Abstract
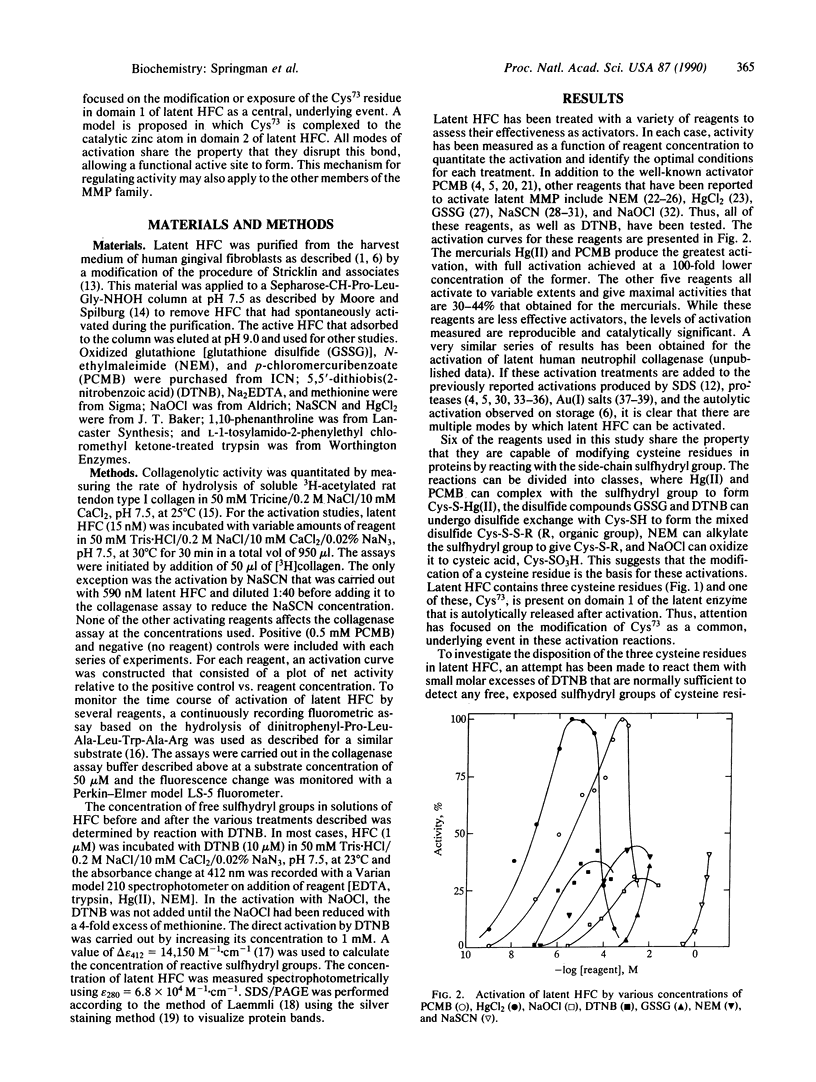
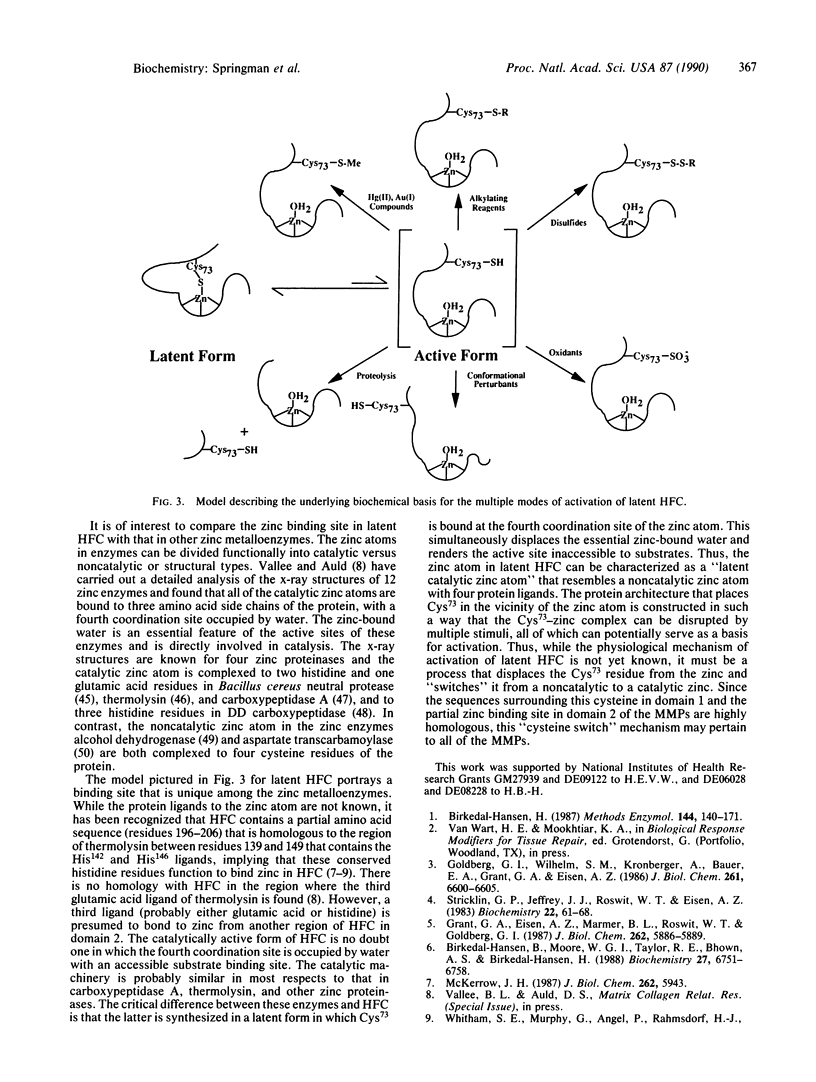
Latent human fibroblast collagenase (HFC) can be activated by a variety of seemingly disparate means. In addition to the well-characterized activation by trypsin and organomercurial compounds, the enzyme can be activated to various extents by surfactants such as sodium dodecyl sulfate, by chaotropic ions such as SCN-, by disulfide compounds such as oxidized glutathione, by sulfhydryl alkylating agents such as N-ethylmaleimide, and by oxidants such as NaOCl. The underlying basis for these activations is the modification, exposure, or proteolytic release of the Cys73 residue from its habitat in the latent enzyme where it is thought to be complexed to the active-site zinc atom. This residue is not accessible for reaction with small molar excesses of dithionitrobenzoate in native, latent HFC. However, on addition of EDTA, this residue becomes fully exposed and is quantitatively labeled. All modes of activation of latent HFC are believed to involve the dissociation of Cys73 from the active-site zinc atom and its replacement by water, with the concomitant exposure of the active site. This is thought to be the primary event that precedes the well-known autolytic cleavages that are observed following the appearance of collagenase activity. The dissociation of Cys73 from the zinc atom in the latent enzyme "switches" the role of the zinc from a noncatalytic to a catalytic one. This "cysteine switch" mechanism of regulation may be applicable to the entire collagenase gene family.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Nagai Y. Evidence for the presence of a latent form of collagenase in human rheumatoid synovial fluid. J Biochem. 1972 May;71(5):919–922. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe S., Shinmei M., Nagai Y. Synovial collagenase and joint diseases: the significancy of latent collagenase with special reference to rheumatoid arthritis. J Biochem. 1973 May;73(5):1007–1011. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Collagenase production by human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):232–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen B., Moore W. G., Taylor R. E., Bhown A. S., Birkedal-Hansen H. Monoclonal antibodies to human fibroblast procollagenase. Inhibition of enzymatic activity, affinity purification of the enzyme, and evidence for clustering of epitopes in the NH2-terminal end of the activated enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6751–6758. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H. Catabolism and turnover of collagens: collagenases. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:140–171. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Cobb C. M., Taylor R. E., Fullmer H. M. Synthesis and release of procollagenase by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3162–3168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Taylor R. E. Detergent-activation of latent collagenase and resolution of its component molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaway J. E., Garcia J. A., Jr, Hersh C. L., Yeh R. K., Gilmore-Hebert M. Use of lectin affinity chromatography for the purification of collagenase from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4757–4762. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dideberg O., Charlier P., Dive G., Joris B., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M. Structure of a Zn2+-containing D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving carboxypeptidase at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):469–470. doi: 10.1038/299469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eeckhout Y., Vaes G. Further studies on the activation of procollagenase, the latent precursor of bone collagenase. Effects of lysosomal cathepsin B, plasmin and kallikrein, and spontaneous activation. