Abstract
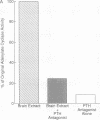
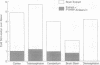
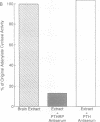
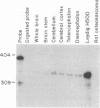
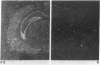
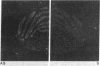
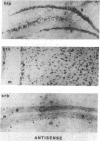
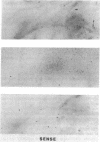
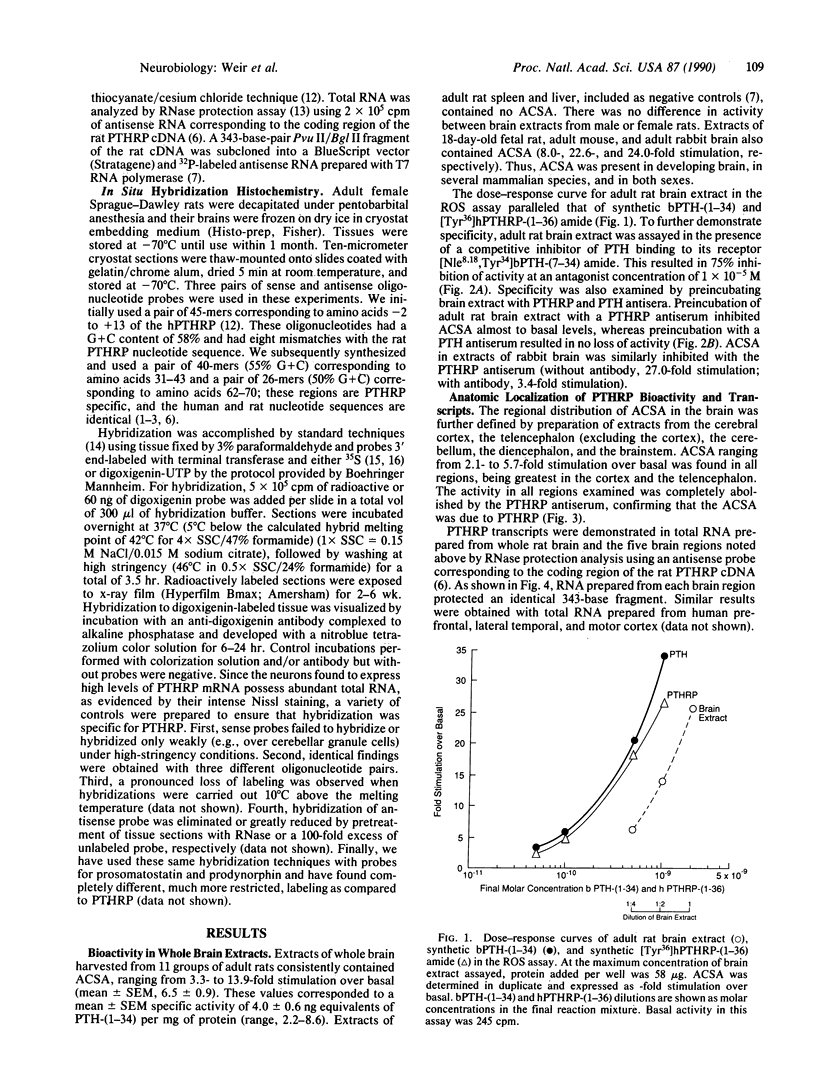
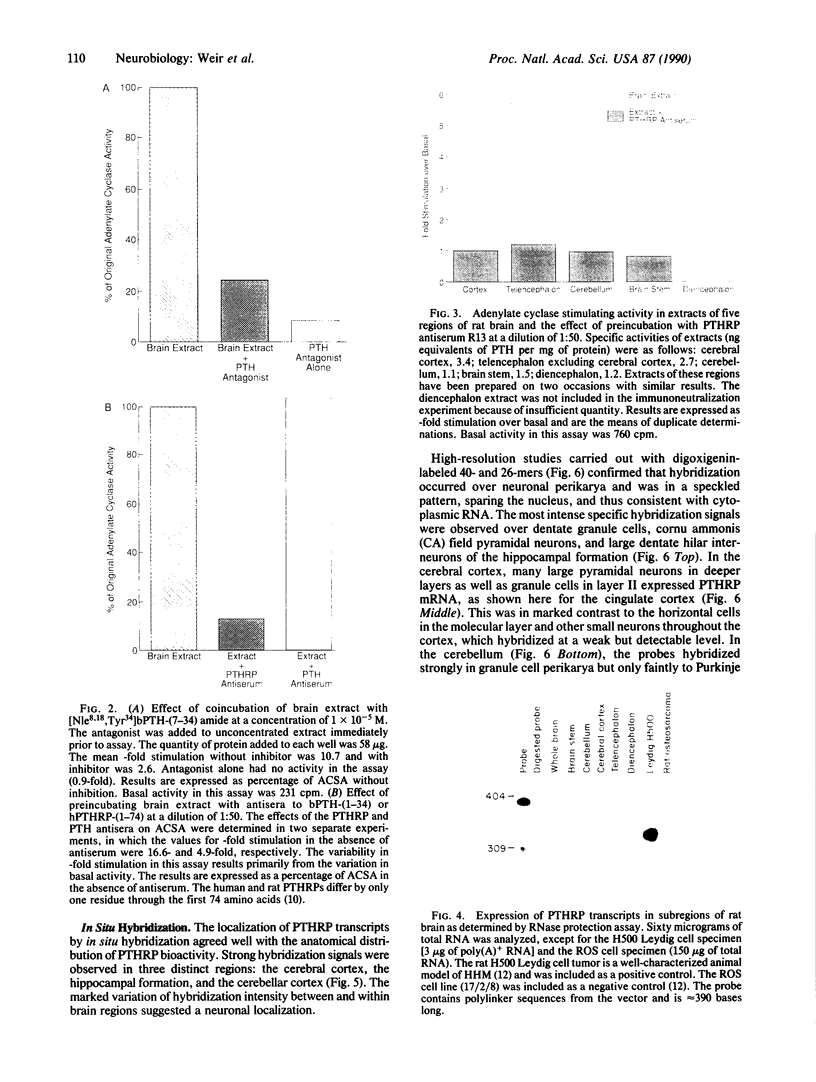
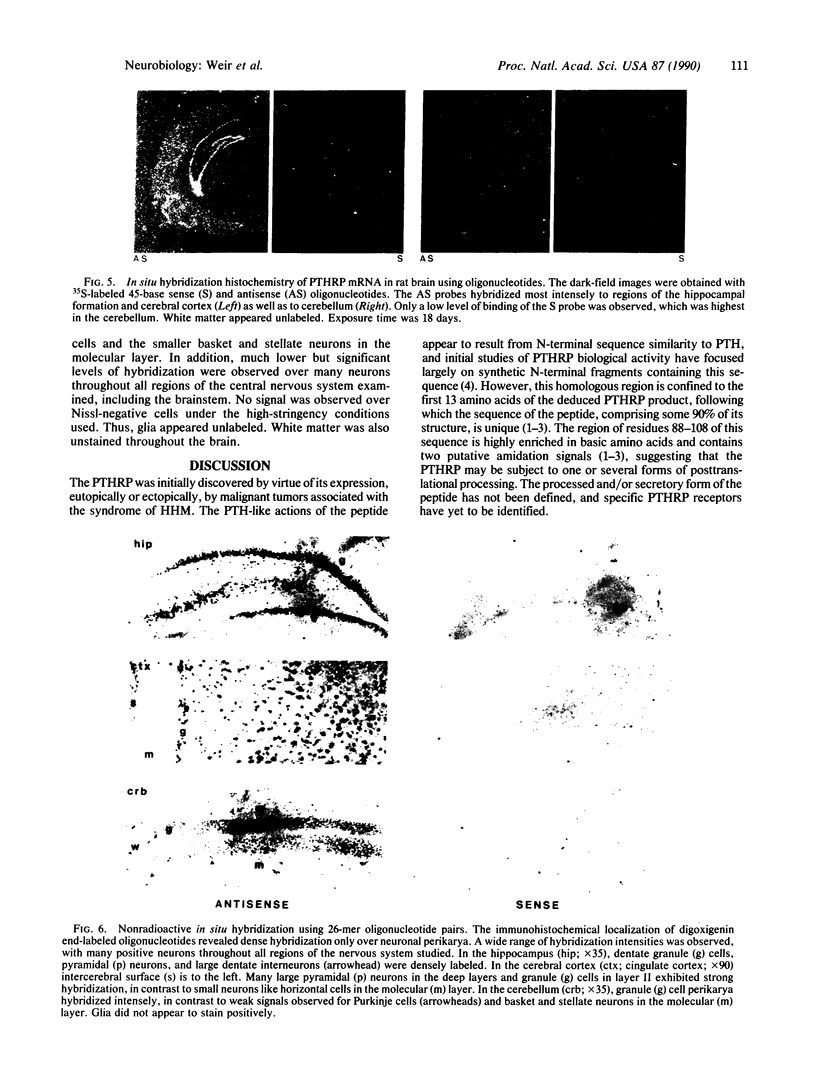
A parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHRP) has been identified in human tumors associated with the syndrome of humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. While parathyroid hormone (PTH) gene expression appears to be limited to the parathyroid glands, PTHRP mRNA has been identified in a variety of normal tissues. To investigate the apparent expression of the PTHRP in the central nervous system, we examined extracts of whole rat brain for PTHRP bioactivity by measuring adenylate cyclase-stimulating activity (ACSA) in a PTH-sensitive assay. Extracts consistently contained ACSA and this activity was completely inhibited by a PTHRP antiserum but was unaffected by a PTH antiserum. ACSA was found in a number of anatomic subregions of rat brain, being greatest in the cortex and telencephalon. RNase protection analysis revealed PTHRP transcripts in total RNA prepared from whole rat brain and from the same anatomic subregions. By in situ hybridization histochemistry, we found that the highest levels of PTHRP gene expression occurred in neurons of the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellar cortex. These studies demonstrate that both PTHRP mRNA and biological activity are present in a number of regions of rat brain. The widespread expression of this peptide by multiple types of neurons suggests that the PTHRP may play a general role in neuronal physiology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer R. N., Siesjö B. K. Biological differences between ischemia, hypoglycemia, and epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):699–707. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Fitzpatrick-McElligott S., Gozes I., Baldino F., Jr Localization of vasopressin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, peptide histidine isoleucine- and somatostatin-mRNA in rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 May;252(2):307–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00214373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens T. L., Garrett K. P., Zhou X. Y., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R., Dempster D. W. Immunocytochemical localization of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor in target cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Apr;122(4):1224–1230. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Hunsaker W. R. Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: a direct comparison with 5'-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés R., Supavilai P., Karobath M., Palacios J. M. Calcium antagonist binding sites in the rat brain: quantitative autoradiographic mapping using the 1,4-dihydropyridines [3H]PN 200-110 and [3H]PY 108-068. J Neural Transm. 1984;60(3-4):169–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01249092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Gazdar A. F., Ikeda K., Broadus A. E. The parathyroid hormone-related protein associated with malignancy is secreted by neuroendocrine tumors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):503–508. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Young A. B., Penney J. B. Quantitative autoradiography of L-[3H]glutamate binding to rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jun 16;37(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska K. A., Goligorsky M., Scoble J., Tsutsumi M., Westbrook S., Moskowitz D. Effects of parathyroid hormone on cytosolic calcium in renal proximal tubular primary cultures. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):F188–F198. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.2.F188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Lu C., Weir E. C., Mangin M., Broadus A. E. Transcriptional regulation of the parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene by glucocorticoids and vitamin D in a human C-cell line. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15743–15746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Mangin M., Dreyer B. E., Webb A. C., Posillico J. T., Stewart A. F., Bander N. H., Weir E. C., Insogna K. L., Broadus A. E. Identification of transcripts encoding a parathyroid hormone-like peptide in messenger RNAs from a variety of human and animal tumors associated with humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):2010–2014. doi: 10.1172/JCI113551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Weir E. C., Mangin M., Dannies P. S., Kinder B., Deftos L. J., Brown E. M., Broadus A. E. Expression of messenger ribonucleic acids encoding a parathyroid hormone-like peptide in normal human and animal tissues with abnormal expression in human parathyroid adenomas. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1230–1236. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R. The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: insights into central nervous system function. