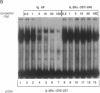
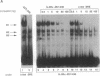
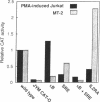
Abstract
High-affinity receptors for interleukin 2 (IL-2) are expressed on T cells following activation. These receptors are composed of both alpha and beta chains. Expression of alpha chains and, therefore, expression of high-affinity receptors are critically regulated at the level of transcription initiation. We have further dissected the regulatory elements involved in controlling transcription of the IL-2 receptor alpha-chain (IL-2R alpha) gene. The IL-2R alpha promoter contains a kappa B site and binding sites for additional nuclear factors within a 50-base-pair region (positions -290 to -240 relative to the major transcription start site). These include one upstream of the kappa B site and one similar to the c-fos serum response element (SRE), which is downstream of the kappa B site. Mutation of the kappa B site decreases IL-2R alpha promoter activity in MT-2 cells (a T-cell line that has been transformed with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I), but not in Jurkat cells (a T-cell leukemia line) that have been activated by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). In contrast, mutation of a region upstream of the kappa B site decreases activity in PMA-induced Jurkat cells but increases activity in MT-2 cells. Mutation of the SRE-like site decreases activity in both cell types but the effect in PMA-induced Jurkat is more pronounced. Thus, these distinct cis-acting elements play different physiological roles in IL-2R alpha gene activation in MT-2 cells and PMA-induced Jurkat T cells. These studies provide direct evidence for a functionally significant SRE-like sequence in a gene other than c-fos and the actin genes and identify other elements that are critical for IL-2R alpha gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Feinberg M. B., Wolf J. B., Holbrook N. J., Wong-Staal F., Leonard W. J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Burt D. W., Cheshire J. K., Woo P. Identification of cis-acting sequences responsible for phorbol ester induction of human serum amyloid A gene expression via a nuclear factor kappaB-like transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1908–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. c-fos promoter trans-activation by the tax1 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Mutation of the c-fos gene dyad symmetry element inhibits serum inducibility of transcription in vivo and the nuclear regulatory factor binding in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Alper D., Cohen L., Leblanc J. F., Sportza L., Wong A., Xanthoudakis S. Induction of human interferon gene expression is associated with a nuclear factor that interacts with the NF-kappa B site of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2557–2566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2557-2566.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Kanehisa M., Krönke M., Peffer N. J., Svetlik P. B., Sullivan M., Greene W. C. Structure of the human interleukin-2 receptor gene. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):633–639. doi: 10.1126/science.2996141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Peffer N. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 receptor gene expression in normal human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6281–6285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. B., Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Roman D. G., Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Delineation of an enhancerlike positive regulatory element in the interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):850–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan-Dinh-Tuy F., Tuil D., Schweighoffer F., Pinset C., Kahn A., Minty A. The 'CC.Ar.GG' box. A protein-binding site common to transcription-regulatory regions of the cardiac actin, c-fos and interleukin-2 receptor genes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Poteat H., Tan T. H., Kawakami K., Roeder R., Haseltine W., Rosen C. A. Cellular transcription factors and regulation of IL-2 receptor gene expression by HTLV-I tax gene product. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.2838905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. A., Jr, Franza B. R., Jr, Gilman M. Z. Two distinct cellular phosphoproteins bind to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Purification of intercalator-released p67, a polypeptide that interacts specifically with the c-fos serum response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10145–10158. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Stewart T. N., Gilman M. Z., Blackshear P. J. Identification of c-fos sequences involved in induction by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1611–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam M., Schmidt L. J., Crutchfield C. E., 3rd, Getz M. J. Negative regulation of serum-responsive enhancer elements. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):64–66. doi: 10.1038/340064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]