Abstract
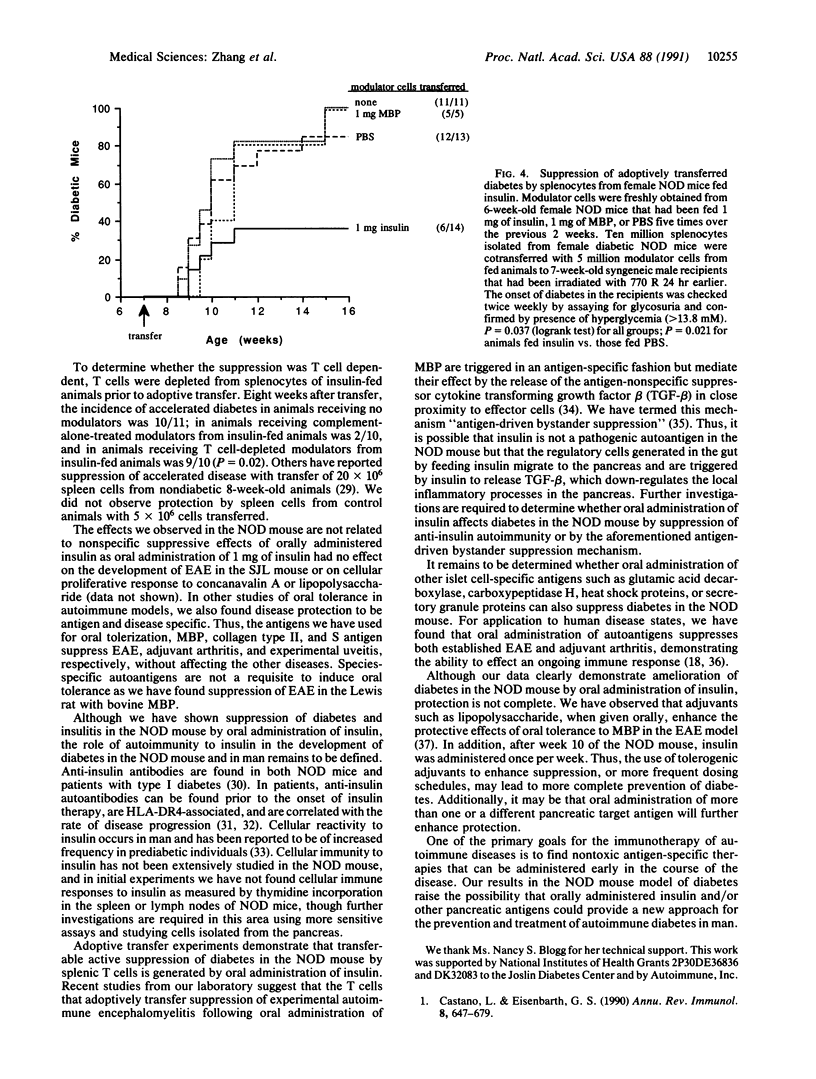
Nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice spontaneously develop an autoimmune form of diabetes associated with insulitis. A number of immunomodulatory therapies have been investigated as a treatment for the disease process. Oral administration of the autoantigens myelin basic protein and collagen type II suppresses experimental models of encephalomyelitis and arthritis. We have now found that oral administration of insulin delays the onset and reduces the incidence of diabetes in NOD mice over a 1-year period in animals administered 1 mg of porcine insulin orally twice a week for 5 weeks and then weekly until 1 year of age. As expected, orally administered insulin had no metabolic effect on blood glucose levels. The severity of lymphocytic infiltration of pancreatic islets was also reduced by oral administration of insulin. Furthermore, splenic T cells from animals orally treated with insulin adoptively transfer protection against diabetes, demonstrating that oral insulin administration generates active cellular mechanisms that suppress disease. These results show that oral insulin affects diabetes and the pancreatic cellular inflammatory process in the NOD mouse and raise the possibility that oral administration of insulin or other pancreatic autoantigens may provide a new approach for the treatment of autoimmune diabetes.