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1654–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.3059497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangin M., Ikeda K., Dreyer B. E., Broadus A. E. Isolation and characterization of the human parathyroid hormone-like peptide gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2408–2412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangin M., Webb A. C., Dreyer B. E., Posillico J. T., Ikeda K., Weir E. C., Stewart A. F., Bander N. H., Milstone L., Barton D. E. Identification of a cDNA encoding a parathyroid hormone-like peptide from a human tumor associated with humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):597–601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodan S. B., Insogna K. L., Vignery A. M., Stewart A. F., Broadus A. E., D'Souza S. M., Bertolini D. R., Mundy G. R., Rodan G. A. Factors associated with humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy stimulate adenylate cyclase in osteoblastic cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1511–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI111108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. M., Olney J. W. Glutamate and the pathophysiology of hypoxic--ischemic brain damage. Ann Neurol. 1986 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Gilmore-Hebert M., Utset M. F., Lai C., Greene A., Benz E. J., Jr Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):284–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sousa R. J., Tannery N. H., Lafer E. M. In situ hybridization mapping of glucocorticoid receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in rat brain. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):481–494. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Elliot J., Burtis W. J., Wu T., Insogna K. L. Synthetic parathyroid hormone-like protein-(1-74): biochemical and physiological characterization. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):642–648. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Insogna K. L., Goltzman D., Broadus A. E. Identification of adenylate cyclase-stimulating activity and cytochemical glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-stimulating activity in extracts of tumors from patients with humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1454–1458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suva L. J., Mather K. A., Gillespie M. T., Webb G. C., Ng K. W., Winslow G. A., Wood W. I., Martin T. J., Hudson P. J. Structure of the 5' flanking region of the gene encoding human parathyroid-hormone-related protein (PTHrP). Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suva L. J., Winslow G. A., Wettenhall R. E., Hammonds R. G., Moseley J. M., Diefenbach-Jagger H., Rodda C. P., Kemp B. E., Rodriguez H., Chen E. Y. A parathyroid hormone-related protein implicated in malignant hypercalcemia: cloning and expression. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):893–896. doi: 10.1126/science.3616618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiede M. A., Rodan G. A. Expression of a calcium-mobilizing parathyroid hormone-like peptide in lactating mammary tissue. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):278–280. doi: 10.1126/science.3175653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiede M. A., Strewler G. J., Nissenson R. A., Rosenblatt M., Rodan G. A. Human renal carcinoma expresses two messages encoding a parathyroid hormone-like peptide: evidence for the alternative splicing of a single-copy gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4605–4609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasicek T. J., McDevitt B. E., Freeman M. W., Fennick B. J., Hendy G. N., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A., Kronenberg H. M. Nucleotide sequence of the human parathyroid hormone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2127–2131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., De Souza E. B., Snyder S. H. Mapping second messenger systems in the brain: differential localizations of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4053–4057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneous localization of protein kinase C in rat brain: autoradiographic analysis of phorbol ester receptor binding. J Neurosci. 1986 Jan;6(1):199–207. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-01-00199.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. S., Tyler G. A., O'Brien R., Caporale L. H., Rosenblatt M. Immunoprecipitation of the parathyroid hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):26–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Hahn T. J., Iida-Klein A., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Parathyroid hormone-activated calcium channels in an osteoblast-like clonal osteosarcoma cell line. cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7711–7718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda T., Banville D., Hendy G. N., Goltzman D. Characterization of the human parathyroid hormone-like peptide gene. Functional and evolutionary aspects. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7720–7725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]