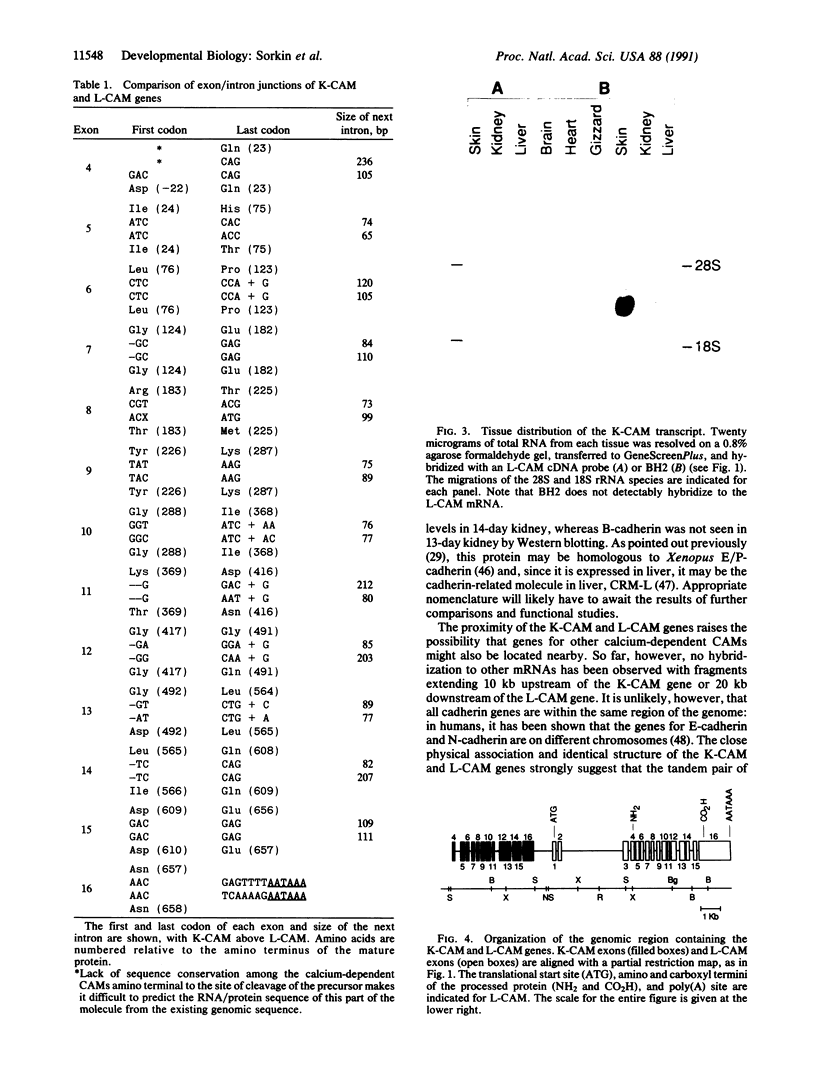
Abstract
Genomic sequences immediately upstream of the translational start site for the chicken liver cell adhesion molecule (L-CAM) gene contain a second closely related gene, which, because of its location, we have designated the K-CAM gene. Less than 700 base pairs separate the presumed poly(A) site in the K-CAM gene from the translation initiation site for L-CAM. The sizes of exons 4-15 of the K-CAM gene are almost identical to those in the L-CAM gene and the exon/intron junctions occur at exactly equivalent positions in both genes. Exon 16, which includes the 3' untranslated region, is much shorter in the K-CAM gene and intron sizes and sequences are not generally conserved between the two genes. Probes from the K-CAM gene hybridized to a 3-kilobase mRNA that was present at high levels in embryonic skin, at lower levels in kidney, heart, and gizzard, and at still lower levels in brain and liver, as determined by Northern blotting. The sequence of the predicted gene product was nearly identical to that of the chicken B-cadherin cDNA, although the distribution of the K-CAM gene transcript differed from that reported for the cadherin. The proximity and identical overall structure of the K-CAM and L-CAM genes strongly suggest that they arose by gene duplication and raise the possibility that genes for other calcium-dependent CAMs may be located in clusters. Moreover, the tandem arrangement of the genes may have important implications for the regulation of their expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angres B., Müller A. H., Kellermann J., Hausen P. Differential expression of two cadherins in Xenopus laevis. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):829–844. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begemann M., Tan S. S., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Expression of chicken liver cell adhesion molecule fusion genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9042–9046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens J., Birchmeier W., Goodman S. L., Imhof B. A. Dissociation of Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells by the monoclonal antibody anti-arc-1: mechanistic aspects and identification of the antigen as a component related to uvomorulin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1307–1315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby J. L., Pratt R. S., Lilien J., Reichardt L. F. Neurite outgrowth on muscle cell surfaces involves extracellular matrix receptors as well as Ca2+-dependent and -independent cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2555–2559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschuk O. W., Pouliot Y., Holland P. C. Identification of a conserved region common to cadherins and influenza strain A hemagglutinins. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):679–682. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90065-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskirk D. R., Thiery J. P., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Antibodies to a neural cell adhesion molecule disrupt histogenesis in cultured chick retinae. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):488–489. doi: 10.1038/285488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden S. L., Rutishauser U., Lilien J. Identification of two structural types of calcium-dependent adhesion molecules in the chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Chuong C. M., Edelman G. M. Expression sequences of cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6942–6946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Prediger E. A., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule: structure, immunoglobulin-like domains, cell surface modulation, and alternative RNA splicing. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):799–806. doi: 10.1126/science.3576199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damsky C. H., Richa J., Solter D., Knudsen K., Buck C. A. Identification and purification of a cell surface glycoprotein mediating intercellular adhesion in embryonic and adult tissue. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):455–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90379-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duband J. L., Dufour S., Hatta K., Takeichi M., Edelman G. M., Thiery J. P. Adhesion molecules during somitogenesis in the avian embryo. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1361–1374. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. Cell adhesion molecules: implications for a molecular histology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Place-dependent cell adhesion, process retraction, and spatial signaling in neural morphogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:303–318. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin W. J., Chuong C. M., Finkel L. H., Edelman G. M. Antibodies to liver cell adhesion molecule perturb inductive interactions and alter feather pattern and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8235–8239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin W. J., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Characterization of L-CAM, a major cell adhesion molecule from embryonic liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1038–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin W. J., Sorkin B. C., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding the liver cell adhesion molecule, L-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2808–2812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., DeSimone D., Geiger B. Expression of a novel cadherin (EP-cadherin) in unfertilized eggs and early Xenopus embryos. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):315–325. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta K., Nose A., Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a neural calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecule: its identity in the cadherin gene family. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):873–881. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta K., Takeichi M. Expression of N-cadherin adhesion molecules associated with early morphogenetic events in chick development. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):447–449. doi: 10.1038/320447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta M., Miyatani S., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Takeichi M. Genomic organization and chromosomal mapping of the mouse P-cadherin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4437–4441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg F., Wildermuth V., Wedlich D. Expression of XBcad, a novel cadherin, during oogenesis and early development of Xenopus. Mech Dev. 1991 Aug;35(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton J. L., Kenny T. P., Legan P. K., Collins J. E., Keen J. N., Sharma R., Garrod D. R. Desmosomal glycoproteins 2 and 3 (desmocollins) show N-terminal similarity to calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecules. J Cell Sci. 1990 Oct;97(Pt 2):239–246. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyafil F., Morello D., Babinet C., Jacob F. A cell surface glycoprotein involved in the compaction of embryonal carcinoma cells and cleavage stage embryos. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):927–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90456-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuzuka H., Miyatani S., Takeichi M. R-cadherin: a novel Ca(2+)-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecule expressed in the retina. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90075-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Nomura K., Hirayama Y., Kitagawa T. Establishment and characterization of a chicken hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, LMH. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 15;47(16):4460–4464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch P. J., Walsh M. J., Schmelz M., Goldschmidt M. D., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W. Identification of desmoglein, a constitutive desmosomal glycoprotein, as a member of the cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;53(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga M., Hatta K., Takeichi M. Role of N-cadherin cell adhesion molecules in the histogenesis of neural retina. Neuron. 1988 Jun;1(4):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki F., Mège R. M., Jaffe S. H., Friedlander D. R., Gallin W. J., Goldberg J. I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. cDNAs of cell adhesion molecules of different specificity induce changes in cell shape and border formation in cultured S180 cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1239–1252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege R. M., Matsuzaki F., Gallin W. J., Goldberg J. I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Construction of epithelioid sheets by transfection of mouse sarcoma cells with cDNAs for chicken cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Shirayoshi Y., Okazaki K., Yasuda K., Takeichi M. Transformation of cell adhesion properties by exogenously introduced E-cadherin cDNA. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):341–343. doi: 10.1038/329341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Transmembrane control of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion: a 94 kDa protein functionally associated with a specific region of the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):37–44. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napolitano E. W., Venstrom K., Wheeler E. F., Reichardt L. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of B-cadherin, a novel chick cadherin. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):893–905. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose A., Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Isolation of placental cadherin cDNA: identification of a novel gene family of cell-cell adhesion molecules. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3655–3661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose A., Takeichi M. A novel cadherin cell adhesion molecule: its expression patterns associated with implantation and organogenesis of mouse embryos. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2649–2658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa M., Baribault H., Kemler R. The cytoplasmic domain of the cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin associates with three independent proteins structurally related in different species. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1711–1717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. A., Pearson D., Shibahara S., Hofsteenge J., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Tenascin: cDNA cloning and induction by TGF-beta. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):2977–2982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringwald M., Schuh R., Vestweber D., Eistetter H., Lottspeich F., Engel J., Dölz R., Jähnig F., Epplen J., Mayer S. The structure of cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin. Insights into the molecular mechanism of Ca2+-dependent cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3647–3653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Okada T. S., Takeichi M. The calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion system regulates inner cell mass formation and cell surface polarization in early mouse development. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin B. C., Hemperly J. J., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Structure of the gene for the liver cell adhesion molecule, L-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7617–7621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Graphic methods to determine the function of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):521–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Sano K., Tanihara H. Diversity of the cadherin family: evidence for eight new cadherins in nervous tissue. Cell Regul. 1991 Apr;2(4):261–270. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Delouvée A., Gallin W. J., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Ontogenetic expression of cell adhesion molecules: L-CAM is found in epithelia derived from the three primary germ layers. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):61–78. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk T., Geiger B. A 135-kd membrane protein of intercellular adherens junctions. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2249–2260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Barton C. H., Putt W., Moore S. E., Kelsell D., Spurr N., Goodfellow P. N. N-cadherin gene maps to human chromosome 18 and is not linked to the E-cadherin gene. J Neurochem. 1990 Sep;55(3):805–812. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida C., Takeichi M. Teratocarcinoma cell adhesion: identification of a cell-surface protein involved in calcium-dependent cell aggregation. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



