Abstract
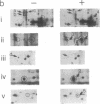
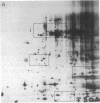
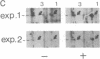
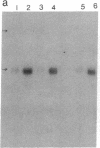
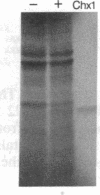
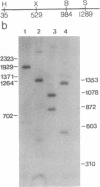
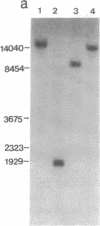
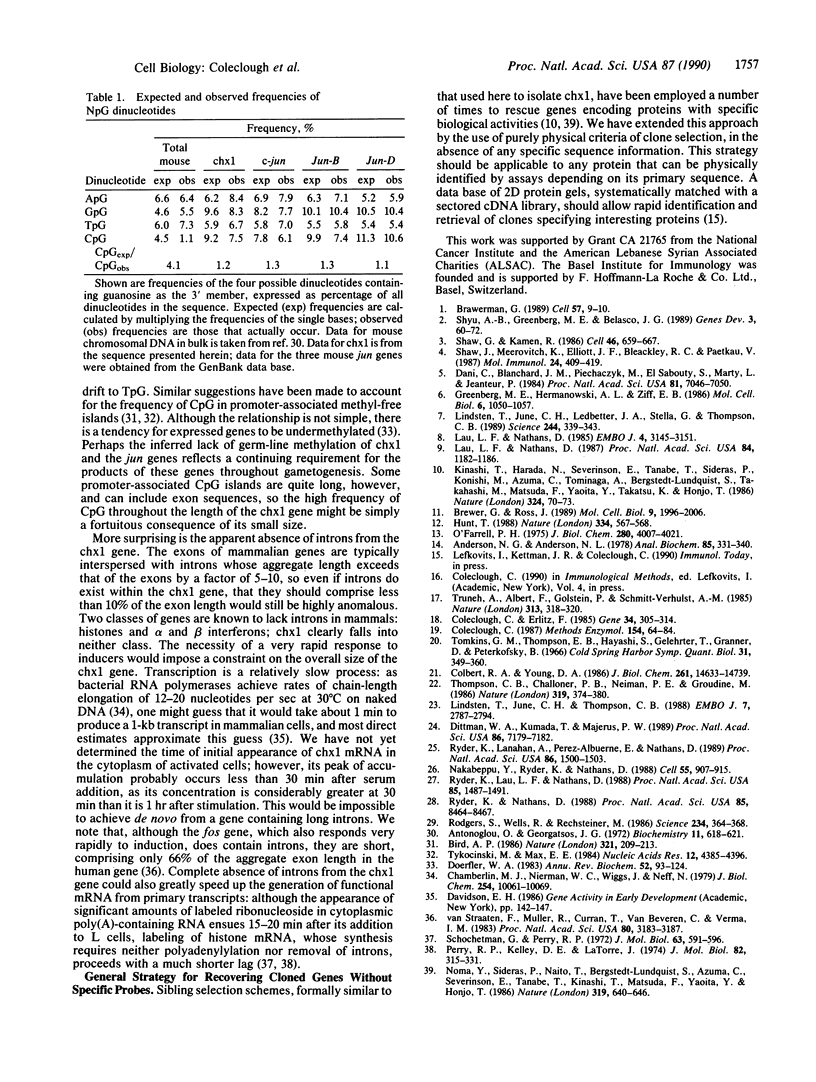
Inhibition of protein synthesis has often been observed to increase the concentration of mRNAs that encode proteins associated with the regulation of cell division. As two-dimensional gel electrophoresis permits the simultaneous monitoring of individual elements in large populations of gene products, we have used this technique to assess the effect of cycloheximide treatment on the mRNA complement of activated mouse T cells in an objective fashion. Two-dimensional gels of proteins generated by cell-free translation of mRNA from T-cell blasts display about 400 spots; only 5 of these are reproducibly enhanced by cycloheximide treatment and about 4 are diminished. The cDNA cloning vector lambda jac allows analysis of large arrays of molecular clones by cell-free expression, and we have used it in a sibling selection scheme to isolate a clone of one of the prominently induced mRNA species, which we refer to as chx1. chx1 mRNA concentration is increased by cycloheximide treatment of activated B cells, as well as T cells, and it is rapidly and transiently induced, in a cycloheximide-enhanced manner, upon serum stimulation of resting 3T3 fibroblastoid cells. The chx1 protein is hydrophilic, is slightly basic, and has patches of homology with the Jun-D gene product. The chx1 gene is remarkable in its lack of detectable introns and of strong bias against CpG dinucleotides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXI. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonoglou O., Georgatsos J. G. Nearest-neighbor frequencies of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid in mouse liver. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):618–621. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Regulation of c-myc mRNA stability in vitro by a labile destabilizer with an essential nucleic acid component. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1996–2006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J., Nierman W. C., Wiggs J., Neff N. A quantitative assay for bacterial RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10061–10069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
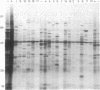
- Colbert R. A., Young D. A. Electrophoretic separation of in vitro translation products on giant two-dimensional gels allows detailed analysis of cellular mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14733–14739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Erlitz F. L. Use of primer-restriction-end adapters in a novel cDNA cloning strategy. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C. Use of primer-restriction end adapters in cDNA cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:64–83. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Kumada T., Majerus P. W. Transcription of thrombomodulin mRNA in mouse hemangioma cells is increased by cycloheximide and thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7179–7182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Controlling mRNA lifespan. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):567–568. doi: 10.1038/334567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi T., Harada N., Severinson E., Tanabe T., Sideras P., Konishi M., Azuma C., Tominaga A., Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., Takahashi M. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding T-cell replacing factor and identity with B-cell growth factor II. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):70–73. doi: 10.1038/324070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Identification of a set of genes expressed during the G0/G1 transition of cultured mouse cells. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3145–3151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstein T., June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Stella G., Thompson C. B. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):339–343. doi: 10.1126/science.2540528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., June C. H., Thompson C. B. Multiple mechanisms regulate c-myc gene expression during normal T cell activation. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2787–2794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma Y., Sideras P., Naito T., Bergstedt-Lindquist S., Azuma C., Severinson E., Tanabe T., Kinashi T., Matsuda F., Yaoita Y. Cloning of cDNA encoding the murine IgG1 induction factor by a novel strategy using SP6 promoter. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):640–646. doi: 10.1038/319640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., LaTorre J. Synthesis and turnover of nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylic acid in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lanahan A., Perez-Albuerne E., Nathans D. jun-D: a third member of the jun gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1500–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Nathans D. Induction of protooncogene c-jun by serum growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8464–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schodhetman G., Perry R. P. Early appearance of histone messenger RNA in polyribosomes of cultured L cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):591–596. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J., Meerovitch K., Elliott J. F., Bleackley R. C., Paetkau V. Induction, suppression and superinduction of lymphokine mRNA in T lymphocytes. Mol Immunol. 1987 May;24(5):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Thompson E. B., Hayashi S., Gelehrter T., Granner D., Peterkofsky B. Tyrosine transaminase induction in mammalian cells in tissue culture. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:349–360. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truneh A., Albert F., Golstein P., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Early steps of lymphocyte activation bypassed by synergy between calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):318–320. doi: 10.1038/313318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tykocinski M. L., Max E. E. CG dinucleotide clusters in MHC genes and in 5' demethylated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4385–4396. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten F., Müller R., Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a human c-onc gene: deduced amino acid sequence of the human c-fos protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3183–3187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]