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 15;166(1):21–31. doi: 10.1042/bj1660021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Wilhelm S. M., Kronberger A., Bauer E. A., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z. Human fibroblast collagenase. Complete primary structure and homology to an oncogene transformation-induced rat protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Roswit W. T., Goldberg G. I. The activation of human skin fibroblast procollagenase. Sequence identification of the major conversion products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5886–5889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A., Thomas M. L., Tack B. F. Sequence determination of the thiolester site of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7388–7392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty K. A., Hibbs M. S., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Secreted forms of human neutrophil collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5645–5650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honzatko R. B., Crawford J. L., Monaco H. L., Ladner J. E., Ewards B. F., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., Wiley D. C., Ladner R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):219–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindy S., Sorsa T., Suomalainen K., Turto H. Gold sodium thiomalate activates latent human leukocyte collagenase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):23–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macartney H. W., Tschesche H. Latent and active human polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenases. Isolation, purification and characterisation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya S. K., Mookhtiar K. A., Van Wart H. E. Accurate, quantitative assays for the hydrolysis of soluble type I, II, and III 3H-acetylated collagens by bacterial and tissue collagenases. Anal Biochem. 1986 Nov 1;158(2):334–345. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90558-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya S. K., Van Wart H. E. Mechanism of inhibition of human neutrophil collagenase by Gold(I) chrysotherapeutic compounds. Interaction at a heavy metal binding site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1594–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKerrow J. H. Human fibroblast collagenase contains an amino acid sequence homologous to the zinc-binding site of Serratia protease. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5943–5943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. M., Spilburg C. A. Purification of human collagenases with a hydroxamic acid affinity column. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5189–5195. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Quantin B., Gesnel M. C., Millon-Collard R., Abecassis J., Breathnach R. The collagenase gene family in humans consists of at least four members. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2530187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Bretz U., Baggiolini M., Reynolds J. J. The latent collagenase and gelatinase of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil leucocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):517–525. doi: 10.1042/bj1920517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauptit R. A., Karlsson R., Picot D., Jenkins J. A., Niklaus-Reimer A. S., Jansonius J. N. Crystal structure of neutral protease from Bacillus cereus refined at 3.0 A resolution and comparison with the homologous but more thermostable enzyme thermolysin. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 5;199(3):525–537. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90623-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C., Lewis M., Lipscomb W. N. Refined crystal structure of carboxypeptidase A at 1.54 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):367–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Ellman's reagent: 5,5'-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)--a reexamination. