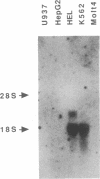
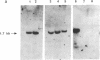
Abstract
Genes expressed in erythroid cells contain binding sites for a cell-specific nuclear factor, GF-1 (NF-E1, Eryf 1), believed to be an important transcriptional regulator. Previously we characterized murine GF-1 as a 413-amino acid polypeptide containing two cysteine-cysteine regions reminiscent of zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. By cross-hybridization to the finger domain of murine GF-1 we have isolated cDNA encoding the human homolog. Peptide sequencing of purified human GF-1 confirmed the authenticity of the human cDNA. The predicted primary sequence of human GF-1 is highly similar to that of murine GF-1, particularly in the DNA-binding region. Although the DNA-binding domains of human, murine, and chicken proteins are remarkably conserved, the mammalian polypeptides are strikingly divergent from the avian counterpart in other regions, most likely those responsible for transcriptional activation. By hybridization to panels of human-rodent DNAs we have assigned the human GF-1 locus to Xp21-11. The localization of the gene to the X chromosome has important implications for hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin syndromes unlinked to the beta-globin cluster and for genetic experiments designed to test the role of the factor in erythroid cell gene expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G., Stroh H., Veldman G. M., Latt S. A., Floros J. The 35 kd pulmonary surfactant-associated protein is encoded on chromosome 10. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):58–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00283051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman D. M., Zon L. I., Orkin S. H. Rapid amplification of lambda gt11 bacteriophage library inserts from plaques using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Biotechniques. 1989 Jun;7(6):568–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Novak U., Gelinas R., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the human beta-globin locus activation region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianni A. M., Bregni M., Cappellini M. D., Fiorelli G., Taramelli R., Giglioni B., Comi P., Ottolenghi S. A gene controlling fetal hemoglobin expression in adults is not linked to the non-alpha globin cluster. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):921–925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Lieber M. R., Felsenfeld G. Regulated gene expression in transfected primary chicken erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Hurst J., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene contains a downstream developmental specific enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5739–5747. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H. Increased gamma-globin expression in a nondeletion HPFH mediated by an erythroid-specific DNA-binding factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):435–438. doi: 10.1038/338435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Kaneto Y., Kawai H., Ohchi H., Niki S., Hasegawa K., Shirakami A., Yamano T. X-linked dominant control of F-cells in normal adult life: characterization of the Swiss type as hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin regulated dominantly by gene(s) on X chromosome. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1854–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C. Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus: implications for a noninactivated region on the short arm of human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Kim K. S., Kogan S., Guarente L. Functional dissection and sequence of yeast HAP1 activator. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. High-level erythroid expression of human alpha-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):37–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]