Abstract
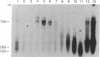
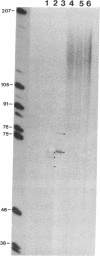
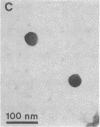
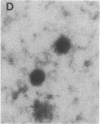
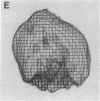
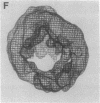
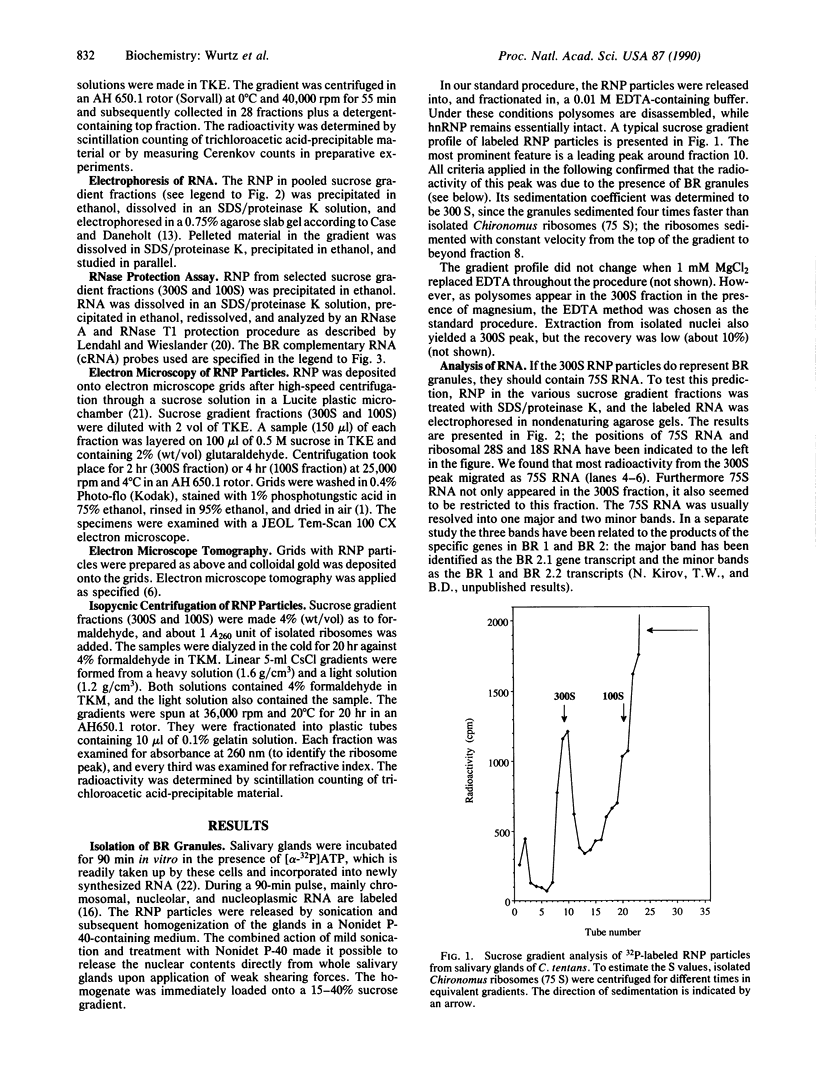
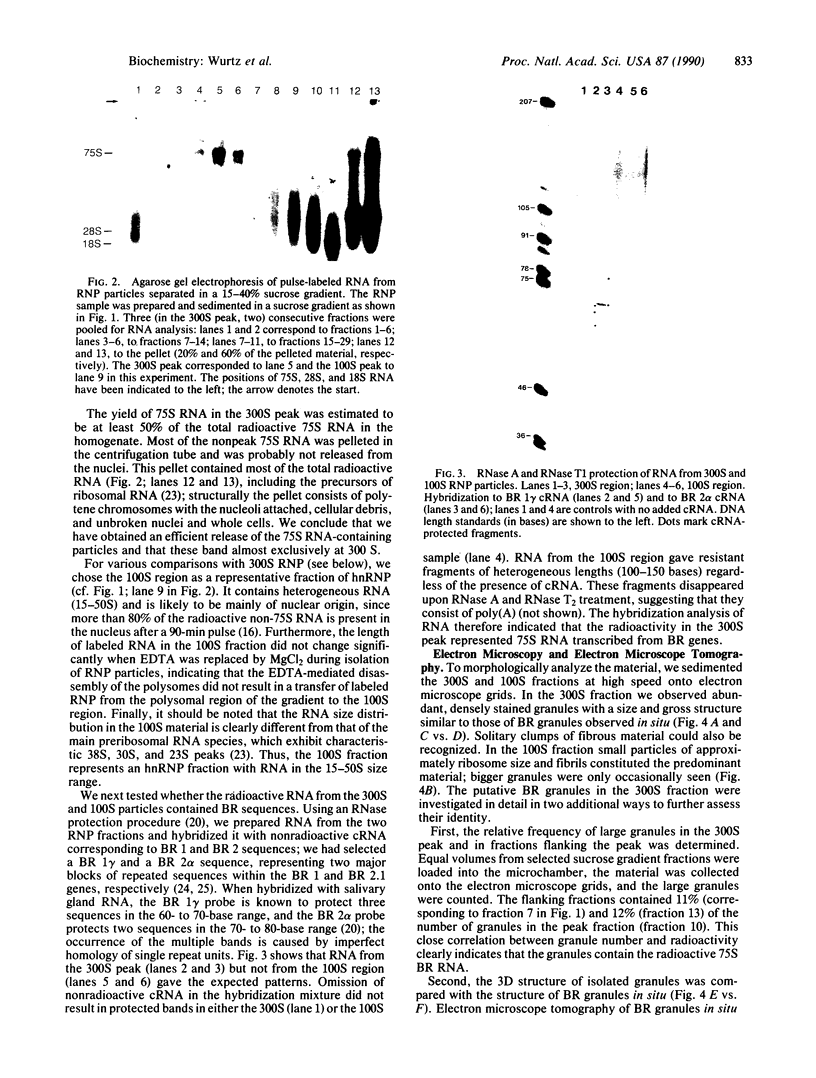
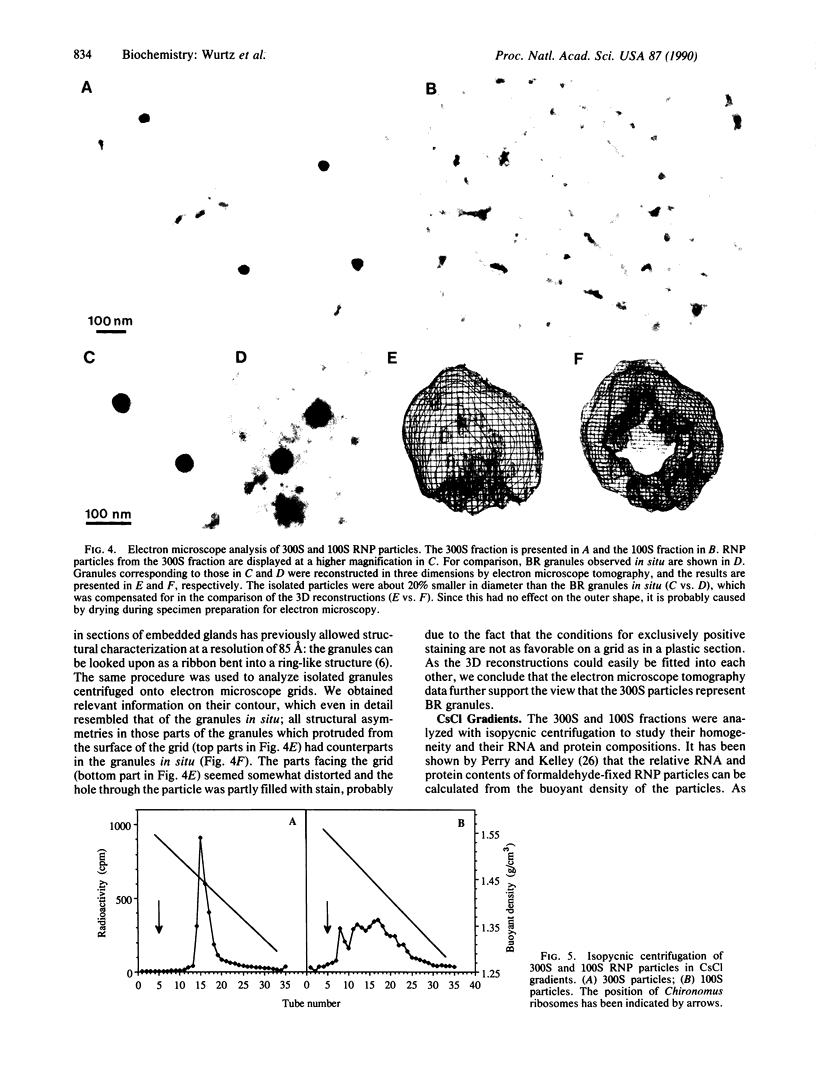
A specific type of premessenger ribonucleoprotein (RNP) particle, Balbiani ring (BR) granules, has been isolated from heterogeneous nuclear RNP (hnRNP) in the salivary glands of the dipteran Chironomus tentans. A BR granule contains a single 75S RNA molecule coding for a large secretory protein (Sp1). The isolation procedure is based on the abundance and exceptional size of the BR granules: in EDTA-containing sucrose gradients they sediment as a sharp 300S peak ahead of the remainder of the hnRNP population. The isolated BR granules were identified on the basis of both ultrastructural and biochemical criteria: large spherical particles that contain 75S RNA and BR sequences. A three-dimensional reconstruction of isolated particles by electron microscope tomography further supported the identification of the isolated particles as BR granules. In contrast to the entire hnRNP population, the BR granules exhibited a sharp peak in CsCl gradients with a buoyant density of 1.45 g/cm3. This result indicates that a BR granule consists of 40% RNA and 60% protein by weight, corresponding to a 75S RNA molecule of 12 megadaltons and a total protein content of 18 megadaltons, or about 500 average-sized protein molecules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERMANN W., BAHR G. F. The submicroscopic structure of Balbiani-ring. Exp Cell Res. 1954 Feb;6(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(54)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T., Daneholt B. The size of the transcription unit in Balbiani ring 2 of Chironomus tentans as derived from analysis of the primary transcript and 75 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Wooley J. Set of novel, conserved proteins fold pre-messenger RNA into ribonucleosomes. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):195–210. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B., Hosick H. Evidence for transport of 75S RNA from a discrete chromosome region via nuclear sap to cytoplasm in Chironomus tentans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidis I. V., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: heterogeneous nuclear RNA is complexed with a major sextet of proteins in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1599–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egyházi E., Pigon A., Rydlander L. 5,6-Dichlororibofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits the rate of transcription initiation in intact Chironomus cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):445–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galler R., Saiga H., Widmer R. M., Lezzi M., Edström J. E. Two genes in Balbiani ring 2 with metabolically different 75S transcripts. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2977–2982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosick H., Daneholt B. Isolation and characterization of polysomes from Chironomus salivary glands. Cell Differ. 1974 Dec;3(5):273–286. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(74)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C., Engberg C., Wieslander L. A BR 1 gene in Chironomus tentans has a composite structure: a large repetitive core block is separated from a short unrelated 3'-terminal domain by a small intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):703–719. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Characterization of active transcription units in Balbiani rings of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):835–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: sequence components of heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):77–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Bakken A. H. Morphological studies of transcription. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1972;168:155–177. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.071s155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Buoyant densities of cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles of mammalian cells: distinctive character of ribosome subunits and the rapidly labeled components. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):255–268. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringborg U., Daneholt B., Edström J. E., Egyházi E., Lambert B. Electrophoretic characterization of nucleolar RNA from Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):327–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Edström J. E. Large sized nascent protein as dominating component during protein synthesis in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):85–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00292424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarina O. P., Lukanidin E. M., Molnar J., Georgiev G. P. Structural organization of nuclear complexes containing DNA-like RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund U., Andersson K., Björkroth B., Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Visualization of the formation and transport of a specific hnRNP particle. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund U., Andersson K., Strandberg B., Daneholt B. Three-dimensional structure of a specific pre-messenger RNP particle established by electron microscope tomography. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):560–564. doi: 10.1038/319560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. J., Swift H. RNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm in Chironomus salivary glands. J Cell Biol. 1966 Oct;31(1):55–77. doi: 10.1083/jcb.31.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtz T., Fakan S. Isolation and characterisation of a transcribing polynucleosomal chromatin fraction. Biol Cell. 1983;48(2-3):109–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]