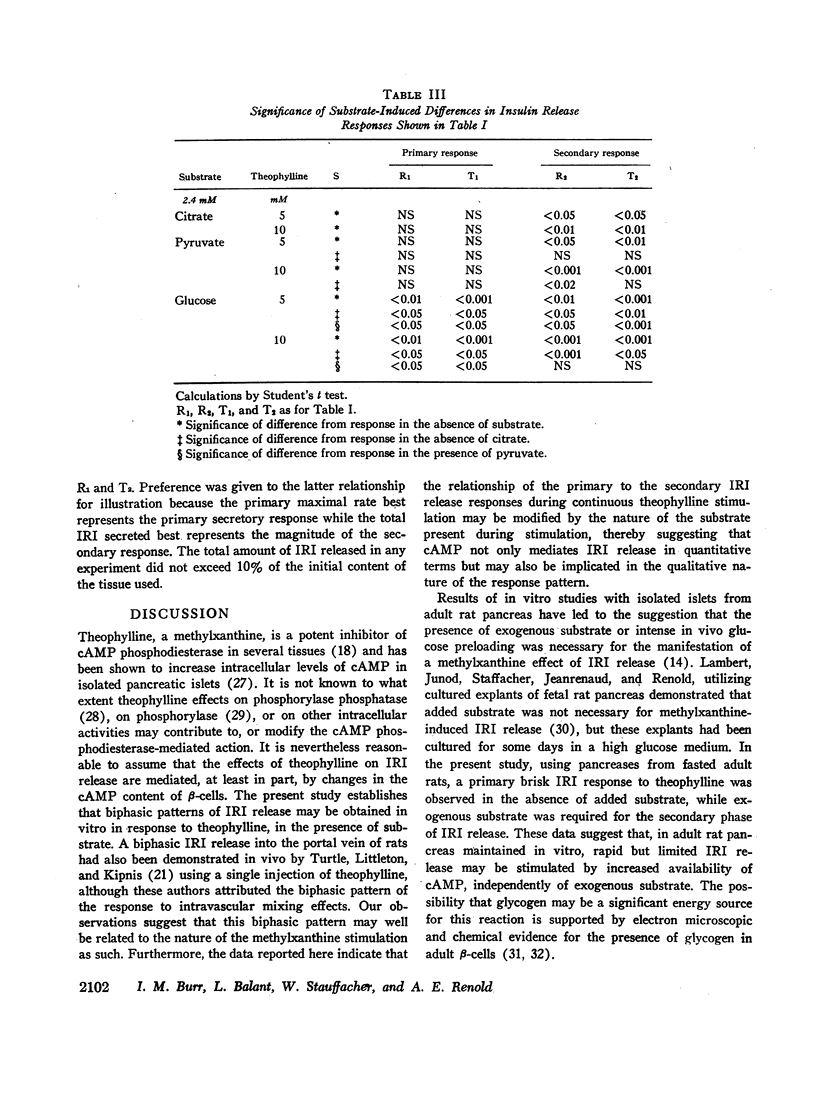
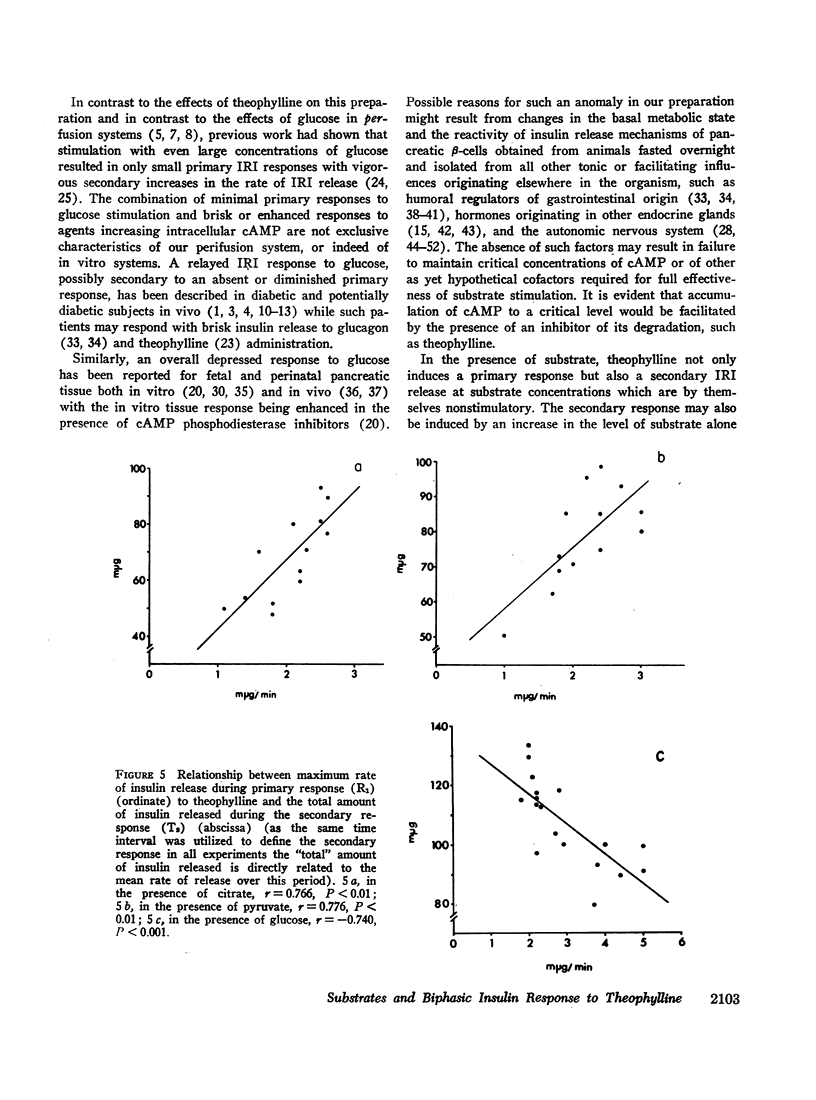
Abstract
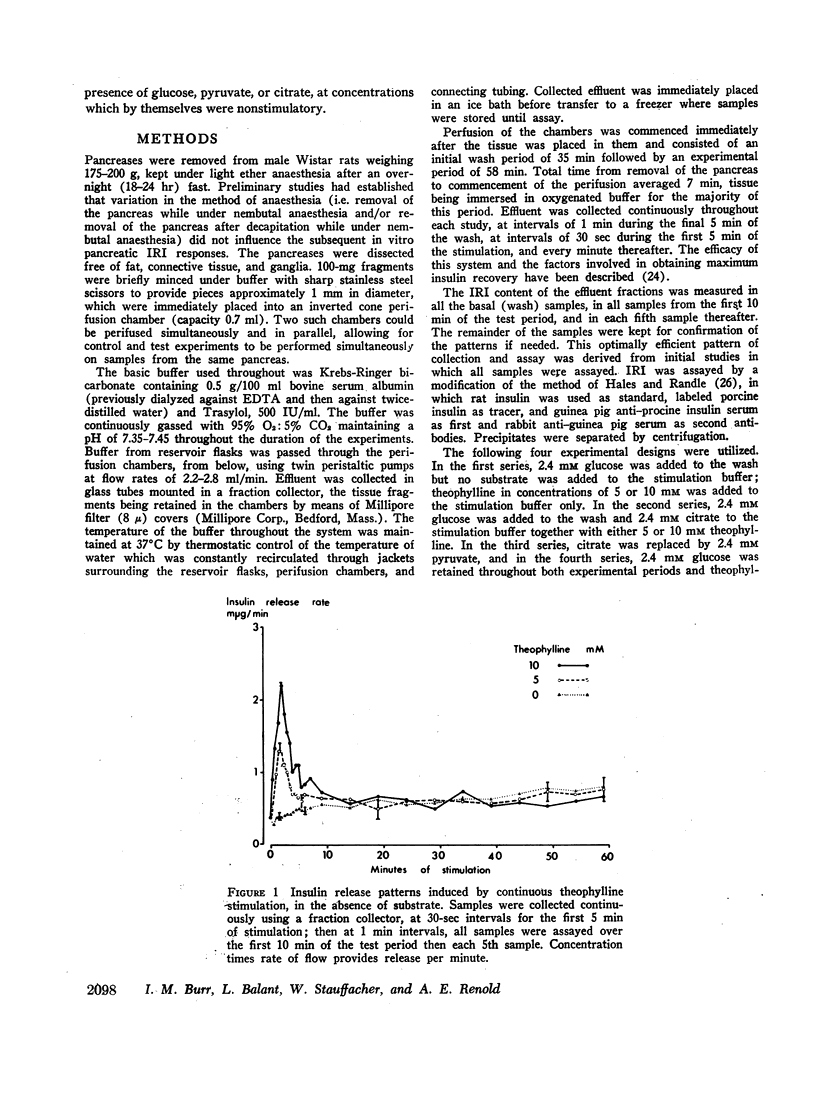
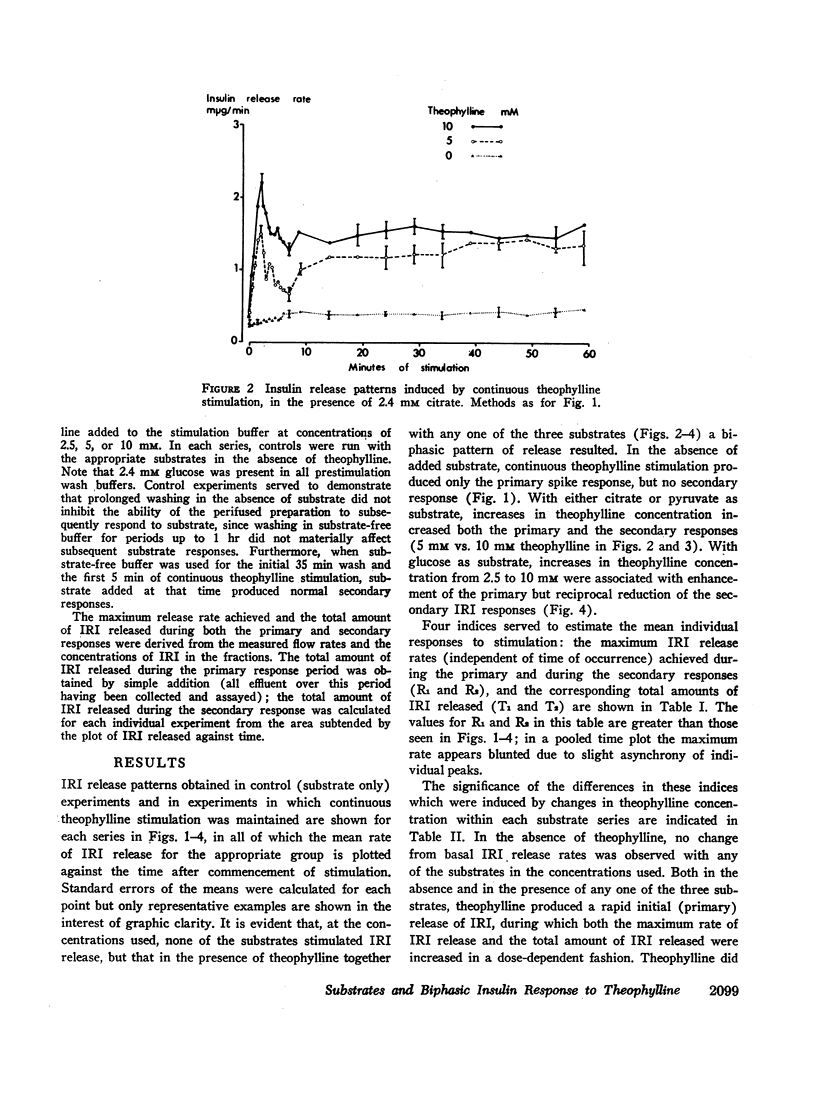
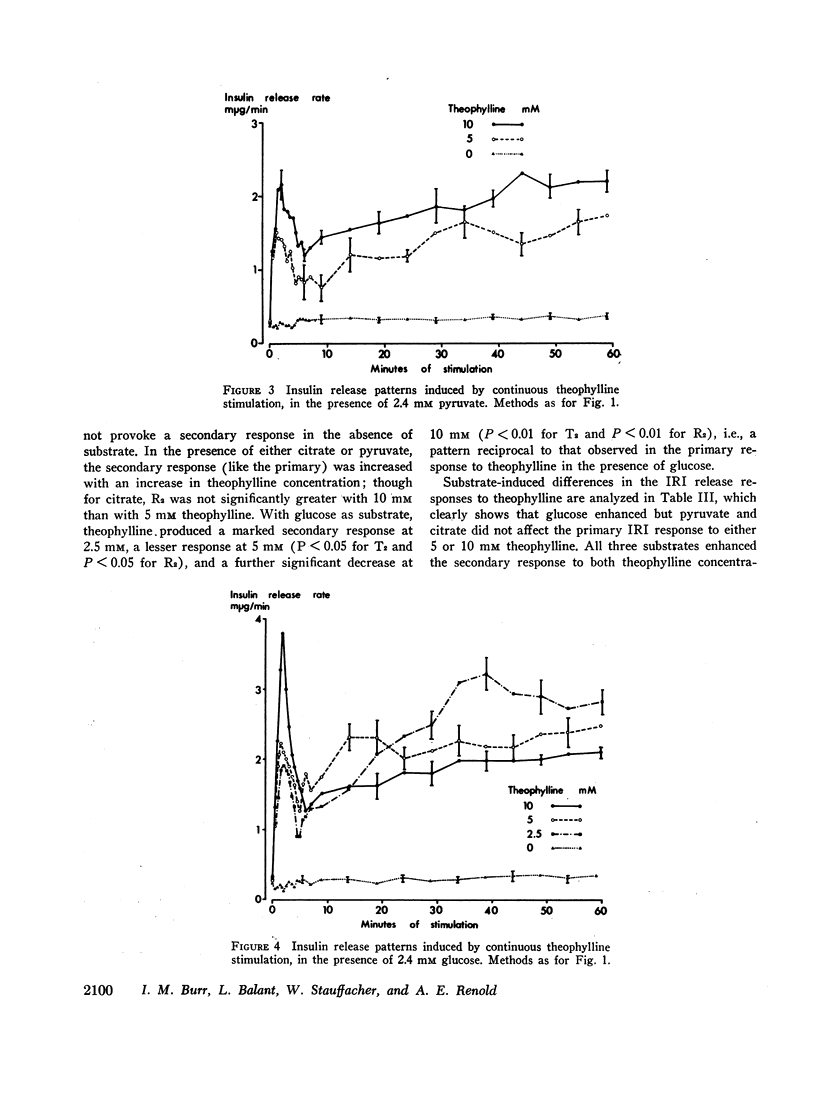
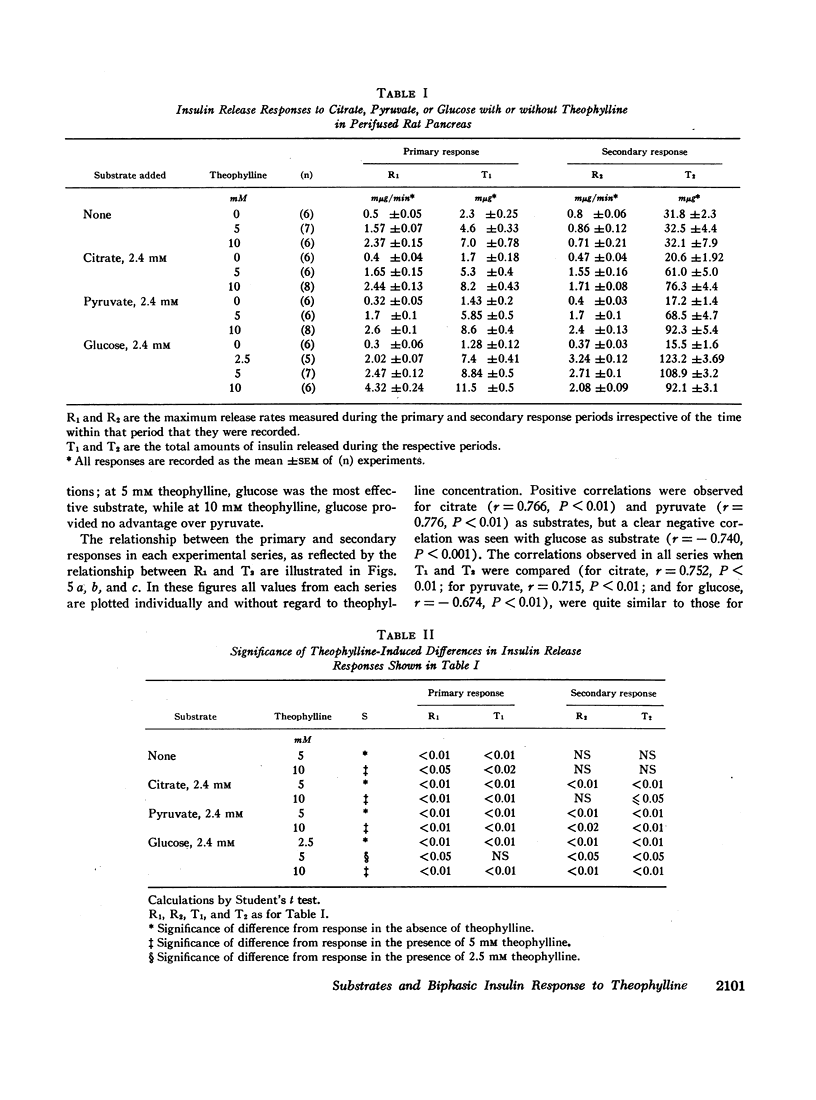
The immunoreactive insulin (IRI) release patterns produced by continuous theophylline stimulation of rat pancreas have been defined, using an in vitro perfusion system. In the presence of glucose, citrate, and pyruvate at concentrations which were nonstimulatory by themselves, continuous stimulation with theophylline produced a biphasic IRI release profile. In the absence of substrate, continuous theophylline stimulation produced only an abrupt and limited primary response. Of the substrates tested, only glucose significantly enhanced this primary response. With increasing theophylline concentrations, whether in the presence or absence of substrate, significant increases were noted in the primary response as estimated by either the maximum rate of IRI release attained or by the total amount of IRI released during this time. Similarly, the secondary responses to theophylline increased with theophylline concentration in the presence of either citrate or pyruvate. With glucose as substrate, however, increasing theophylline concentrations from 2.5 to 5, then 10 mM produced a progressive reduction in both indices of the secondary response, which was inversely related to the primary response. These findings suggest that cyclic AMP not only mediates IRI release in quantitative terms but is also implicated in the qualitative nature of the response pattern. They also indicate a possible metabolic basis for