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90792-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lopez R., Nicholson R., Gesnel M. C., Matrisian L. M., Breathnach R. Structure-function relationships in the collagenase family member transin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11892–11899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa T. A. Activation of latent collagenase purified from human leukocytes. Scand J Rheumatol. 1987;16(3):167–175. doi: 10.3109/03009748709165270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa T., Suomalainen K., Turto H., Lindy S. Latent human leukocyte collagenase can be activated by gold thioglucose and gold sodium thiomalate, but not by auranofin. Biosci Rep. 1987 Dec;7(12):965–968. doi: 10.1007/BF01122130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa T., Suomalainen K., Turto H., Lindy S. Partial purification and characterization of latent human leukocyte collagenase. Med Biol. 1985;63(2):66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Stepanik T. M., Kristensen T., Wierzbicki D. M., Jones C. M., Lønblad P. B., Magnusson S., Petersen T. E. Primary structure of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. V. The complete structure. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8318–8327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack M. S., Gray R. D. Comparison of vertebrate collagenase and gelatinase using a new fluorogenic substrate peptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4277–4281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Bauer E. A., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Human skin collagenase: isolation of precursor and active forms from both fibroblast and organ cultures. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1607–1615. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Roswit W. T., Eisen A. Z. Human skin fibroblast procollagenase: mechanisms of activation by organomercurials and trypsin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):61–68. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L., Janatova J., Gray W. R., Tack B. F. Third component of human complement: localization of the internal thiolester bond. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto V. J., Turto H., Huttunen A., Lindy S., Uitto J. Activation of human leukocyte collagenase by compounds reacting with sulfhydryl groups. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;613(1):168–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto V. J., Turto H., Huttunen A., Lindy S., Uitto J. Activation of human leukocyte collagenase by compounds reacting with sulfhydryl groups. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;613(1):168–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. The release of collagenase as an inactive proenzyme by bone explants in culture. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(2):275–289. doi: 10.1042/bj1260275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Peppin G., Ortiz X., Ragsdale C., Test S. T. Oxidative autoactivation of latent collagenase by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):747–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2982211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Burleigh M. C. A specific collagenase from rabbit fibroblasts in monolayer culture. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):373–385. doi: 10.1042/bj1370373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Mainardi C. L., Vater C. A., Harris E. D., Jr Endogenous activiation of latent collagenase by rheumatoid synovial cells. Evidence for a role of plasminogen activator. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 5;296(18):1017–1023. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705052961801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Reynolds J. J. Stimulation by endocytosis of the secretion of collagenase and neutral proteinase from rabbit synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1482–1497. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitham S. E., Murphy G., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Smith B. J., Lyons A., Harris T. J., Reynolds J. J., Herrlich P., Docherty A. J. Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2400913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



