Abstract
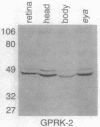
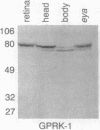
G protein-coupled receptors are regulated via phosphorylation by a variety of protein kinases. Recently, termination of the active state of two such receptors, the beta-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin, has been shown to be mediated by agonist- or light-dependent phosphorylation of the receptor by members of a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases (here referred to as G protein-coupled receptor kinases). We now report the isolation of a family of genes encoding a set of Drosophila protein kinases that appear to code for G protein-coupled receptor kinases. These proteins share a high degree of sequence homology with the bovine beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. The presence of a conserved family of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in vertebrates and invertebrates points to the central role of these kinases in signal transduction cascades.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., DeBlasi A., Stone W. C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: primary structure delineates a multigene family. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):235–240. doi: 10.1126/science.2552582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Mayor F., Jr, Somers R. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin by beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):869–872. doi: 10.1038/321869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Mayor F., Jr, Staniszewski C., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Purification and characterization of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9026–9032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Onorato J. J., Arriza J. L., Stone W. C., Lohse M., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2. A new member of the receptor kinase family. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14939–14946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Regan J. W., Matsui H., Mayor F., Jr, Cotecchia S., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17251–17253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Guilbault N., Bonin H. Phorbol-ester-induced phosphorylation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor decreases its coupling to Gs. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80159-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgi L. L., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90475-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie G. Pseudosubstrates turn off protein kinases. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):592–593. doi: 10.1038/335592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Campbell P. T., Ostrowski J., Yu S. S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. A small region of the beta-adrenergic receptor is selectively involved in its rapid regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Rubin G. M. Isolation and characterization of Drosophila cAMP-dependent protein kinase genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1539–1556. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra M. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Hosey M. M. Phosphorylation of chick heart muscarinic cholinergic receptors by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4543–4547. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Cook J. H., Dreyer W. J. Phosphorylation of rhodopsin in bovine photoreceptor membranes. A dark reaction after illumination. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2495–2502. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Dreyer W. J. Light dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin by ATP. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Hall S. W., Wilden U. Light-induced binding of 48-kDa protein to photoreceptor membranes is highly enhanced by phosphorylation of rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Wilden U. Deactivation of photoactivated rhodopsin by rhodopsin-kinase and arrestin. J Recept Res. 1987;7(1-4):283–298. doi: 10.3109/10799898709054990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G. Role of phosphorylation in desensitization of the beta-adrenoceptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90113-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr ATP mediates rapid reversal of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase activation in visual receptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):734–736. doi: 10.1038/287734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. beta-Arrestin: a protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1547–1550. doi: 10.1126/science.2163110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Structure of the adrenergic and related receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:67–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Carruth M. E., Adamus G., McDowell J. H., Hargrave P. A. Molecular, enzymatic and functional properties of rhodopsin kinase from rat pineal gland. Vision Res. 1990;30(8):1129–1137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(90)90170-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., McDowell J. H., Hargrave P. A. Purification and characterization of rhodopsin kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14067–14073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., McDowell J. H., Hargrave P. A. Rhodopsin kinase: substrate specificity and factors that influence activity. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2306–2313. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Smith D., Mardon G., Quinn W., Zuker C. Isolation and characterization of two new drosophila protein kinase C genes, including one specifically expressed in photoreceptor cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):403–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90915-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Homologous desensitization of adenylate cyclase is associated with phosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):3883–3886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Shieh B. H., Chuman L., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is a tissue-specific integral membrane protein required for the proper synthesis of a subset of Drosophila rhodopsins. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90156-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P., Findlay J. B. Phosphorylation of ovine rhodopsin. Identification of the phosphorylated sites. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):773–780. doi: 10.1042/bj2200773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]