Abstract
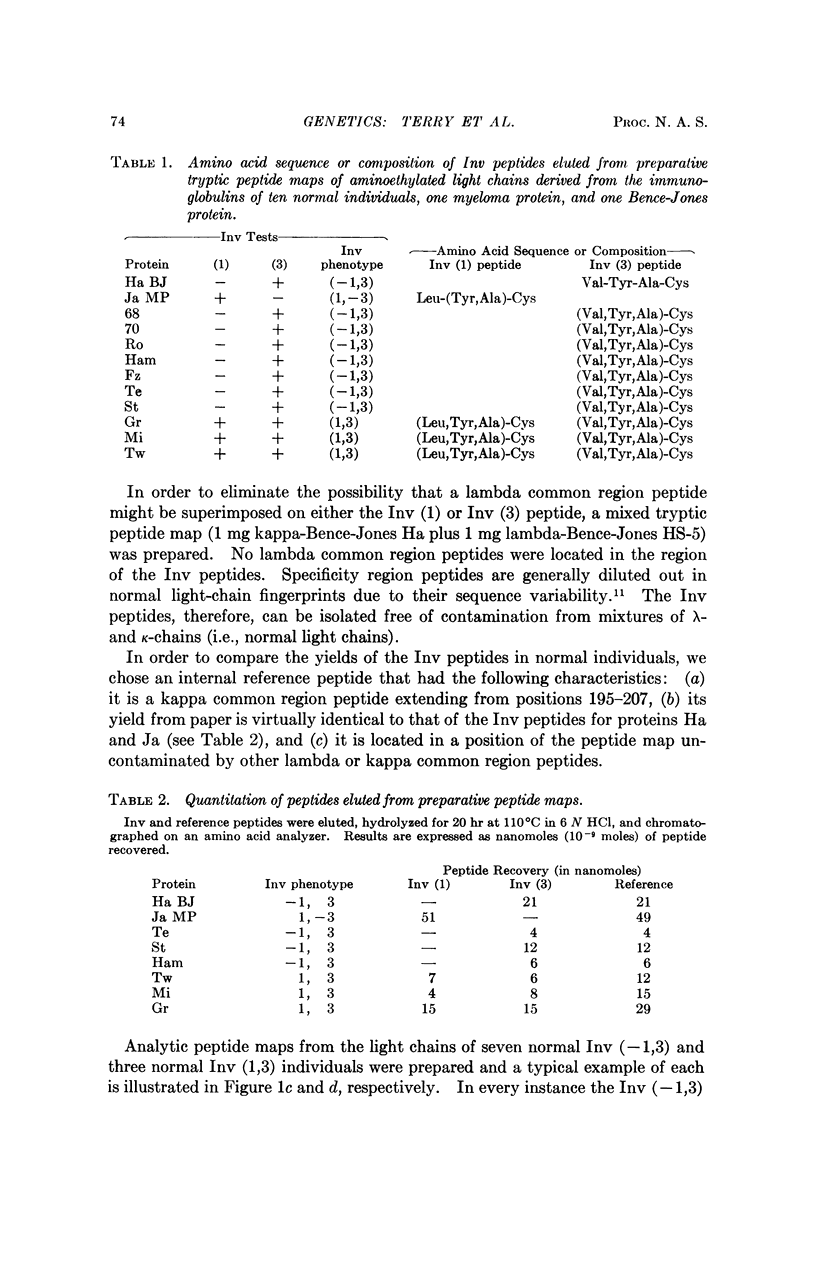
The relationship between Inv phenotype and the amino acid residue at position 191 in κ-type light polypeptide chains derived from the immunoglobulins of ten normal human sera was investigated. In each case, the amino acid present at position 191 correlated with the Inv phenotype of the individual. Kappa chains of seven Inv (—1,3) homozygotes had valine, while those of three Inv (1,3) heterozygotes had some chains with leucine and some with valine at this position. Genes encoding the Inv (1) and Inv (3) variants appear to be expressed equally in the heterozygous state, since approximately equal amounts of each gene product was recovered from heterozygotes.
