Full text
PDF

























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayne-Jones S. BACTERIAL CALORIMETRY I. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS. DESCRIPTION OF DIFFERENTIAL MICROCALORIMETER. J Bacteriol. 1929 Feb;17(2):105–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.17.2.105-122.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne-Jones S., Rhees H. S. BACTERIAL CALORIMETRY II. RELATIONSHIP OF HEAT PRODUCTION TO PHASES OF GROWTH OF BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1929 Feb;17(2):123–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.17.2.123-140.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk D., Lineweaver H. THE INFLUENCE OF FIXED NITROGEN ON AZOTOBACTER. J Bacteriol. 1930 Jun;19(6):389–414. doi: 10.1128/jb.19.6.389-414.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D. A Quantitative Study of the Respiration of Staphylococcus Cultures Lysed by Bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1931 Mar;21(3):143–156. doi: 10.1128/jb.21.3.143-156.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett E. H., Acree S. F. THE PROBLEM OF DILUTION IN COLORIMETRIC H-ION MEASUREMENTS I. ISOHYDRIC INDICATOR METHODS FOR ACCURATE DETERMINATION OF pH IN VERY DILUTE SOLUTIONS. J Bacteriol. 1929 Mar;17(3):163–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.17.3.163-204.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee M. C., Smith H. G. A Study of Methods for the Estimation of Reducing Sugar in Bacteriological Media. J Bacteriol. 1930 Feb;19(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.19.2.125-132.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magoon C. A., Brunstetter B. C. A NEW VESSEL FOR THE EFFICIENT AERATION OF BACTERIAL CULTURES IN LIQUID MEDIA. J Bacteriol. 1930 Jun;19(6):415–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.19.6.415-422.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
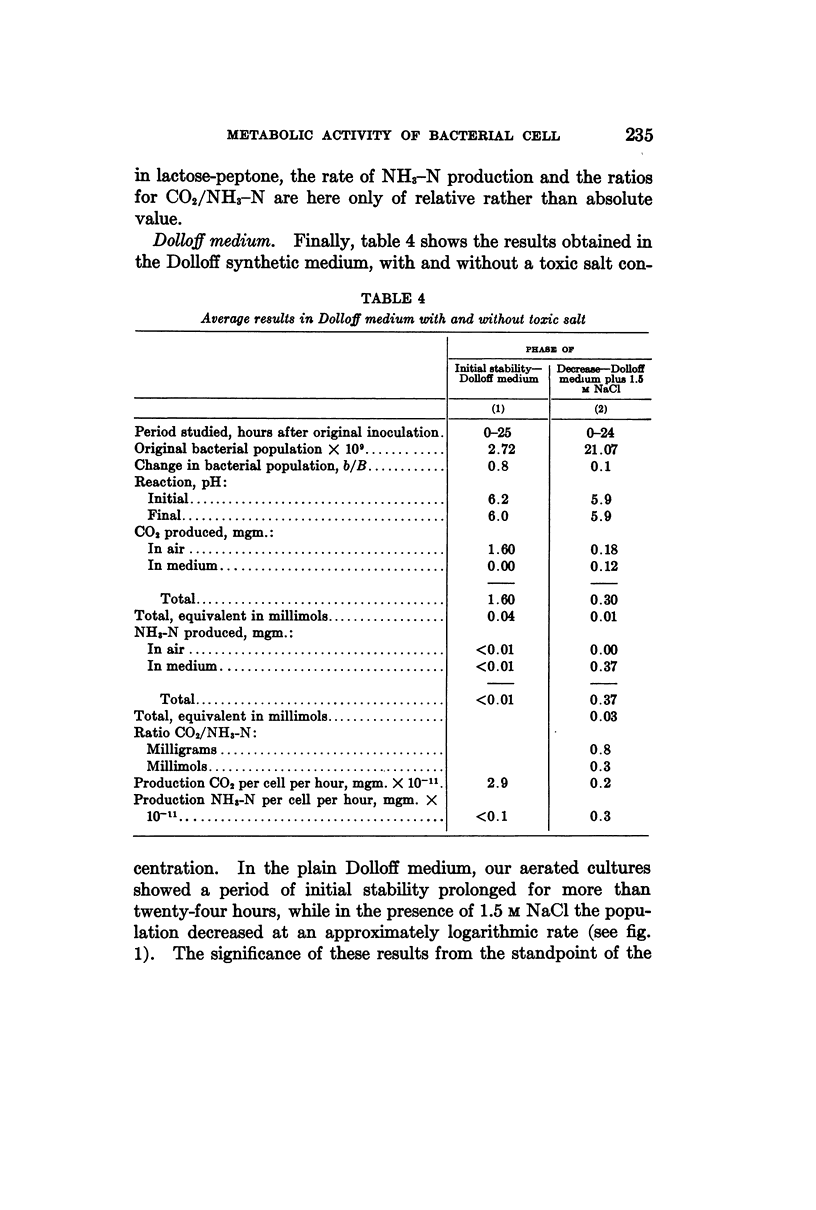
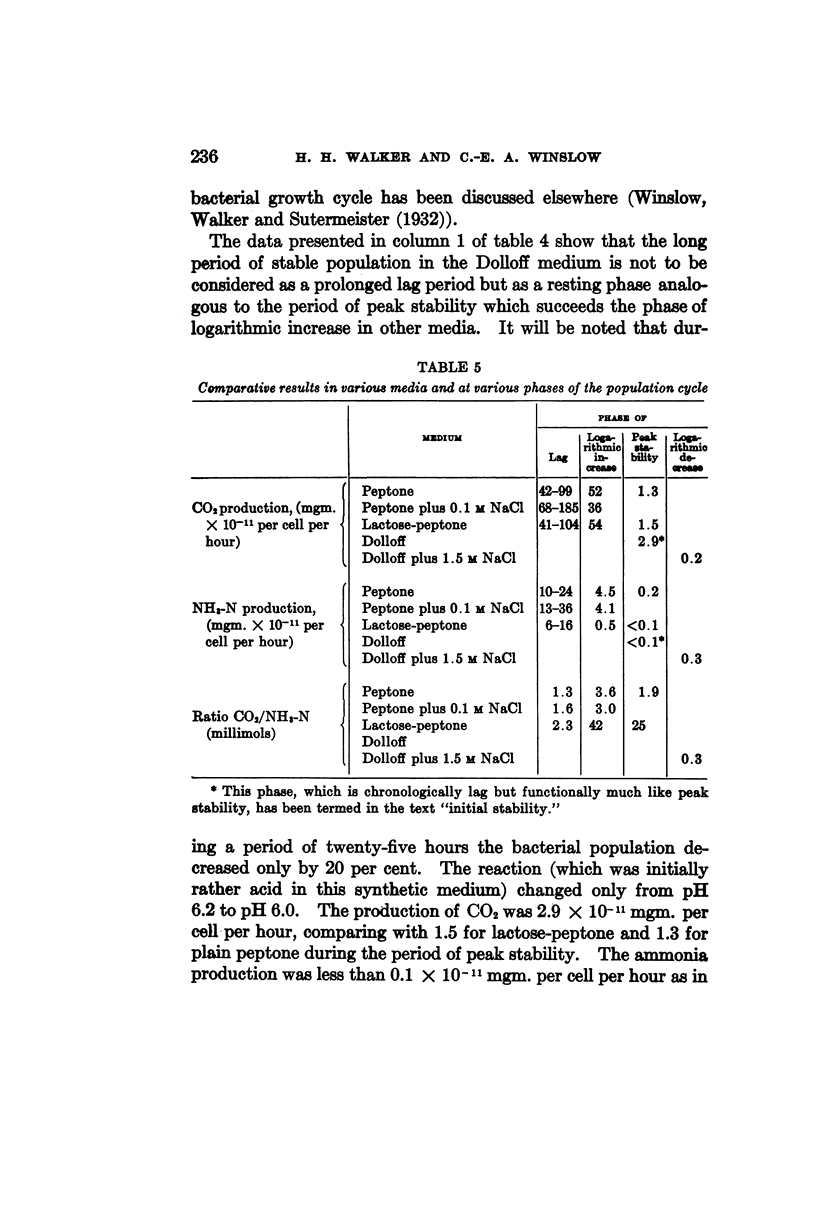
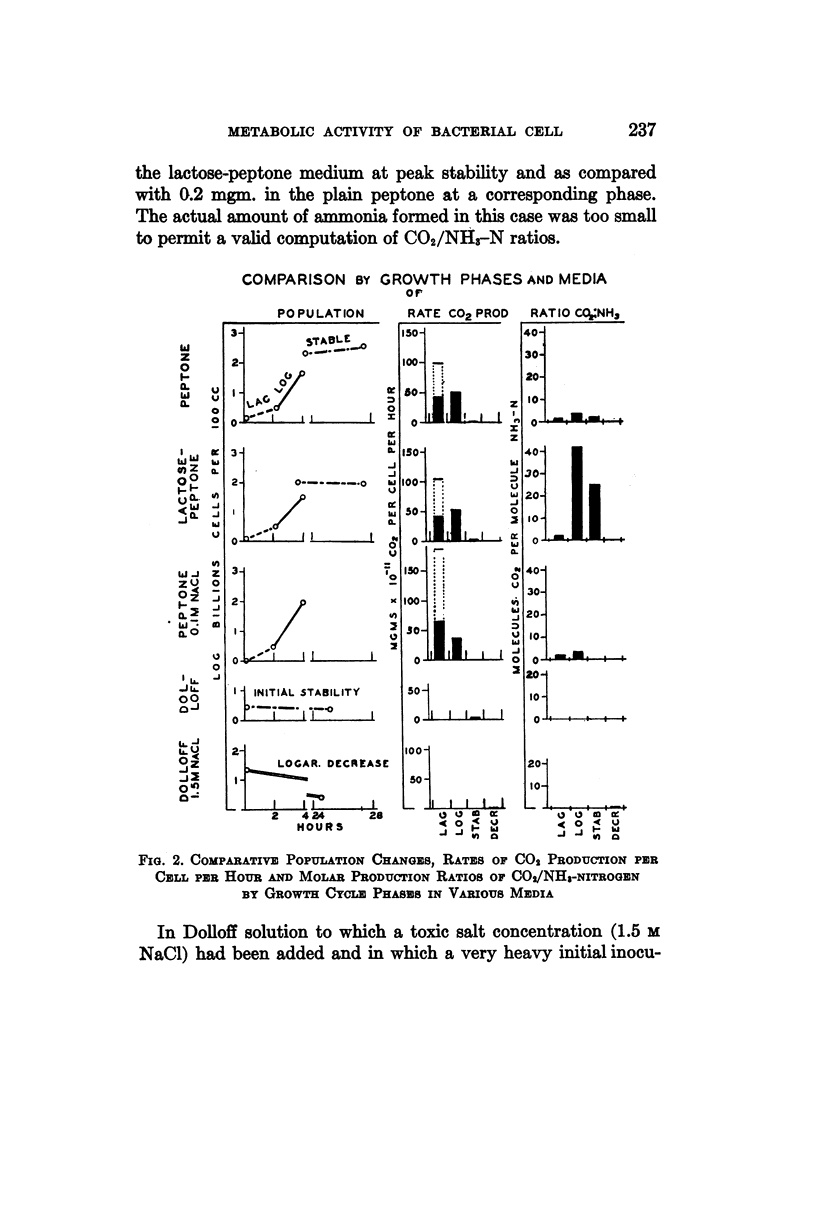
- Merrill M. H. CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM OF ORGANISMS OF THE GENUS MYCOBACTERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1930 Oct;20(4):235–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.20.4.235-286.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn O. THE DECREASING RATE OF FERMENTATION. J Bacteriol. 1929 Sep;18(3):207–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.18.3.207-226.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn O. THE FERMENTOMETER. J Bacteriol. 1929 Sep;18(3):199–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.18.3.199-205.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn O. THE FORMULA FOR THE FERMENTING CAPACITY OF A SINGLE CELL. J Bacteriol. 1930 Jun;19(6):383–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.19.6.383-387.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M., Albus W. R. Physiological Youth in Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1923 Mar;8(2):127–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.8.2.127-139.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles H. R., Peterson W. H., Fred E. B. A RAPID METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF SUGAR IN BACTERIAL CULTURES. J Bacteriol. 1926 Dec;12(6):427–439. doi: 10.1128/jb.12.6.427-439.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker H. H. An Aeration Train for the Study of Products of Bacterial Metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1932 Sep;24(3):169–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.24.3.169-184.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel N. C. A NOTE ON THE APPLICATION OF BUCHANAN'S FORMULA TO HEAT PRODUCTION IN BACTERIAL CULTURES. J Bacteriol. 1929 Aug;18(2):117–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.18.2.117-132.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow C. E., Walker H. H., Sutermeister M. The Influence of Aeration and of Sodium Chloride upon the Growth Curve of Bacteria in Various Media. J Bacteriol. 1932 Sep;24(3):185–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.24.3.185-208.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


