Abstract
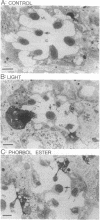
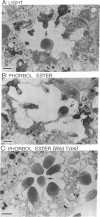
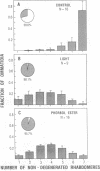
In the retinal degeneration B (rdgB) mutant of Drosophila, the major class of photoreceptors degenerate when the fly is raised in the light for several days; raising the fly in the dark largely prevents the degeneration. Thus, the rdgB is a conditional mutant that requires the operation of some stages of the phototransduction cascade to express its characteristic phenotype. We report here experiments that examine the ability of chemical agents to mimic light by causing photoreceptor-specific degeneration in the dark. Application of a specific activator of protein kinase C, phorbol ester, to eyes of rdgB flies led to a degeneration of the photoreceptors that was indistinguishable from that caused by light: both light and phorbol ester-induced degeneration were characterized by (i) selective degeneration of one class of photoreceptors; (ii) a unique pattern of degeneration; and (iii) the appearance of light-induced regenerative spikes at early stages of degeneration. Application of phorbol ester to the eyes of wild-type flies had no effect. We suggest that light or phorbol ester activates a protein kinase C and results in a sustained or excessive phosphorylation of proteins in the rdgB mutant, leading to photoreceptor degeneration. Furthermore, the results are consistent with identification of the rdgB gene product as a phosphoprotein phosphatase that is nonfunctional or absent in the mutant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer K. M., Saibil H. R. Light- and GTP-activated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in squid photoreceptor membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Rubin L. J., Ghalayini A. J., Tarver A. P., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Anderson R. E. myo-Inositol polyphosphate may be a messenger for visual excitation in Limulus photoreceptors. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):160–163. doi: 10.1038/311160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Watkins D. C., Malbon C. C. Light-induced changes in the content of inositol phosphates in squid (Loligo pealei) retina. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):293–297. doi: 10.1042/bj2470293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary O., Heichal O., Blumenfeld A., Cassel D., Suss E., Barash S., Rubinstein C. T., Minke B., Selinger Z. Coupling of photoexcited rhodopsin to inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in fly photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L. The role of calcium in cell death. Life Sci. 1981 Sep 28;29(13):1289–1295. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90670-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein A. Blockade of visual excitation and adaptation in Limulus photoreceptor by GDP-beta-S. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1543–1545. doi: 10.1126/science.3487116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein A., Payne R., Corson D. W., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Photoreceptor excitation and adaptation by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):157–160. doi: 10.1038/311157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. A., Stark W. S. Hereditary retinal degeneration in Drosophila melanogaster. A mutant defect associated with the phototransduction process. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Mar;69(3):261–291. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. A., Stark W. S., Walker J. A. Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):415–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Benzer S. Genetic dissection of the Drosophila nervous system by means of mosaics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Yoshioka T., Hotta Y. Membrane-associated phospholipase C of Drosophila retina. J Biochem. 1988 Jan;103(1):91–94. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto E., Hirosawa K., Takagawa K., Hotta Y. Structure of retinular cells in a Drosophila melanogaster visual mutant, rdgA, at early stages of degeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 May;252(2):293–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00214371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minke B. Light-induced reduction in excitation efficiency in the trp mutant of Drosophila. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Mar;79(3):361–385. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein C. T., Bar-Nachum S., Selinger Z., Minke B. Chemically induced retinal degeneration in the rdgB (retinal degeneration B) mutant of Drosophila. Vis Neurosci. 1989;2(6):541–551. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800003485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein C. T., Bar-Nachum S., Selinger Z., Minke B. Light-induced retinal degeneration in rdgB (retinal degeneration B) mutant of Drosophila: electrophysiological and morphological manifestations of degeneration. Vis Neurosci. 1989;2(6):529–539. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800003473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Smith D., Mardon G., Quinn W., Zuker C. Isolation and characterization of two new drosophila protein kinase C genes, including one specifically expressed in photoreceptor cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):403–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90915-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Minke B. Inositol lipid cascade of vision studied in mutant flies. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):333–341. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. S., Carlson S. D. Ultrastructural pathology of the compound eye and optic neuropiles of the retinal degeneration mutant (w rdg BKS222) Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;225(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00216214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. S., Sapp R. Ultrastructure of the retina of Drosophila melanogaster: the mutant ora (outer rhabdomeres absent) and its inhibition of degeneration in rdgB (retinal degeneration-B). J Neurogenet. 1987 Aug;4(5):227–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong J. A., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W., Kaczmarek L. K. Stimulation of protein kinase C recruits covert calcium channels in Aplysia bag cell neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):714–717. doi: 10.1038/325714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szuts E. Z., Wood S. F., Reid M. S., Fein A. Light stimulates the rapid formation of inositol trisphosphate in squid retinas. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bj2400929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowell S. C. Inositol trisphosphatase and bisphosphatase activities in the retina of crab. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80497-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Franceschini N. Illumination induces dye incorporation in photoreceptor cells. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):851–854. doi: 10.1126/science.6206565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. F., Szuts E. Z., Fein A. Inositol trisphosphate production in squid photoreceptors. Activation by light, aluminum fluoride, and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12970–12976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Inoue H., Hotta Y. Absence of phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase in the head of a Drosophila visual mutant, norpA (no receptor potential A). J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1251–1254. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]