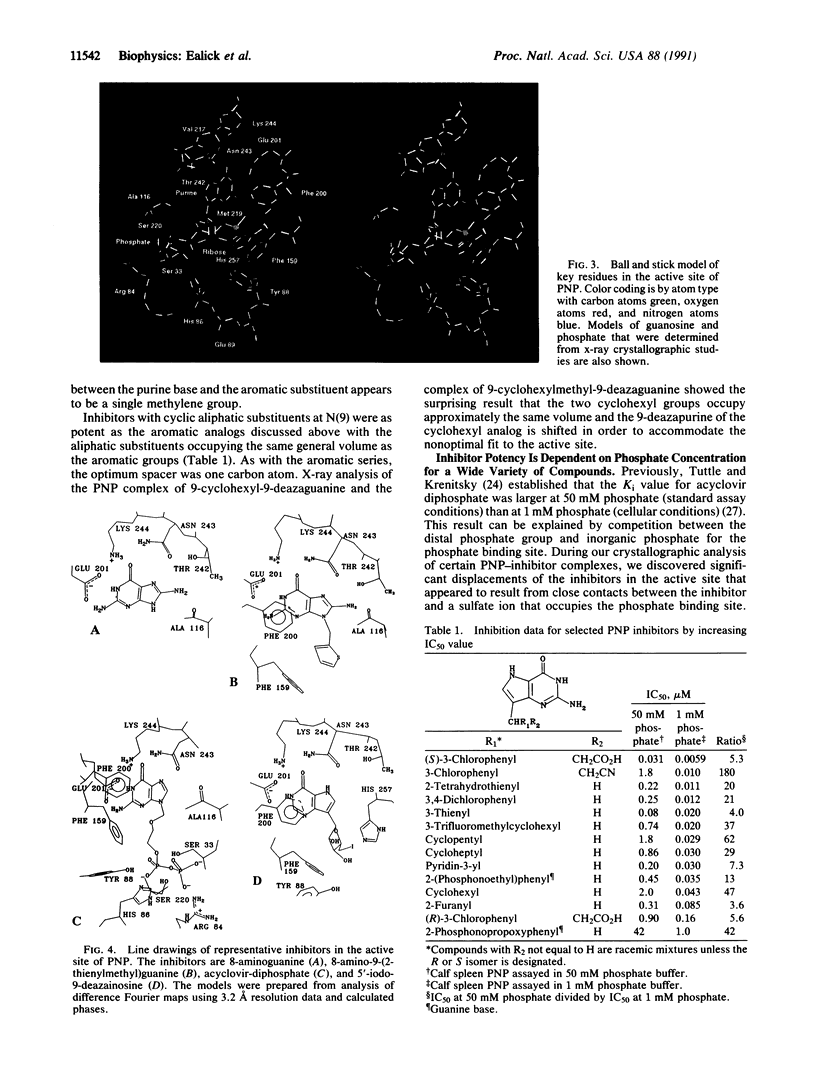
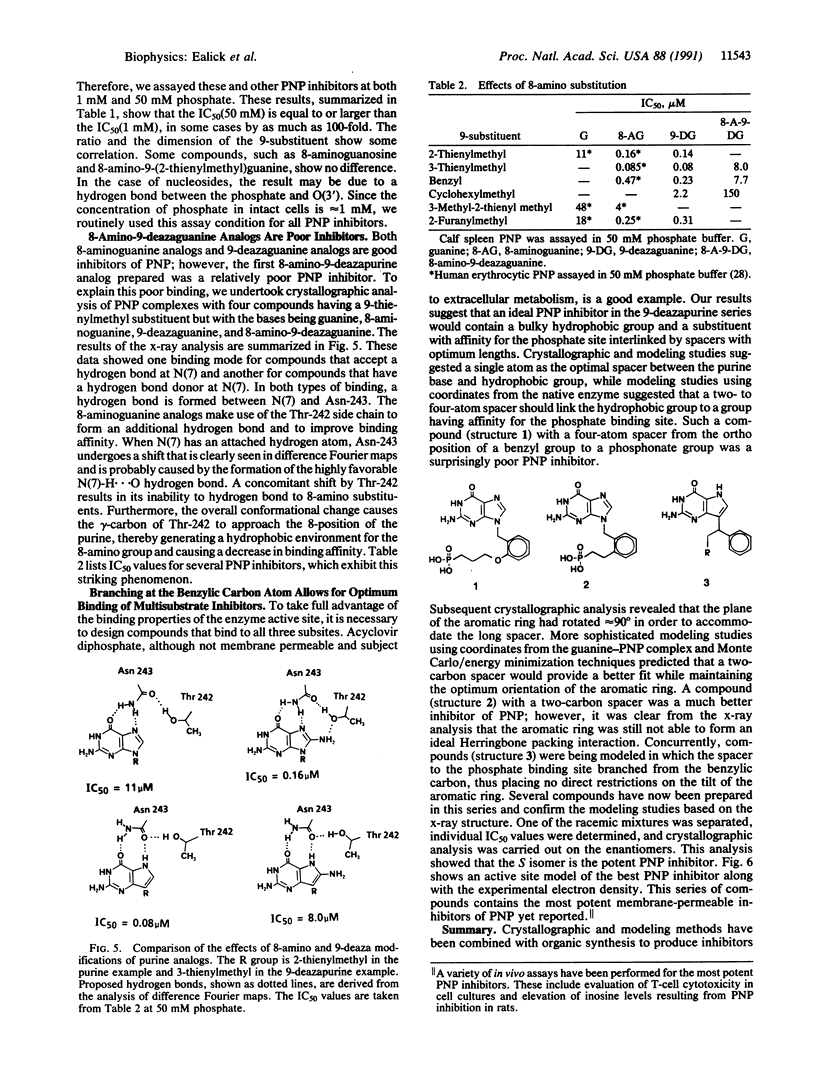
Abstract
Competitive inhibitors of the salvage pathway enzyme purine-nucleoside phosphorylase (purine-nucleoside:orthophosphate ribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.1) have been designed by using the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme as determined by x-ray crystallography. The process was an iterative one that utilized interactive computer graphics, Monte Carlo-based conformational searching, energy minimization, and x-ray crystallography. The proposed compounds were synthesized and tested by an in vitro assay. Among the compounds designed and synthesized are the most potent competitive inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylase thus far reported.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. C., Agarwal R. P., Stoeckler J. D., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Microheterogeneity and comparison of kinetic behavior of the enzyme from several tissues and species. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):79–84. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelt K., Bacquet R. J., Bartlett C. A., Booth C. L., Freer S. T., Fuhry M. A., Gehring M. R., Herrmann S. M., Howland E. F., Janson C. A. Design of enzyme inhibitors using iterative protein crystallographic analysis. J Med Chem. 1991 Jul;34(7):1925–1934. doi: 10.1021/jm00111a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., Petsko G. A. Aromatic-aromatic interaction: a mechanism of protein structure stabilization. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.3892686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzowska A., Kulikowska E., Shugar D. Properties of purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) of mammalian and bacterial origin. Z Naturforsch C. 1990 Jan-Feb;45(1-2):59–70. doi: 10.1515/znc-1990-1-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealick S. E., Rule S. A., Carter D. C., Greenhough T. J., Babu Y. S., Cook W. J., Habash J., Helliwell J. R., Stoeckler J. D., Parks R. E., Jr Three-dimensional structure of human erythrocytic purine nucleoside phosphorylase at 3.2 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1812–1820. doi: 10.2210/pdb2pnp/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J., Neidhart D. J., VanDrie J., Kempf D. J., Wang X. C., Norbeck D. W., Plattner J. J., Rittenhouse J. W., Turon M., Wideburg N. Design, activity, and 2.8 A crystal structure of a C2 symmetric inhibitor complexed to HIV-1 protease. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):527–533. doi: 10.1126/science.2200122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertsen R. B., Scott M. E., Dong M. K., Kossarek L. M., Bennett M. K., Schrier D. J., Sircar J. C. Preliminary report on 8-amino-9-(2-thienylmethyl)guanine (PD 119,229), a novel and potent purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitor. Agents Actions. 1987 Aug;21(3-4):272–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01966488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPAGE G. A., JUNGA I. G., BOWMAN B. BIOCHEMICAL AND CARCINOSTATIC EFFECTS OF 2'-DEOXYTHIOGUANOSINE. Cancer Res. 1964 Jun;24:835–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewach D. S., Chern J. W., Pillote K. E., Townsend L. B., Daddona P. E. Potentiation of 2'-deoxyguanosine cytotoxicity by a novel inhibitor of purine nucleoside phosphorylase, 8-amino-9-benzylguanine. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):519–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckler J. D., Agarwal R. P., Agarwal K. C., Schmid K., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from human erythrocytes: physiocochemical properties of the crystalline enzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):278–283. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckler J. D., Cambor C., Kuhns V., Chu S. H., Parks R. E., Jr Inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylase, C(8) and C(5') substitutions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 15;31(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckler J. D., Ealick S. E., Bugg C. E., Parks R. E., Jr Design of purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitors. Fed Proc. 1986 Nov;45(12):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckler J. D., Ryden J. B., Parks R. E., Jr, Chu M. Y., Lim M. I., Ren W. Y., Klein R. S. Inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylase: effects of 9-deazapurine ribonucleosides and synthesis of 5'-deoxy-5'-iodo-9-deazainosine. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 1):1774–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle J. V., Krenitsky T. A. Effects of acyclovir and its metabolites on purine nucleoside phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4065–4069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Goddard J. M., Martin D. W., Jr Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequence and genomic clone characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5779–5787. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]