Abstract
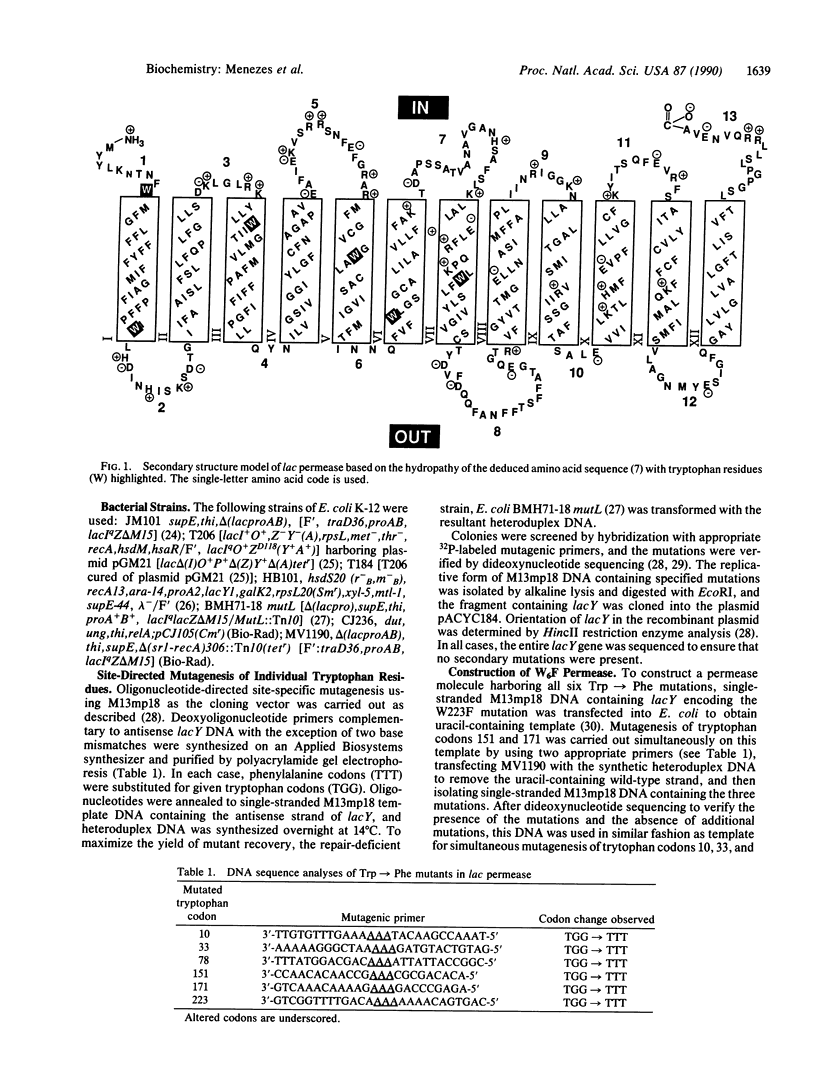
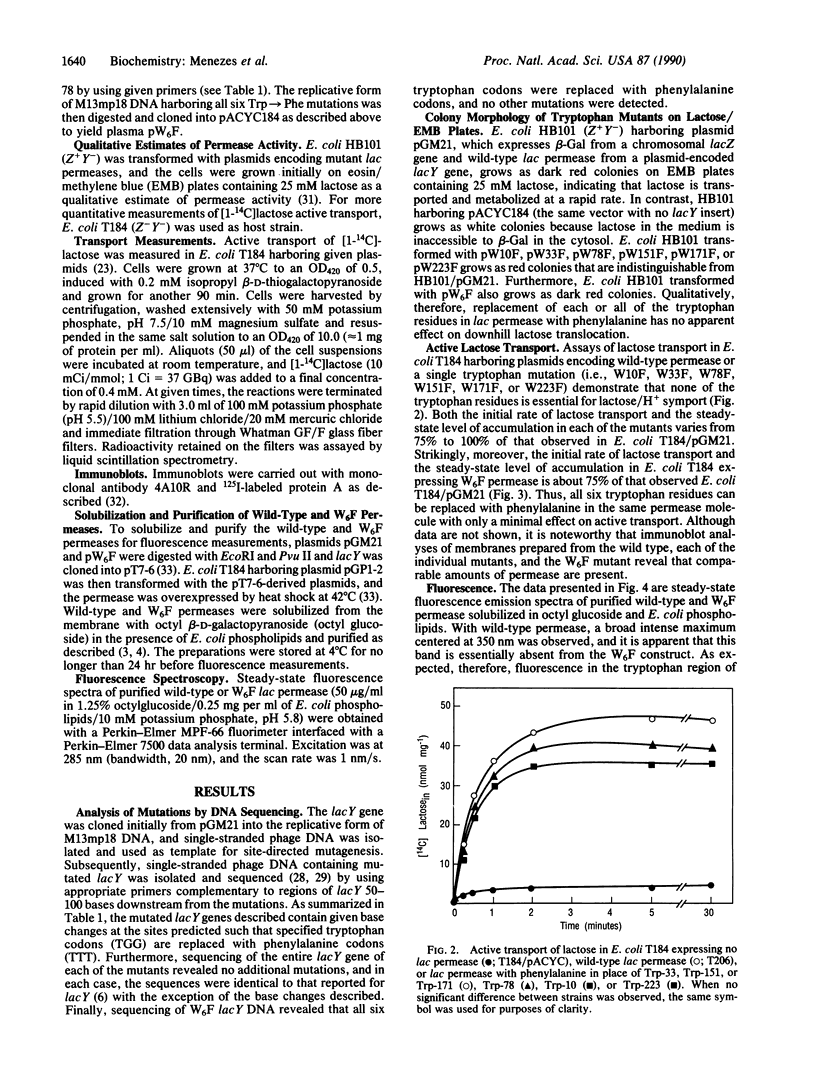
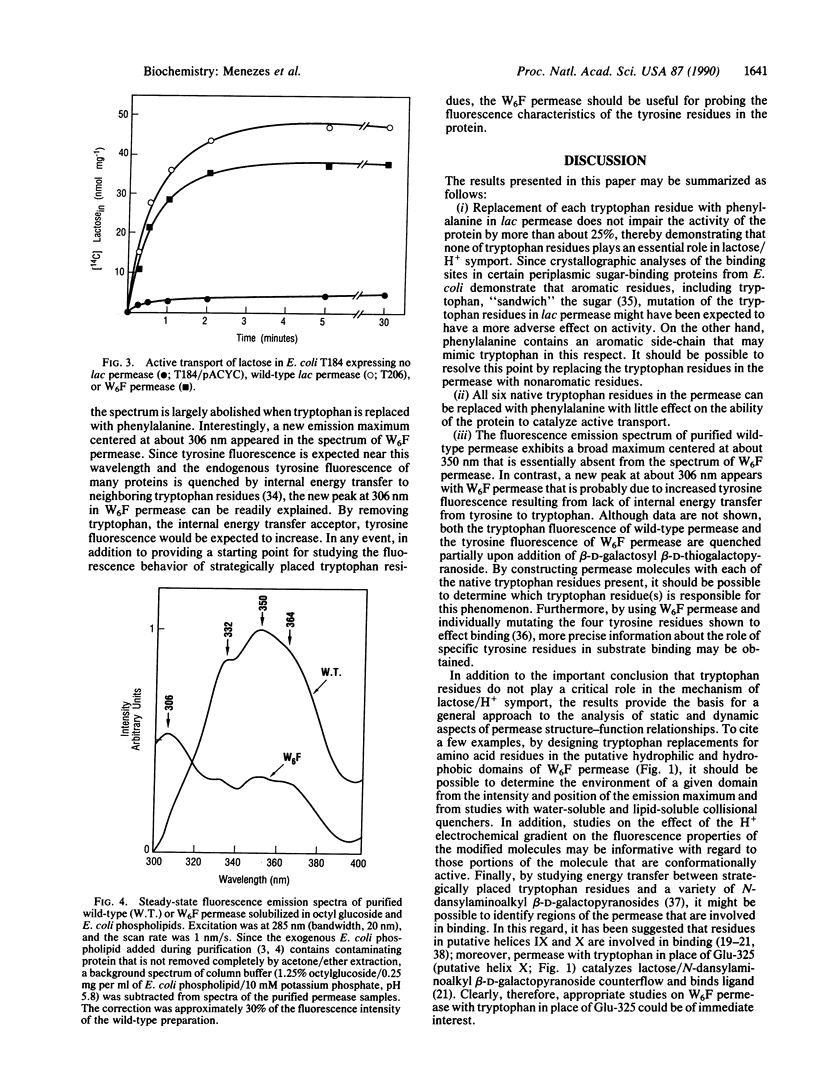
To modify the lac permease of Escherichia coli for fluorescence spectroscopy, six tryptophan residues at positions 10, 33, 78, 151, 171, and 223 were first replaced individually with phenylalanine by using oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis. None of the tryptophan residues is critical for activity, as evidenced by the finding that the mutant permease molecules catalyze lactose/H+ symport almost as well as wild-type permease. Subsequently, a permease molecule was designed in which all of the tryptophan residues were replaced with phenylalanine. Remarkably, the lac permease harboring all six mutations catalyzes active lactose transport about 75% as well as wild-type permease. The fluorescence emission spectrum of purified wild-type permease solubilized in octyl beta-D-glucopyranoside and phospholipid exhibits a broad maximum centered at 350 nm, and the peak is almost completely absent from the spectrum of permease devoid of tryptophan. Furthermore, a new maximum centered at about 306 nm is apparent in the spectrum of the modified permease, suggesting that tyrosine fluorescence in the native protein is quenched by internal energy transfer to tryptophan residues. By using site-directed mutagenesis to replace specified residues in the molecule without tryptophan, it should now be possible to utilize tryptophan fluorescence spectroscopy to study static and dynamic aspects of permease structure and function.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchel D. E., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lactose permease gene. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):541–545. doi: 10.1038/283541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Herzlinger D., Mitchell R., DeChiara S., Danho W., Gabriel T. F., Kaback H. R. Intramolecular dislocation of the COOH terminus of the lac carrier protein in reconstituted proteoliposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Püttner I. B., Antes L. M., Lee J. A., Larigan J. D., Lolkema J. S., Roepe P. D., Kaback H. R. Characterization of site-directed mutants in the lac permease of Escherichia coli. 2. Glutamate-325 replacements. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2533–2539. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Tahara S. M., Patel L., Goldkorn T., Kaback H. R. Preparation, characterization, and properties of monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6894–6898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Viitanen P., Herzlinger D., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 1. Functional studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3681–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. C., Permuth S. F., Brooker R. J. Isolation and characterization of lactose permease mutants with an enhanced recognition of maltose and diminished recognition of cellobiose. