Abstract
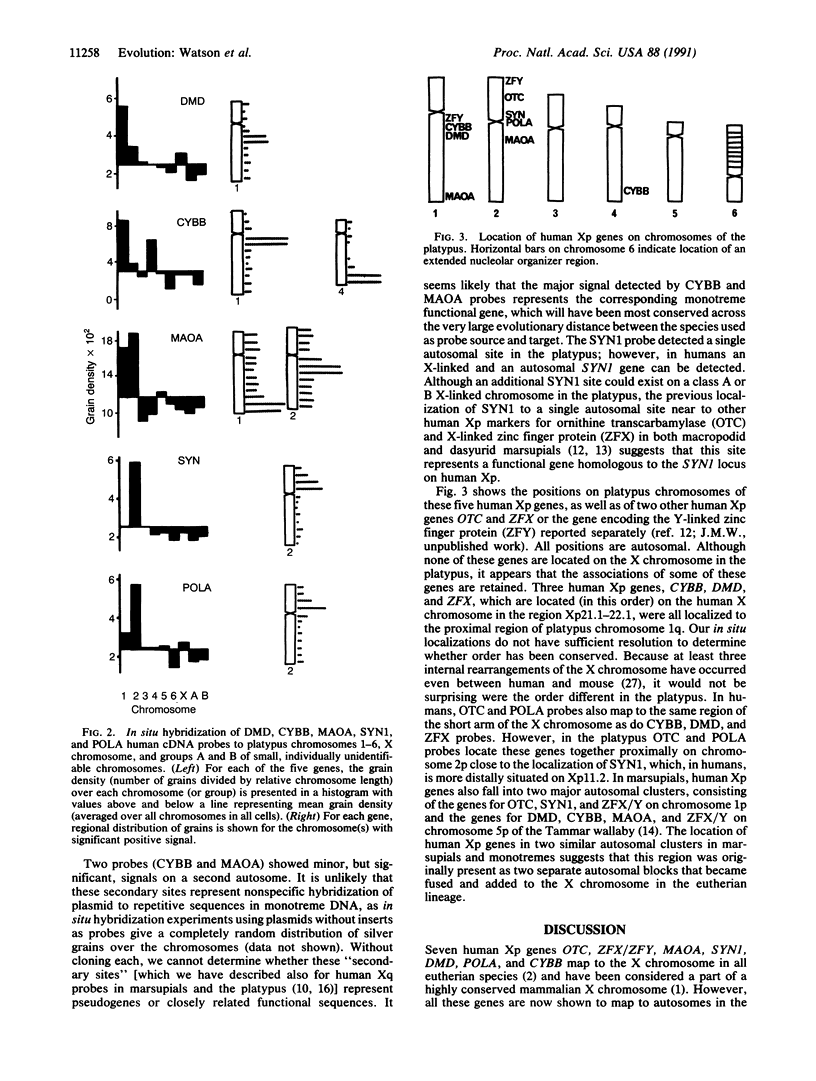
To investigate the evolution of the mammalian sex chromosomes, we have compared the gene content of the X chromosomes in the mammalian groups most distantly related to man (marsupials and monotremes). Previous work established that genes on the long arm of the human X chromosome are conserved on the X chromosomes in all mammals, revealing that this region was part of an ancient mammalian X chromosome. However, we now report that several genes located on the short arm of the human X chromosome are absent from the platypus X chromosome, as well as from the marsupial X chromosome. Because monotremes and marsupials diverged independently from eutherian mammals, this finding implies that the whole human X short arm region is a relatively recent addition to the X chromosome in eutherian mammals.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler D. A., Bressler S. L., Chapman V. M., Page D. C., Disteche C. M. Inactivation of the Zfx gene on the mouse X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4592–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Heerema N., Orkin S. H. DNA linkage analysis of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3398–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Pearson P. L., Harper P. S., Murray J. M., O'Brien T., Sarfarazi M., Williamson R. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2303–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson G. W., Graves J. A. Gene mapping in marsupials and monotremes. I. The chromosomes of rodent-marsupial (Macropus) cell hybrids, and gene assignments to the X chromosome of the grey kangaroo. Chromosoma. 1984;91(1):20–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00286481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald J. A., Hope R. M. Mapping a marsupial X chromosome using kangaroo-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;29(3):127–137. doi: 10.1159/000131561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. M., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Ridley A., McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. B., Willard H. F., Bieber F. R., Page D. C. Homologous ribosomal protein genes on the human X and Y chromosomes: escape from X inactivation and possible implications for Turner syndrome. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1205–1218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90416-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu Y. P., Weyler W., Chen S., Sims K. B., Rinehart W. B., Utterback M. C., Powell J. F., Breakefield X. O. Structural features of human monoamine oxidase A elucidated from cDNA and peptide sequences. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1321–1324. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., DeGennaro L. J. Molecular cloning of cDNAs for the nerve-cell specific phosphoprotein, synapsin I. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1997–2002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau E. C., Mohandas T. K., Shapiro L. J., Slavkin H. C., Snead M. L. Human and mouse amelogenin gene loci are on the sex chromosomes. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. The William Allan memorial award address: X-chromosome inactivation and the location and expression of X-linked genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):8–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Shapiro L. J., Norum R. A., Mohandas T., Axelman J., Dabora R. L. Differential expression of steroid sulphatase locus on active and inactive human X chromosome. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):838–840. doi: 10.1038/299838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh V., Eddy R., Bruns G. A., Shih V. E., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Localization of the ornithine aminotransferase gene and related sequences on two human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1987 Jun;76(2):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00284906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. J., Czuppon A. B., Sharman G. B. Inheritance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variation in kangaroos. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 31;230(13):154–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio230154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Nussbaum R., Page D. C. ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative human sex determinant, and escapes X inactivation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1247–1258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Foster J. W., Spencer J. A., Page D. C., Palmer M., Goodfellow P. N., Graves J. A. Sequences homologous to ZFY, a candidate human sex-determining gene, are autosomal in marsupials. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):780–783. doi: 10.1038/336780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Wrigley J. M., Marshall Graves J. A. Autosomal assignment of OTC in marsupials and monotremes: implications for the evolution of sex chromosomes. Genet Res. 1987 Oct;50(2):131–136. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300023533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. A., Sinclair A. H., Watson J. M., Graves J. A. Genes on the short arm of the human X chromosome are not shared with the marsupial X. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90141-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. A., Watson J. M., Graves J. A. The X chromosome of marsupials shares a highly conserved region with eutherians. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):598–604. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90352-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Pearson B. E., Suomalainen H. A., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Schröder J., Korn D. Assignment of the gene for human DNA polymerase alpha to the X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5270–5274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Graves J. A. Gene mapping in marsupials and monotremes, V. Synteny between hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase and phosphoglycerate kinase in the platypus. Aust J Biol Sci. 1988;41(2):231–237. doi: 10.1071/bi9880231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. M., Spencer J. A., Riggs A. D., Graves J. A. The X chromosome of monotremes shares a highly conserved region with the eutherian and marsupial X chromosomes despite the absence of X chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7125–7129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley J. M., Graves J. A. Karyotypic conservation in the mammalian order monotremata (subclass Prototheria). Chromosoma. 1988;96(3):231–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00302363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley J. M., Graves J. A. Two monotreme cell lines, derived from female platypuses (Ornithorhynchus anatinus; Monotremata, Mammalia). In Vitro. 1984 Apr;20(4):321–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02618595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]