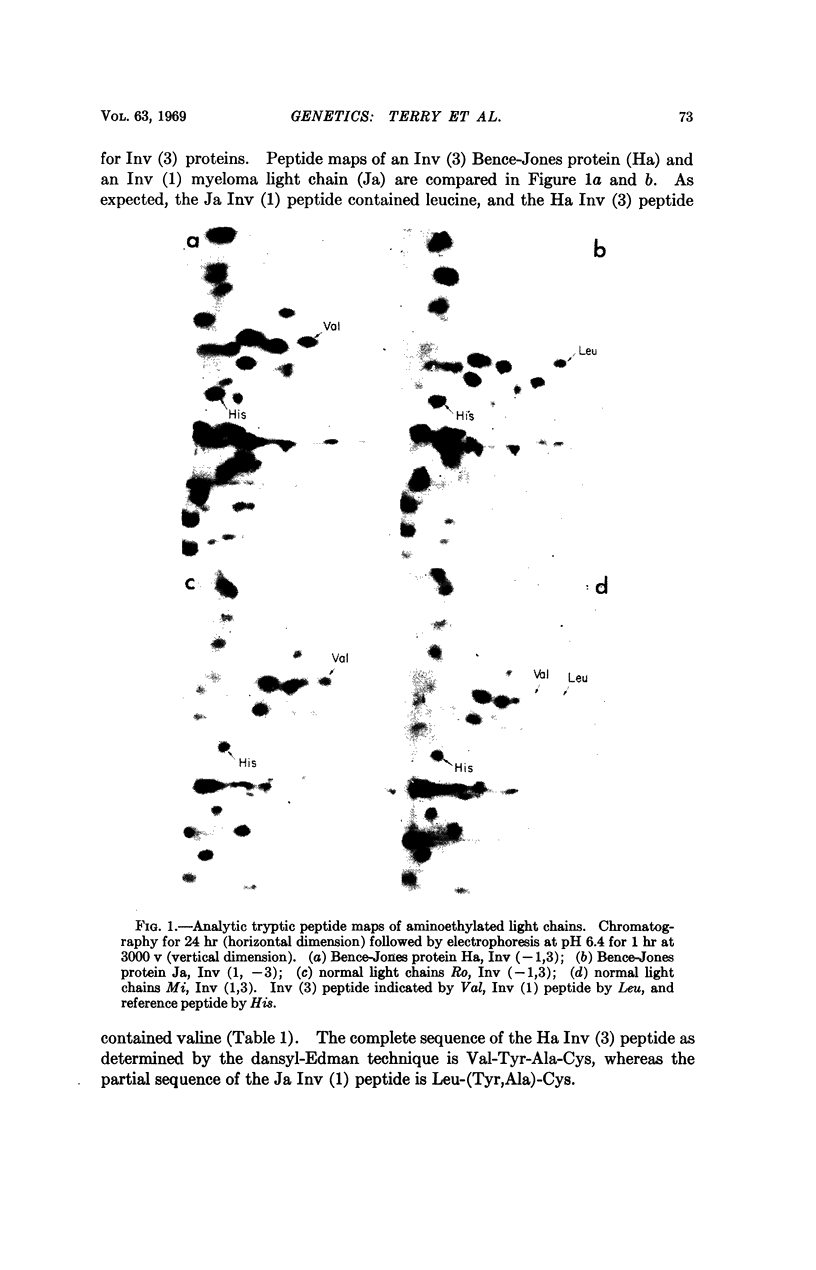
The correlation between Inv phenotype and the amino acid residue present at position 191 is identical to that previously established for κ-type Bence-Jones proteins and myeloma protein light chains. These observations support the hypothesis that the valine-leucine interchange is encoded by two allelic forms of a single κ-chain common region gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Ein D. Two types of lambda polypeptide chains in human immunoglobulins based on an amino acid substitution at position 190. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1449–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT J. C., HOOD L. E., DREYER W. J., POTTER M. EVIDENCE FOR AMINO ACID SEQUENCE DIFFERENCES AMONG PROTEINS RESEMBLING THE L-CHAIN SUBUNITS OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:81–87. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Alescio Zonta L., Cioli D., Carbonara A. Allelic antigenic factor Inv(a) of the light chains of human immunoglobulins: chemical basis. Science. 1966 Jun 10;152(3728):1517–1519. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3728.1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Milstein C. Structure of antibody molecules. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):449–passim. doi: 10.1038/214449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer W. J., Bennett J. C. The molecular basis of antibody formation: a paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):864–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D., Fahey J. L. 2 types of lambda polypeptide chains in human immunoglobulins. Science. 1967 May 19;156(3777):947–948. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3777.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D. Nonallelic behavior of the Oz groups in human lambda immunoglobulin chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):982–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilschmann N., Craig L. C. Amino acid sequence studies with Bence-Jones proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1403–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilschmann N. Die chemische Struktur von zwei Bence-Jones-Proteinen (roy und Cum.) vom kappa-Typ. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Aug;348(8):1077–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Kunkel H. G. The relationship between the Inv (1) and (2) genetic antigens of kappa human light chains. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):603–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Immunoglobulin kappa-chains. Comparative sequences in selected stretches of Bence-Jones proteins. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):352–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1010352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Linked groups of residues in immunoglobulin k chains. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):330–332. doi: 10.1038/216330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. The disulphide bridges of immunoglobulin kappa-chains. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):338–351. doi: 10.1042/bj1010338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPARTZ C., LENOIR J., RIVAT L. A new inheritable property of human sera: the InV factor. Nature. 1961 Feb 18;189:586–586. doi: 10.1038/189586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPARTZ C., RIVAT L., ROUSSEAU P. Y. DEUX NOUVEAUX FACTEURS DANS LES SYST'EMES H'ER'EDITAIRES DE GAMMA-GLOBULINE: LE GM(E) ET L'INV(I) Bibl Haematol. 1964;19:455–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Cole R. D. On the aminoethylation of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3457–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG A. G., WILSON J. A., LANSET S. A new human gamma globulin factor determined by an allele at the Inv locus. Vox Sang. 1962;7:151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb03239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]