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14698–14703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello M. J., Escaig J., Matsushita K., Viitanen P. V., Menick D. R., Kaback H. R. Purified lac permease and cytochrome o oxidase are functional as monomers. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17072–17082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Rimon G., Kaback H. R. Topology of the lac carrier protein in the membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3322–3326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D., Viitanen P., Carrasco N., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 2. Binding studies with membrane vesicles and proteoliposomes reconstituted with purified lac carrier protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3688–3693. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Molecular biology of active transport: from membrane to molecule to mechanism. Harvey Lect. 1987;83:77–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis and ion-gradient driven active transport: on the path of the proton. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:243–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Different base/base mismatches are corrected with different efficiencies by the methyl-directed DNA mismatch-repair system of E. coli. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A., Püttner I. B., Kaback H. R. Effect of distance and orientation between arginine-302, histidine-322, and glutamate-325 on the activity of lac permease from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2540–2544. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolkema J. S., Püttner I. B., Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of Pro327 in the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8307–8310. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menick D. R., Carrasco N., Antes L., Patel L., Kaback H. R. lac permease of Escherichia coli: arginine-302 as a component of the postulated proton relay. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6638–6644. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menick D. R., Lee J. A., Brooker R. J., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Role of cysteine residues in the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1132–1136. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Foster D. L., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Purification and reconstitution of functional lactose carrier from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11804–11808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. G., Rosenbusch J. P. Topography of lactose permease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15906–15914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Püttner I. B., Sarkar H. K., Padan E., Lolkema J. S., Kaback H. R. Characterization of site-directed mutants in the lac permease of Escherichia coli. 1. Replacement of histidine residues. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2525–2533. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A. Carbohydrate-binding proteins: tertiary structures and protein-sugar interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:287–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D., Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of tyrosine residues in the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):6127–6132. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D., Zbar R. I., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R. A five-residue sequence near the carboxyl terminus of the polytopic membrane protein lac permease is required for stability within the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar H. K., Viitanen P. V., Padan E., Trumble W. R., Poonian M. S., McComas W., Kaback H. R. Oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis of the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:214–230. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Möröy T., Wright J. K., Overath P. Anti-peptide antibodies and proteases as structural probes for the lactose/H+ transporter of Escherichia coli: a loop around amino acid residue 130 faces the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2403–2409. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Wright J. K., Overath P. Peptide-specific antibody locates the COOH terminus of the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10817–10820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Wright J. K. Sidedness of native membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and orientation of the reconstituted lactose: H+ carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):269–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stochaj U., Bieseler B., Ehring R. Limited proteolysis of lactose permease from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Bramhall J., Riede I., Wright J. K., Fürst M., Aichele G., Wilhelm U., Overath P. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Structure and expression of plasmids carrying the Y gene of the lac operon. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P., Newman M. J., Foster D. L., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Purification, reconstitution, and characterization of the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:429–452. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Wright J. K., Jähnig F. The structure of the lactose permease derived from Raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3625–3631. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


