Abstract
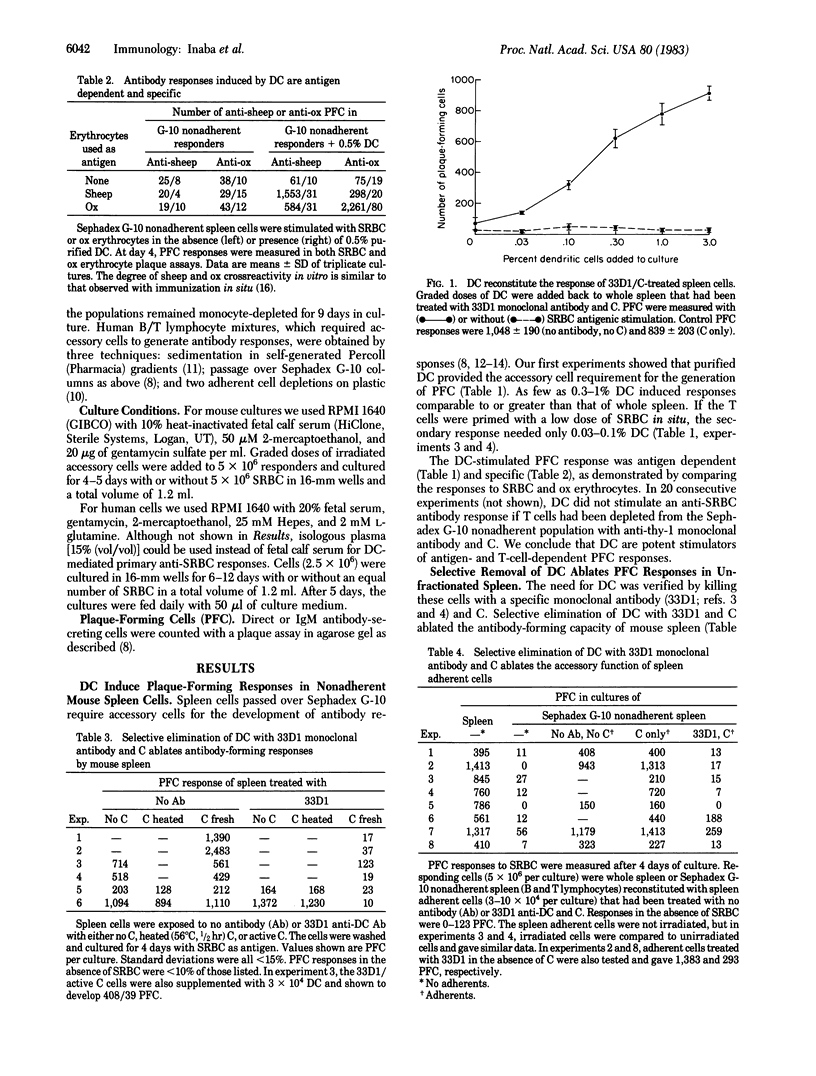
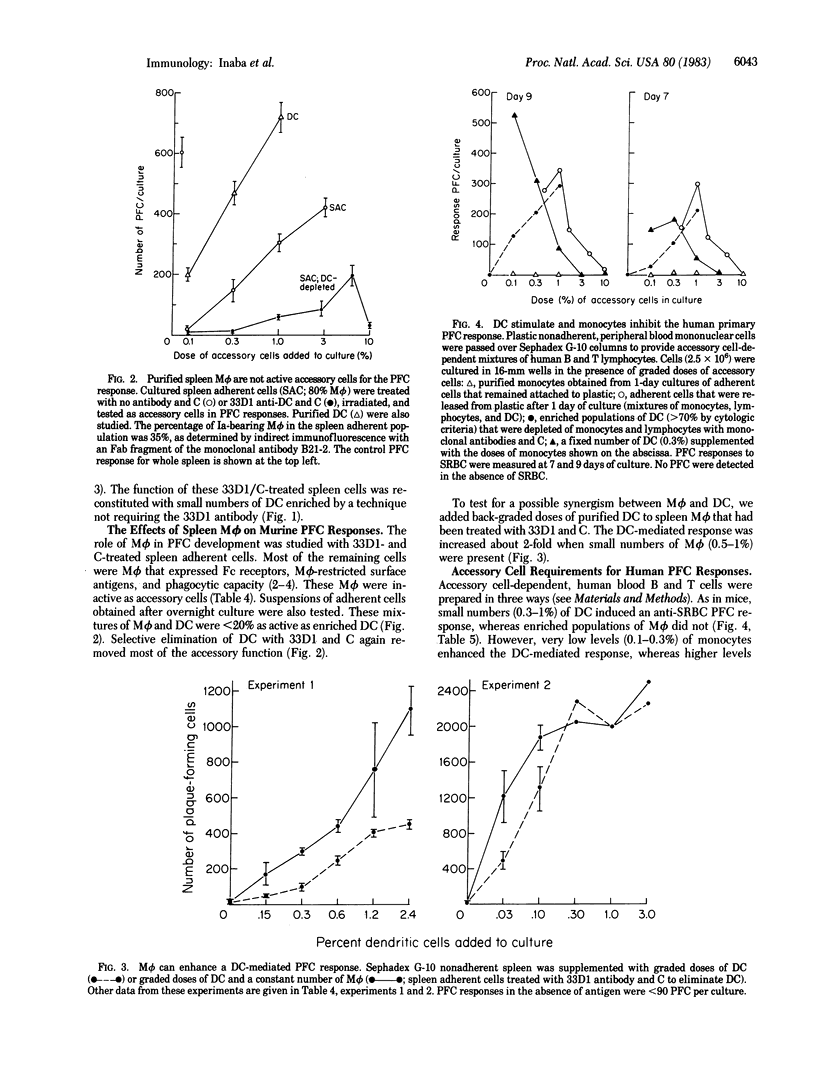
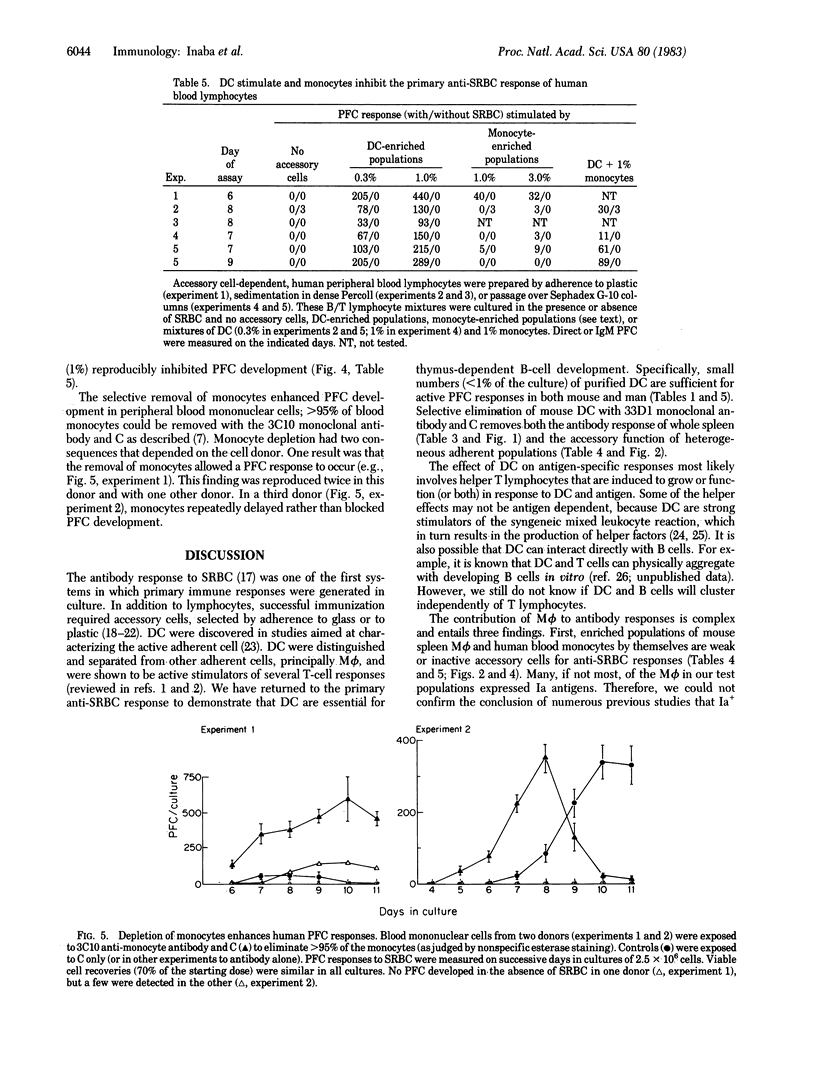
We report that dendritic cells (DC) are necessary and potent accessory cells for anti-sheep erythrocyte responses in both mouse and man. In mice, a small number of DC (0.3-1% of the culture) restores the response of B/T-lymphocyte mixtures to that observed in unfractionated spleen. An even lower dose (0.03-0.1% DC) is needed if the T cells have been primed to antigen. Responses are both antigen and T cell dependent. Selective depletion of DC from unfractionated spleen with the monoclonal antibody 33D1 and complement ablates the antibody response. In contrast to DC, purified spleen macrophages are weak or inactive stimulators. However, when mixed with DC, macrophages can increase the yield of antibody-secreting cells about 2-fold. In man, small numbers (0.3-1%) of blood DC stimulate antibody formation in vitro. Purified human monocytes do not stimulate but in low doses (1% of the culture) inhibit the antibody response. Likewise, selective removal of human monocytes with antibody and complement enhances or accelerates the development of antibody-secreting cells. We conclude that DC are required for the development of T-dependent antibody responses by mouse and human lymphocytes in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen C., Hirsch J. G. The effects of mercaptoethanol and of peritoneal macrophages on the antibody-forming capacity of nonadherent mouse spleen cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):604–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiorazzi N., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Induction of polyclonal antibody synthesis by human allogeneic and autologous helper factors. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1543–1548. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Galanaud P., Dormont J., Wallon C. Primary in vitro antibody response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes: role of phagocytic mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1283–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkoff R., Kettman J. Differential stimulation of precursor cells and carrier-specific thymus-derived cell activity in the in vivo reponse to heterologous erythrocytes in mice. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):54–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Waldmann T. A. Separation of human blood monocytes and lymphocytes on a continuous Percoll gradient. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman P. B., Stobo J. D. Specificity and function of a human autologous reactive T cell. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1537–1542. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes R. J., Singer A. Cellular and genetic control of antibody responses in vitro. I. Cellular requirements for the generation of genetically controlled primary IgM responses to soluble antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Dec;7(12):892–897. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. Peritoneal macrophages in the immune response to SRBC in vitro. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):791–797. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Muramatsu S. Participation of Ia antigen-bearing nonmacrophage cells in the manifestation of accessory cell activity for in vitro antibody response. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(7):683–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Nakano K., Muramatsu S. Cellular synergy in the manifestation of accessory cell activity for in vitro antibody response. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):452–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Gomez de la Concha E., Luquetti A., Snajdr M. J., Waxdal M. J., Platts-Mills T. A. T-cell regulation of immunoglobulin synthesis and proliferation in pokeweed (Pa-1)-stimulated human lymphocyte cultures. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(1-2):109–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiti J., Waldmann T. A. In vitro generation of antigen-specific hemolytic plaque-forming cells from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1069–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Todd R. F., 3rd, Distaso J. A., Schlossman S. F. The role of the macrophage in in vitro primary anti-DNP antibody production in man. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1137–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. A requirement for two cell types for antibody formation in vitro. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1573–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Coppleson L. W. A THREE-CELL INTERACTION REQUIRED FOR THE INDUCTION OF THE PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):542–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Lemke H., Opitz H. G. The role of adherent cells in the immune response. Fibroblasts and products released by fibroblasts and peritoneal cells can substitute for adherent cells. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(3):269–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Steinman R. M. Contribution of dendritic cells to stimulation of the murine syngeneic mixed leukocyte reaction. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1196–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Steinman R. M., Witmer M. D., Gutchinov B. A monoclonal antibody specific for mouse dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):161–165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W. Immune responses in vitro. I. Cellular requirements for the immune response by nonprimed and primed spleen cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):345–364. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radovich J., Talmage D. W. Antigenic competition: cellular or humoral. Science. 1967 Oct 27;158(3800):512–514. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3800.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Diener E., Russell P., Armstrong W. D. The role of nonlymphoid accessory cells in the immune response to different antigens. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):461–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1142–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Gutchinov B., Witmer M. D., Nussenzweig M. C. Dendritic cells are the principal stimulators of the primary mixed leukocyte reaction in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):613–627. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nogueira N., Witmer M. D., Tydings J. D., Mellman I. S. Lymphokine enhances the expression and synthesis of Ia antigens on cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1248–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nussenzweig M. C. Dendritic cells: features and functions. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:127–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Hair L. S., Steinman R. M., Kaplan G. Human dendritic cells. Enrichment and characterization from peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1172–1187. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Steinman R. M., Hair L. S., Luban J., Witmer M. D., Koide S., Cohn Z. A. Specific antimononuclear phagocyte monoclonal antibodies. Application to the purification of dendritic cells and the tissue localization of macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):126–145. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Gaul S. L. Enhancement of the humoral response of T cell-depleted murine spleens by a factor derived from human monocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):925–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


