Abstract
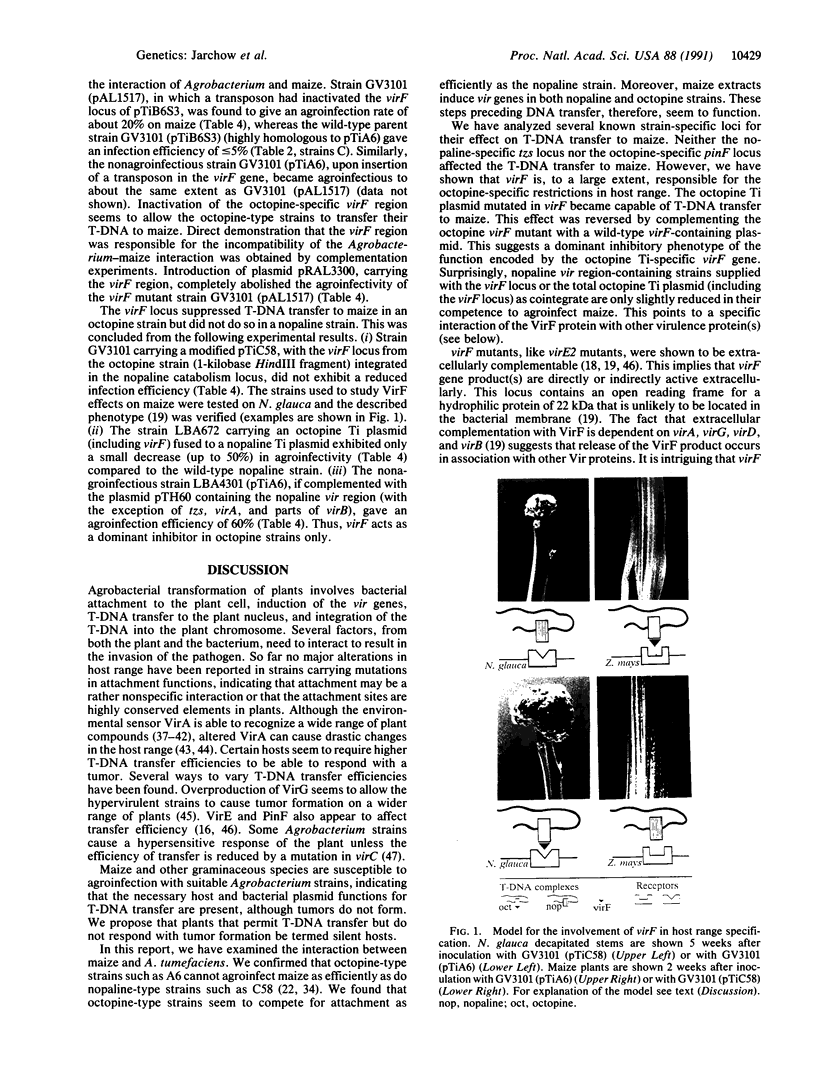
The monocotyledonous plant Zea mays does not develop tumors after inoculation with Agrobacterium tumefaciens and is thus defined as nonhost. Agroinfection, Agrobacterium-mediated delivery of maize streak virus, demonstrates that transferred DNA (T-DNA) transfer to the plant does occur. Nopaline-type Agrobacterium strains such as C58 are efficient in the transfer process whereas the octopine-type strain A6 is unable to transfer T-DNA to maize. This phenotypic difference maps to the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid but not to the T-DNA. Steps preceding T-DNA transfer, such as attachment and induction of the virulence genes, were shown to take place in the octopine strain. The nopaline-plasmid-specific locus tzs and the octopine-plasmid-specific locus pinF (virH) are not involved in the strain specificity. However, mutations in the virF locus rendered the octopine strain agroinfectious on maize, whereas such virF-defective octopine strains, when complemented by virF on a plasmid, completely lost their agroinfectivity. We propose that VirF, known to increase the host range of the bacteria in other systems, acts as an inhibitor of T-DNA transfer to maize.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D. A., Jen G., Gordon M. P. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the tzs gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain T37. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2773–2788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Ward J. E., Winans S. C., Nester E. W. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virE2 gene product is a single-stranded-DNA-binding protein that associates with T-DNA. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2659–2667. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2659-2667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsley N., Hohn B., Ramos C., Kado C., Rogowsky P. DNA transfer from Agrobacterium to Zea mays or Brassica by agroinfection is dependent on bacterial virulence functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):309–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02464898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka T., Kado C. I. Location of the right boundary of the virulence region on Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58 and a host-specifying gene next to the boundary. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):237–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.237-243.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsters M., Silva B., Van Vliet F., Genetello C., De Block M., Dhaese P., Depicker A., Inzé D., Engler G., Villarroel R. The functional organization of the nopaline A. tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):212–230. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., Hofker M., den Dulk-Ras H., Schilperoort R. A. A comparison of virulence determinants in an octopine Ti plasmid, a nopaline Ti plasmid, and an Ri plasmid by complementation analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutants. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J. Transformation of plant cells via Agrobacterium. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Sep;13(3):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00025321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto R. H., Powell A. T., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D. A., Kerstetter R. A., Nester E. W., Hawes M. C., Gordon M. P. Nucleotide sequence and analysis of the plant-inducible locus pinF from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2506–2512. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2506-2512.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapwijk P. M., van Beelen P., Schilperoort R. A. Isolation of a recombination deficient Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jun 7;173(2):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00330307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leemans J., Shaw C., Deblaere R., De Greve H., Hernalsteens J. P., Maes M., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Site-specific mutagenesis of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids and transfer of genes to plant cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):149–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott B. B., Whatley M. H., Lippincott J. A. Tumor induction by agrobacterium involves attachment of the bacterium to a site on the host plant cell wall. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):388–390. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers L. S., Maroney M. J., den Dulk-Ras A., Thompson D. V., van Vuuren H. A., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Octopine and nopaline strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens differ in virulence; molecular characterization of the virF locus. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;14(2):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00018565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers L. S., Regensburg-Tuïnk A. J., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Specificity of signal molecules in the activation of Agrobacterium virulence gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):969–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messens E., Dekeyser R., Stachel S. E. A nontransformable Triticum monococcum monocotyledonous culture produces the potent Agrobacterium vir-inducing compound ethyl ferulate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4368–4372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel P., Powell B. S., Rogowsky P. M., Kado C. I. Characterization of the virA virulence gene of the nopaline plasmid, pTiC58, of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1237–1246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okker R. J., Spaink H., Hille J., van Brussel T. A., Lugtenberg B., Schilperoort R. A. Plant-inducible virulence promoter of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):564–566. doi: 10.1038/312564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. K., Hommes N. G., Kuo J., Castle L. A., Morris R. O. Inducible expression of cytokinin biosynthesis in Agrobacterium tumefaciens by plant phenolics. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1988 Jul-Aug;1(6):235–242. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-1-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier D. A., Morris R. O. Secretion of trans-zeatin by Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a function determined by the nopaline Ti plasmid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1560–1566. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91429-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P. M., Close T. J., Chimera J. A., Shaw J. J., Kado C. I. Regulation of the vir genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5101–5112. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5101-5112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W. The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W., Zambryski P. C. A plant cell factor induces Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):379–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait R. C., Kado C. I. Regulation of the virC and virD promoters of pTiC58 by the ros chromosomal mutation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):385–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Kumatori A., Shin S., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A., Tokunaga F., Aruga R., Iwanaga S., Kakizuka A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for proteasomes from rat liver: primary structure of component C3 with a possible tyrosine phosphorylation site. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 17;29(15):3777–3785. doi: 10.1021/bi00467a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaine F., Casse-Delbart F. A new vector derived from Agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmids: a micro-Ri plasmid and its use to construct a mini-Ri plasmid. Gene. 1987;55(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P. Basic processes underlying Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer to plant cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



