Abstract
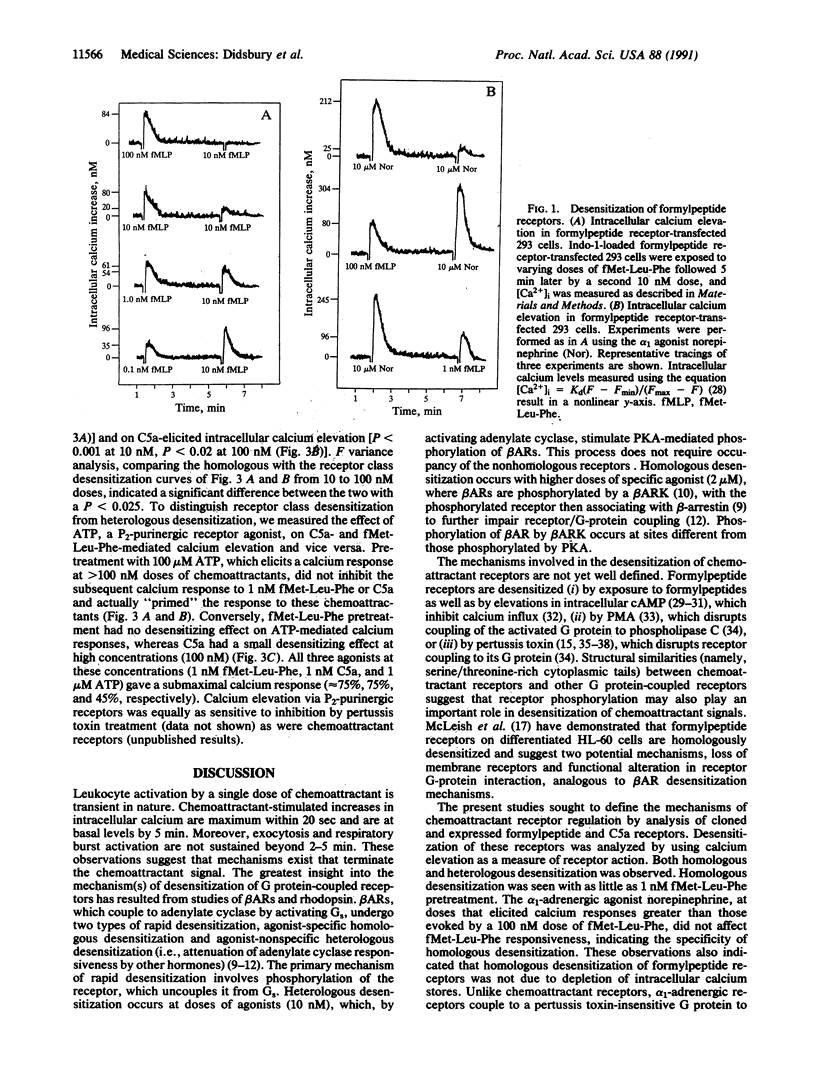
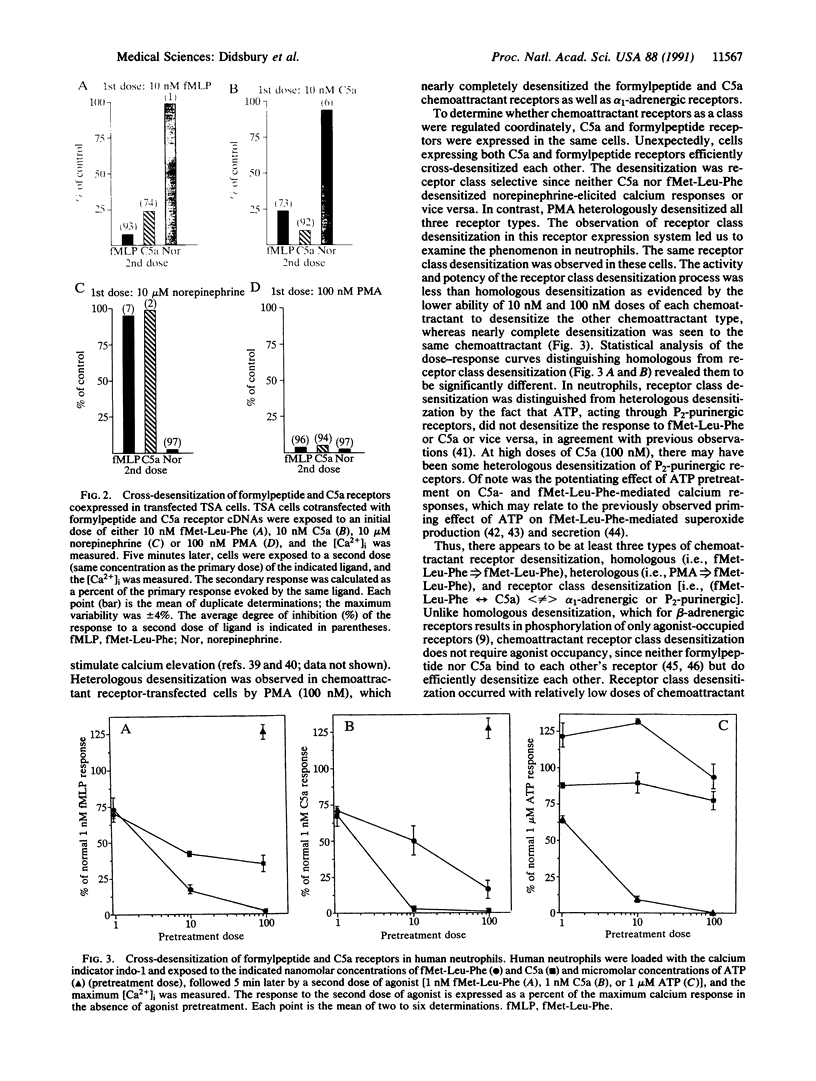
To better define their regulation, formylpeptide and C5a chemoattractant receptor cDNAs were transiently expressed with high efficiency (approximately 35-54%) in human kidney cells. As in neutrophils, both receptors were active in elevating intracellular calcium (ED50 approximately 0.5-1 nM). Agonist-specific desensitization for calcium elevation was observed for both chemoattractant receptors at doses of approximately 1 nM. Heterologous desensitization of formylpeptide, C5a, and alpha 1-adrenergic receptors required high doses of phorbol ester (100 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate). To further study the phenomenon of desensitization, formylpeptide and C5a receptor cDNAs were cotransfected resulting in approximately 80% of receptor-positive cells expressing both receptors. These cells also possessed endogenous alpha 1-adrenergic receptors. Interestingly, chemoattractant receptors were cross-desensitized by pretreatment with low doses of either C5a or formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (10 nM) but not by the alpha 1-adrenergic agonist norepinephrine (up to 10 microM). Neither chemoattractant desensitized alpha 1-adrenergic receptors. This phenomenon was reproduced in human neutrophils. These data suggest a previously uncharacterized mechanism of receptor regulation, which is intermediate between homologous and heterologous desensitization. Class desensitization of chemoattractant receptors is less selective than homologous desensitization but is far more efficient and specific than heterologous desensitization. Receptor class desensitization may affect functional classes of receptors via modification of either the receptor or the shared guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. A., Traynor A. E., Omann G. M., Jesaitis A. J. The chemotactic peptide receptor. A model for future understanding of chemotactic disorders. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;2(1):33–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. G., Van Epps D. E., Chenoweth D. E. Independent regulation of human neutrophil chemotactic receptors after activation. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3028–3033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Tardif M., Brouchon L., Vignais P. Synthesis and use of a novel N-formyl peptide derivative to isolate a human N-formyl peptide receptor cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1103–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91143-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Tardif M., Brouchon L., Vignais P. The human N-formylpeptide receptor. Characterization of two cDNA isolates and evidence for a new subfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11123–11133. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3106–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Dougherty R. W., Lapetina E. G., Niedel J. E. Pertussis toxin inhibits chemotactic peptide-stimulated generation of inositol phosphates and lysosomal enzyme secretion in human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3277–3280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushfield M., Griffiths S. L., Murphy G. J., Pyne N. J., Knowler J. T., Milligan G., Parker P. J., Mollner S., Houslay M. D. Diabetes-induced alterations in the expression, functioning and phosphorylation state of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi-2 in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):365–372. doi: 10.1042/bj2710365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushfield M., Murphy G. J., Lavan B. E., Parker P. J., Hruby V. J., Milligan G., Houslay M. D. Hormonal regulation of Gi2 alpha-subunit phosphorylation in intact hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):449–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2680449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Kunkel M. W., Friedman J., Goka T. J., Johnson J. A. Activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase is required for heterologous desensitization of adenylyl cyclase in S49 wild-type lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P. H., Rink T. J. Fluorescence and bioluminescence measurement of cytoplasmic free calcium. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):313–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2480313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. The receptors for ATP and fMetLeuPhe are independently coupled to phospholipases C and A2 via G-protein(s). Relationship between phospholipase C and A2 activation and exocytosis in HL60 cells and human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):715–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2630715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Kobilka B. K., Daniel K. W., Nolan R. D., Lapetina E. Y., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Multiple second messenger pathways of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes expressed in eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Snyderman R. Molecular cloning of a new human G protein. Evidence for two Gi alpha-like protein families. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 13;219(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. A family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2657–2664. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Wood W. I., Eaton D., Hass P. E., Hollingshead P., Wion K., Mather J., Lawn R. M., Vehar G. A., Gorman C. Construction and characterization of an active factor VIII variant lacking the central one-third of the molecule. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8343–8347. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Mechanisms of action of calcium-mobilizing agonists: some variations on a young theme. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2670–2676. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.2456243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Sandler J. A., Clyman R. I., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Agents that increase cyclic AMP inhibit accumulation of cGMP and depress human monocyte locomotion. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):492–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Gerard C. The chemotactic receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):614–617. doi: 10.1038/349614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen R. E., Devreotes P. N. In vivo receptor-mediated phosphorylation of a G protein in Dictyostelium. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):591–593. doi: 10.1126/science.2110382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12657–12665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda Z., Nakamura M., Miki I., Minami M., Watanabe T., Seyama Y., Okado H., Toh H., Ito K., Miyamoto T. Cloning by functional expression of platelet-activating factor receptor from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):342–346. doi: 10.1038/349342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Naemura J. R., Painter R. G., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G. The fate of an N-formylated chemotactic peptide in stimulated human granulocytes. Subcellular fractionation studies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1968–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Tolley J. O., Allen R. A. Receptor-cytoskeleton interactions and membrane traffic may regulate chemoattractant-induced superoxide production in human granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13662–13669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhns D. B., Wright D. G., Nath J., Kaplan S. S., Basford R. E. ATP induces transient elevations of [Ca2+]i in human neutrophils and primes these cells for enhanced O2- generation. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G. Role of phosphorylation in desensitization of the beta-adrenoceptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90113-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. beta-Arrestin: a protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1547–1550. doi: 10.1126/science.2163110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeish K. R., Gierschik P., Jakobs K. H. Desensitization uncouples the formyl peptide receptor-guanine nucleotide-binding protein interaction in HL60 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;36(3):384–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., White J. R., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol esters inhibit the fMet-Leu-Phe- and leukotriene B4-stimulated calcium mobilization and enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin I., Rosenblatt J., Becker E. L. The role of cyclic AMP in the chemotactic responsiveness and spontaneous motility of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. The inhibition of neutrophil movement and the elevation of cyclic AMP levels by catecholamines, prostaglandins, theophylline and cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1126–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Springer M. S. Identification of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte C5a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7157–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Burde R., Schultz G. Activation of NADPH oxidase by purine and pyrimidine nucleotides involves G proteins and is potentiated by chemotactic peptides. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):813–819. doi: 10.1042/bj2590813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Atkinson J. P., Spilberg I. Stimulus-specific deactivation of chemotactic factor-induced cyclic AMP response and superoxide generation by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):736–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI109911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Fischbein L. C., Spilberg I., Atkinson J. P. Induction of a transient elevation in intracellular levels of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate by chemotactic factors: an early event in human neutrophil activation. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1482–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Finney D. A., Oades Z. G., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G. The dynamics of ligand-receptor interactions. Real-time analyses of association, dissociation, and internalization of an N-formyl peptide and its receptors on the human neutrophil. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5661–5669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Snyderman R. Guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in receptor-mediated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in human leukocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:261–271. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Uhing R. J., Snyderman R. Nucleotide regulatory protein-mediated activation of phospholipase C in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes is disrupted by phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6121–6127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Ishitoya J., Nagai Y. Inhibitory effect of prostaglandin E2, forskolin, and dibutyryl cAMP on arachidonic acid release and inositol phospholipid metabolism in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1092–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Smith C. D., Snyderman R. Potential role for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in chemoattractant receptor mediated polyphosphoinositide metabolism, Ca++ mobilization and cellular responses by leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Shefcyk J., Huang C. K., Marsh M. L., Munoz J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits fMet-Leu-Phe- but not phorbol ester-stimulated changes in rabbit neutrophils: role of G proteins in excitation response coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. A., Hagenlocker B. E., Douglas V. K., Tarapchak S. J., Ward P. A. Nucleotide responses of human neutrophils. Lab Invest. 1991 Jan;64(1):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