Full text
PDF

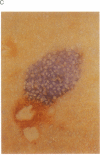
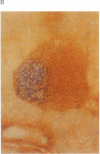
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., McDevitt H. O. The role of class II molecules in development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in mice, rats and humans. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;156:103–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75239-1_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Luchetta R. Insulitis and diabetes in NOD mice reduced by prophylactic insulin therapy. Diabetes. 1990 Aug;39(8):933–937. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.8.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitar D. M., Whitacre C. C. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by the oral administration of myelin basic protein. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boitard C., Yasunami R., Dardenne M., Bach J. F. T cell-mediated inhibition of the transfer of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1669–1680. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Bingley P. J., Shattock M., Dean B. M., Dunger D., Gale E. A., Bottazzo G. F. Quantification of islet-cell antibodies and prediction of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jan 20;335(8682):147–149. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90013-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bougnères P. F., Landais P., Boisson C., Carel J. C., Frament N., Boitard C., Chaussain J. L., Bach J. F. Limited duration of remission of insulin dependency in children with recent overt type I diabetes treated with low-dose cyclosporin. Diabetes. 1990 Oct;39(10):1264–1272. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.10.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brod S. A., al-Sabbagh A., Sobel R. A., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin antigens: IV. Suppression of chronic relapsing disease in the Lewis rat and strain 13 guinea pig. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):615–622. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño L., Eisenbarth G. S. Type-I diabetes: a chronic autoimmune disease of human, mouse, and rat. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:647–679. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Markovits D., Reshef T., van der Zee R., Cohen I. R. Induction and therapy of autoimmune diabetes in the non-obese diabetic (NOD/Lt) mouse by a 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein and its fragments. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):440–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. J. Cellular immunity to human insulin in individuals at high risk for the development of type I diabetes mellitus. J Autoimmun. 1990 Jun;3(3):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(90)90150-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury S. J., Lider O., al-Sabbagh A., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein. III. Synergistic effect of lipopolysaccharide. Cell Immunol. 1990 Dec;131(2):302–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90256-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Serreze D. V., Prochazka M. The genetics and epidemiology of diabetes in NOD mice. Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):147–149. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90057-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lider O., Santos L. M., Lee C. S., Higgins P. J., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein. II. Suppression of disease and in vitro immune responses is mediated by antigen-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):748–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael J. G. The role of digestive enzymes in orally induced immune tolerance. Immunol Invest. 1989 Nov-Dec;18(9-10):1049–1054. doi: 10.3109/08820138909030606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Antigen-driven bystander suppression after oral administration of antigens. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):791–798. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Suko M., Okudaira H., Matsuba I., Tsuruoka A., Sasaki A., Yokoyama H., Tanase T., Shida T., Nishimura M. Preventive effects of cyclosporin on diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetologia. 1986 Apr;29(4):244–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00454884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., Bober L. A., Robinson M. E., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Suppression of type II collagen-induced arthritis by intragastric administration of soluble type II collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7443–7446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Caspi R. R., Mahdi R., Chan C. C., Roberge F., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Inhibition of S-antigen induced experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by oral induction of tolerance with S-antigen. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1689–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Asplin C. M., Clemons P., Lyen K., Tatpati O., Raghu P. K., Paquette T. L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6362005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roep B. O., Arden S. D., de Vries R. R., Hutton J. C. T-cell clones from a type-1 diabetes patient respond to insulin secretory granule proteins. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):632–634. doi: 10.1038/345632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Mordes J. P., Greiner D. L. The pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(4):598–603. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(90)90017-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shizuru J. A., Taylor-Edwards C., Banks B. A., Gregory A. K., Fathman C. G. Immunotherapy of the nonobese diabetic mouse: treatment with an antibody to T-helper lymphocytes. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):659–662. doi: 10.1126/science.2966437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein J., Maclaren N., Riley W., Spillar R., Radjenovic D., Johnson S. Immunosuppression with azathioprine and prednisone in recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 8;319(10):599–604. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809083191002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. S., Staines N. A. Gastric administration of type II collagen delays the onset and severity of collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):581–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Miller B. J., Mullen Y. Transfer of autoimmune diabetes mellitus with splenocytes from nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes. 1986 Aug;35(8):855–860. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.8.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Lee C. S., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats by oral administration of type II collagen. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2489–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A. G., Herskowitz R. D., Jackson R. A., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. Predicting type I diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jul;13(7):762–765. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.7.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A. G., Vardi P., Ricker A. T., Hattori M., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. Radioassay determination of insulin autoantibodies in NOD mice. Correlation with increased risk of progression to overt diabetes. Diabetes. 1989 Mar;38(3):358–363. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.3.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler R., Alper C. A., Awdeh Z. L., Castano L., Brink S. J., Soeldner J. S., Jackson R. A., Eisenbarth G. S. Specific association of HLA-DR4 with increased prevalence and level of insulin autoantibodies in first-degree relatives of patients with type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Jun;40(6):709–714. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.6.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]