs (alpha, beta, and gamma) bind in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand N. J., Petkovich M., Chambon P. Characterization of a functional promoter for the human retinoic acid receptor-alpha (hRAR-alpha). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6799–6806. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Shean M. L., McBride M. S., Stewart M. J. Retinoic acid response element in the human alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH3: implications for regulation of retinoic acid synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1638–1646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Bellard M., Scheuer I., Chambon P., Sassone-Corsi P. Activation of the ovalbumin gene by the estrogen receptor involves the fos-jun complex. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1267–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90422-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Husmann M., Graupner G., Pfahl M. A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Krust A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Zelent A., Leroy P., Staub A., Chambon P. Murine isoforms of retinoic acid receptor gamma with specific patterns of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Ryffel G. U., Heitlinger E., Cato A. C. A 13 bp palindrome is a functional estrogen responsive element and interacts specifically with estrogen receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):647–663. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Krust A., Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Kastner P., Dierich A., Chambon P. Multiple isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha are generated by alternative splicing and differential induction by retinoic acid. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin S., Gilliland G. Site-specific mutagenesis using asymmetric polymerase chain reaction and a single mutant primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7433–7438. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman J. N., Widom R. L., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V., Karathanasis S. K. A retinoic acid-responsive element in the apolipoprotein AI gene distinguishes between two different retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3814–3820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Nakshatri H., Leroy P., Rees J., Chambon P. A retinoic acid response element is present in the mouse cellular retinol binding protein I (mCRBPI) promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2223–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., Gaub M. P., Mader S., Dierich A., Bellard M., Chambon P. Cell-specific activity of a GGTCA half-palindromic oestrogen-responsive element in the chicken ovalbumin gene promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3771–3778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G., Mader S., Gold J. D., Leid M., Lutz Y., Gaub M. P., Chambon P., Gudas L. The late retinoic acid induction of laminin B1 gene transcription involves RAR binding to the responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]