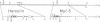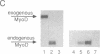Abstract
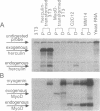
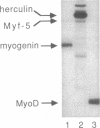
We have identified and cloned herculin, a fourth mouse muscle regulatory gene. Comparison of its DNA and deduced amino acid sequences with those of the three known myogenic genes (MyoD, myogenin, and Myf-5) reveals scattered short spans with similarity to one or more of these genes and a long span with strong similarity to all three. This long span includes a sequence motif that is also present in proteins of the myc, achaete-scute, and immunoglobulin enhancer-binding families. The herculin gene is physically linked to the Myf-5 gene on the chromosome; only 8.5 kilobases separate their translational start sites. A putative 27-kDa protein is encoded by three exons contained within a 1.7-kilobase fragment of the herculin gene. When expressed under the control of the simian virus 40 early promoter, transfected herculin renders murine NIH 3T3 and C3H/10T1/2 fibroblasts myogenic. In doing so, it also activates expression of myogenin, MyoD, and endogenous herculin in NIH 3T3 recipients. In adult mice, herculin is expressed in skeletal muscle but is absent from smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and all nonmuscle tissues assayed. Direct comparison of the four known myogenic regulators in adult muscle showed that herculin is expressed at a significantly higher level than is any of the others. This quantitative dominance suggests an important role in the establishment or maintenance of adult skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blau H. M., Pavlath G. K., Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Miller S. C., Webster C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):758–766. doi: 10.1126/science.2414846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Diggelmann H. Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929–2931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Kohtz S., Grzeschik K. H., Arnold H. H., Kotz S. Differential expression of myogenic determination genes in muscle cells: possible autoactivation by the Myf gene products. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3617–3625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmenares C., Stavnezer E. The ski oncogene induces muscle differentiation in quail embryo cells. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkhart T. A., Clegg C. H., Hauschika S. D. Myogenic differentiation in permanent clonal mouse myoblast cell lines: regulation by macromolecular growth factors in the culture medium. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90311-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Stockdale F. E. Developmental origins of skeletal muscle fibers: clonal analysis of myogenic cell lineages based on expression of fast and slow myosin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Pearson-White S. H., Konieczny S. F., Latham K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Myogenic lineage determination and differentiation: evidence for a regulatory gene pathway. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Adam M. A., Lassar A. B., Miller A. D. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]