Abstract
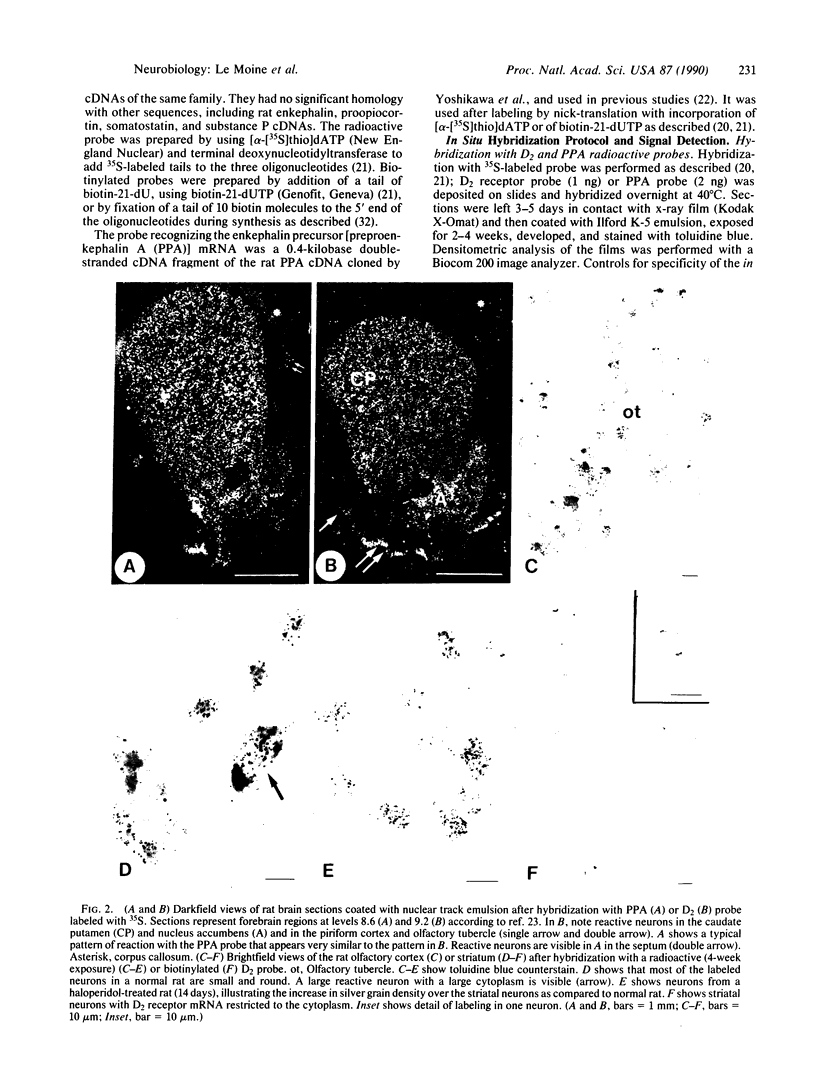
In situ hybridization experiments were performed with brain sections from normal, control and haloperidol-treated rats to identify and map the cells expressing the D2 dopamine receptor gene. D2 receptor mRNA was detected with radioactive or biotinylated oligonucleotide probes. D2 receptor mRNA was present in glandular cells of the pituitary intermediate lobe and in neurons of the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and forebrain, especially in caudate putamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle, and piriform cortex. Hybridization with D2 and preproenkephalin A probes in adjacent sections, as well as combined hybridization with the two probes in the same sections, demonstrated that all detectable enkephalin neurons in the striatum contained the D2 receptor mRNA. Large neurons in caudate putamen, which were unlabeled with the preproenkephalin A probe and which may have been cholinergic, also expressed the D2 receptor gene. Haloperidol treatment (14 or 21 days) provoked an increase in mRNA content for D2 receptor and preproenkephalin A in the striatum. This suggests that the increase in D2 receptor number observed after haloperidol treatment is due to increased activity of the D2 gene. These results indicate that in the striatum, the enkephalin neurons are direct targets for dopamine liberated from mesostriatal neurons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agid Y., Guyenet P., Glowinski J., Beaujouan J. C., Javoy F. Inhibitory influence of the nigrostriatal dopamine system on the striatal cholinergic neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 28;86(3):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90901-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon M. J., Elliott P. J., Bunney E. B. Striatal tachykinin biosynthesis: regulation of mRNA and peptide levels by dopamine agonists and antagonists. Brain Res. 1987 Dec;427(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch B., Popovici T., Le Guellec D., Normand E., Chouham S., Guitteny A. F., Bohlen P. In situ hybridization histochemistry for the analysis of gene expression in the endocrine and central nervous system tissues: a 3-year experience. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(1):183–200. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Premont J., Glowinski J., Thierry A. M., Tassin J. P. Topographical distribution of dopaminergic innervation and of dopaminergic receptors in the rat striatum. II. Distribution and characteristics of dopamine adenylate cyclase--interaction of d-LSD with dopaminergic receptors. Brain Res. 1976 May 7;107(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote T. E., Grewe C. W., Kebabian J. W. Stimulation of a D-2 dopamine receptor in the intermediate lobe of the rat pituitary gland decreases the responsiveness of the beta-adrenoceptor: biochemical mechanism. Endocrinology. 1981 Feb;108(2):420–426. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-2-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Sibley D. R., Hamblin M. W., Leff S. E. The classification of dopamine receptors: relationship to radioligand binding. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois A., Savasta M., Curet O., Scatton B. Autoradiographic distribution of the D1 agonist [3H]SKF 38393, in the rat brain and spinal cord. Comparison with the distribution of D2 dopamine receptors. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guitteny A. F., Fouque B., Mougin C., Teoule R., Bloch B. Histological detection of messenger RNAs with biotinylated synthetic oligonucleotide probes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Jun;36(6):563–571. doi: 10.1177/36.6.3259249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce J. N., Marshall J. F. Quantitative autoradiography of dopamine D2 sites in rat caudate-putamen: localization to intrinsic neurons and not to neocortical afferents. Neuroscience. 