biphasic IRI release, the acute or primary response being dependent upon the basal state of the cell and the availability of endogenous energy sources, the secondary response upon the availability of exogenous substrate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asplund K., Westman S., Hellerström C. Glucose stimulation of insulin secretion from the isolated pancreas of foetal and newborn rats. Diabetologia. 1969 Aug;5(4):260–262. doi: 10.1007/BF01212095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD J. D., FARQUHAR J. W. Insulin-secreting capacity in newborn infants of normal and diabetic women. Lancet. 1962 Jan 13;1(7220):71–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91720-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E., Grodsky G. Dynamic aspects of proinsulin release from perifused rat pancreas. Lancet. 1969 Oct 25;2(7626):882–883. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Renold A. E., Stauffacher W., Grodsky G. M., Balant L. [Regulation of insulin release in perifused pancreatic tissue]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1969 Sep;6 (Suppl 1):580–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E. An analogue computer model for the insulin response to glucose infusion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 May;55(1):163–183. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Effendic S., Luft R. Role of adrenergic receptors in glucose-induced insulin secretion in man. Lancet. 1969 Aug 9;2(7615):301–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. Insulin response to glucose infusion in diabetic and non-diabetic monozygotic twin pairs. Genetic control of insulin response? Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):330–345. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The effect of an adenosine--3'5'--monophosphate diesterase inhibitor (aminophylline) on the insulin response to glucose infusion in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. Horm Metab Res. 1969 Jul;1(4):162–168. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm D. J., Young J. D., Lazarus L. The gastrointestinal stimulus to insulin release. I. Secretin. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1453–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI106111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Randle P. J. Regulation of insulin secretion studied with pieces of rabbit pancreas incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):66–78. doi: 10.1042/bj0930066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockford P. M., Hazzard W. R., Williams R. H. Insulin response to glucagon. The opposing effects of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 1969 Apr;18(4):216–224. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.4.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Ezdinli E. Z., Javid R. Effect of vagotomy and vagal stimulation on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1967 Jul;16(7):443–448. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.7.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRODSKY G. M., BENNETT L. L. INSULIN SECRETION FROM THE ISOLATED PANCREAS IN ABSENCE OF INSULINOGENESIS: EFFECT OF GLUCOSE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Dec;114:769–771. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kajinuma H., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Stimulation of insulin secretion by parasympathomimetic agents. Endocrinology. 1968 Oct;83(4):651–658. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-4-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E. The pancreatic beta cell. Structure and function. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 26;276(4):187–195. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701262760401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert A. E., Jeanrenaud B., Renold A. E. Enhancement by caffeine of glucagon-induced and tolbutamide-induced insulin release from isolated foetal pancreatic tissue. Lancet. 1967 Apr 15;1(7494):819–820. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92782-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert A. E., Junod A., Stauffahcer W., Jeanrenaud B., Renold A. E. Organ culture of fetal rat pancreas. I. Insulin release induced by caffeine and by sugars and some derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 2;184(3):529–539. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mayhew D. A possible role for the adenylcyclase system in insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1724–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI105663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., McCraw E. F. Effects of thyroid function upon insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1967 Sep;16(9):643–646. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.9.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Burgess J. A., Rabinowitz D. Influence of growth hormone on insulin secretion. Studies of growth-hormone deficient subjects. Diabetes. 1967 Jul;16(7):478–482. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.7.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Beta adrenergic stimulation of insulin release in man. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):150–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Williams R. H. Inhibition of insulin release by norepinephrine in man. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1248–1250. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts H. T., Cherry R. A., Kirsteins L. Biochemical studies of "prediabetes". Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):880–888. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rull J. A., Conn J. W., Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S. Levels of plasma insulin during cortisone glucose tolerance tests in "nondiabetic" relatives of diabetic patients. Implications of diminished insulin secretory reserve in subclinical diabetes. Diabetes. 1970 Jan;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STIMMLER L., BRAZIE J. V., O'BRIEN D. PLASMA-INSULIN LEVELS IN THE NEWBORN INFANTS OF NORMAL AND DIABETIC MOTHERS. Lancet. 1964 Jan 18;1(7325):137–138. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W. The effect of the hyperglycemic factor and epinephrine on enzyme systems of liver and muscle. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1951 Dec;54(4):693–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1951.tb46623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shochat G., Wilansky D. L. Serum insulin in early latent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1968 Oct;17(10):928–935. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. G., Benedetti A., Grodsky G. M., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Stimulation of insulin release by glucagon in noninsulin-dependent diabetics. Metabolism. 1966 Nov;15(11):1046–1049. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman K. E., Vaughan G. D. Insulin release after ACTH, glucagon and adenosine-3'-5'-phosphate (cyclic AMP) in the perfused isolated rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jul;16(7):449–454. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.7.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland E. W., Robison G. A. The role of cyclic AMP in the control of carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetes. 1969 Dec;18(12):797–819. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.12.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtle J. R., Kipnis D. M. An adrenergic receptor mechanism for the control of cyclic 3'5' adenosine monophosphate synthesis in tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):797–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtle J. R., Littleton G. K., Kipnis D. M. Stimulation of insulin secretion by theophylline. Nature. 1967 Feb 18;213(5077):727–728. doi: 10.1038/213727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ohneda A., Valverde I., Eisentraut A. M., Exton J. Characterization of the responses of circulating glucagon-like immunoreactivity to intraduodenal and intravenous administration of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):48–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI105714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