1987 Mar;20(3):773–795. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Inagaki S., Kito S., Takagi H., Smith A. D. Ultrastructural evidence of dopaminergic input to enkephalinergic neurons in rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 5;367(1-2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laduron P., Leysen J. Specific in vivo binding of neuroleptic drugs in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 May 15;26(10):1003–1007. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Langer S. Z. The striatal cholinergic interneuron: synaptic target of dopaminergic terminals? Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1105–1120. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri N., Bernardi G., Calabresi P., Cotugno A., Levi G., Stanzione P. Dopamine decreases cell excitability in rat striatal neurons by pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 9;358(1-2):110–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90954-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Naranjo J. R., Costa E. Regulation of striatal enkephalin turnover in rats receiving antagonists of specific dopamine receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):1120–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the dopamine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:129–169. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Höllt V., Herz A. Dopaminergic regulation of striatal proenkephalin mRNA and prodynorphin mRNA: contrasting effects of D1 and D2 antagonists. Neuroscience. 1988 May;25(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand E., Popovici T., Fellmann D., Bloch B. Anatomical study of enkephalin gene expression in the rat forebrain following haloperidol treatment. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 29;83(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand E., Popovici T., Onteniente B., Fellmann D., Piatier-Tonneau D., Auffray C., Bloch B. Dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra modulate preproenkephalin A gene expression in rat striatal neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 26;439(1-2):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91459-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J. [3H]Spiperone binding sites in brain: autoradiographic localization of multiple receptors. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 1;213(2):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roget A., Bazin H., Teoule R. Synthesis and use of labelled nucleoside phosphoramidite building blocks bearing a reporter group: biotinyl, dinitrophenyl, pyrenyl and dansyl. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7643–7651. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trugman J. M., Geary W. A., 2nd, Wooten G. F. Localization of D-2 dopamine receptors to intrinsic striatal neurones by quantitative autoradiography. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):267–269. doi: 10.1038/323267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kooy D., Weinreich P., Nagy J. I. Dopamine and opiate receptors: localization in the striatum and evidence for their axoplasmic transport in the nigrostriatal and striatonigral pathways. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. J., Wang R. Y. Pharmacological characterization of dopamine autoreceptors in the rat ventral tegmental area: microiontophoretic studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Nov;231(2):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Williams C., Sabol S. L. Rat brain preproenkephalin mRNA. cDNA cloning, primary structure, and distribution in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14301–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]