Abstract
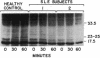
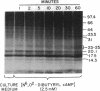
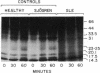
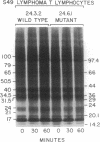
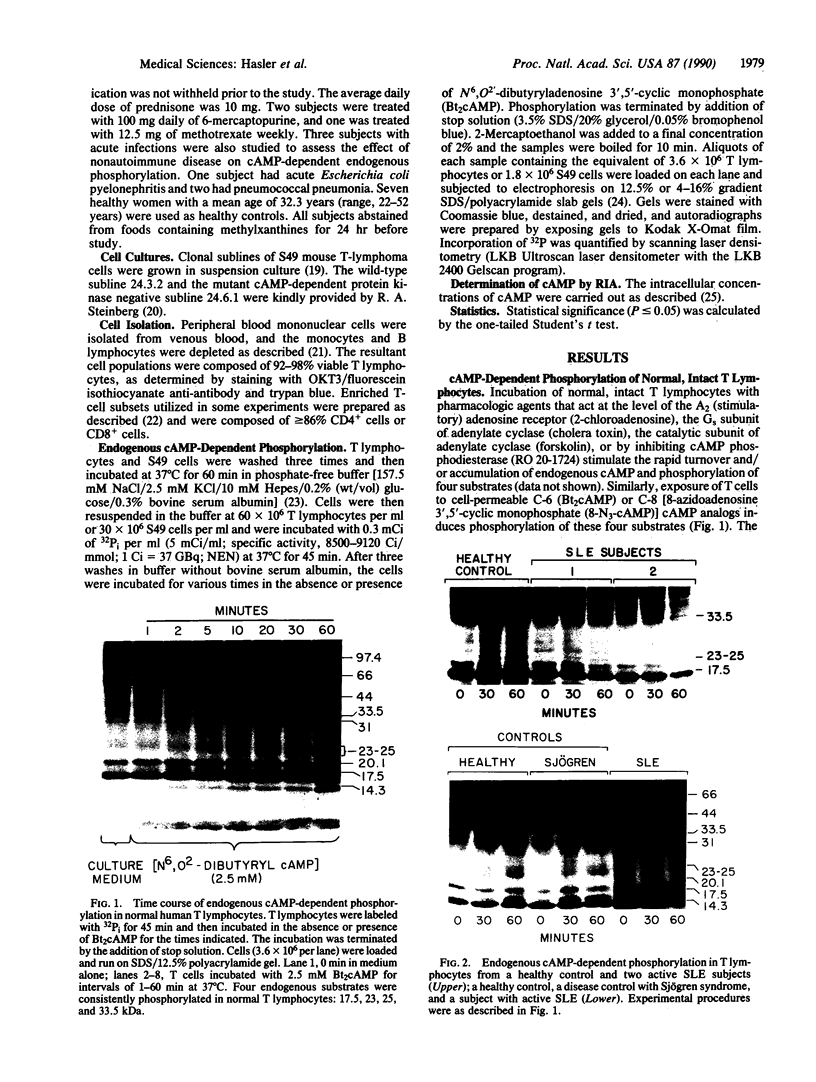
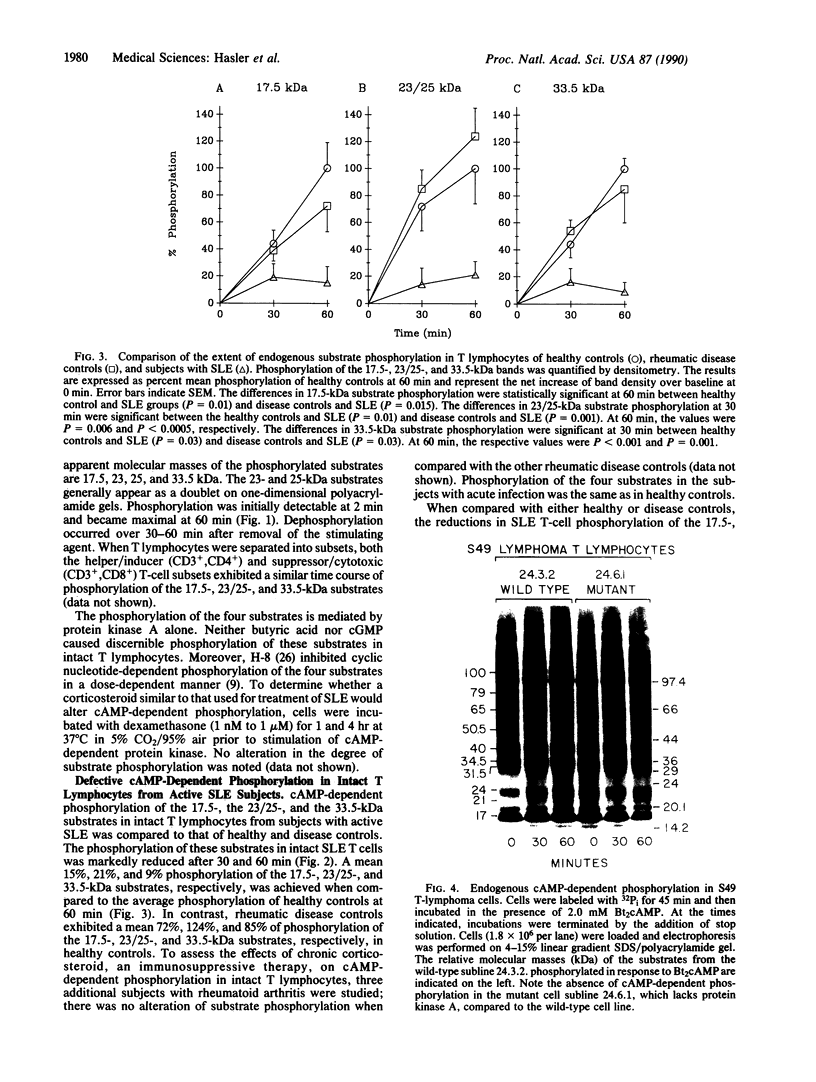
The present study was undertaken to establish whether cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous substrates is impaired in T lymphocytes from subjects with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In normal human T lymphocytes, the cell-permeable cAMP analog, N6,O2'-dibutyryladenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate, induced phosphorylation of substrates with molecular masses of 17.5, 23/25, 33.5 kDa on one-dimensional SDS/PAGE. Maximal phosphorylation occurred at 60 min. In contrast to healthy T cells, the extent of substrate phosphorylation achieved in active SLE T cells (n = 8) was only 15% at 60 min in the 17.5-kDa substrate, 21% in the 23/25-kDa substrate, and 9% in the 33.5-kDa substrate. The rheumatic disease controls (rheumatoid arthritis; primary Sjögren syndrome; n = 8) exhibited a mean 72%, 124%, and 85%, respectively, of phosphorylation observed in healthy T cells. Because the only known mechanism by which cAMP acts is via cAMP-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase A), these data raise the possibility of a defect at the level of this kinase in SLE T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averill L. E., Stein R. L., Kammer G. M. Control of human T-lymphocyte interleukin-2 production by a cAMP-dependent pathway. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):88–99. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch R. E., Rosenthal A. K., Polmar S. H. Pharmacological modification of immunoregulatory T lymphocytes . II. Modulation of T lymphocyte cell surface characteristics. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):231–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Glazer R. I. Inhibition of interleukin-2 messenger RNA in mouse lymphocytes by 2'-deoxycoformycin and adenosine metabolites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;451:180–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb27109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Evans S. W., Rapp U. R., Cleveland J. L. Effects of anti-proliferative cyclic AMP on interleukin 2-stimulated gene expression. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2075–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt L. P., Kresina T. F., Kammer G. M. Effect of anti-T cell autoantibodies from systemic lupus erythematosus sera upon T lymphocyte functions. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):646–654. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., LeCam A., Bukowski M., Pastan I. Isolation of multiple classes of mutants of CHO cells resistant to cyclic AMP. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Jan;6(1):45–61. doi: 10.1007/BF01538695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horibata K., Harris A. W. Mouse myelomas and lymphomas in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Apr;60(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H. Impaired immunoregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus: defective adenosine-induced suppressor T lymphocyte generation. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1706–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Boehm C. A., Rudolph S. A. Role of adenylate cyclase in human T-lymphocyte surface antigen capping. Cell Immunol. 1986 Aug;101(1):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Boehm C. A., Rudolph S. A., Schultz L. A. Mobility of the human T lymphocyte surface molecules CD3, CD4, and CD8: regulation by a cAMP-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):792–796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. Impaired T cell capping and receptor regeneration in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Evidence for a disorder intrinsic to the T lymphocyte. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1686–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI111128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Kurrasch R., Scillian J. J. Capping of the surface OKT3 binding molecule prevents the T-cell proliferative response to antigens: evidence that this molecule conveys the activation signal. Cell Immunol. 1984 Aug;87(1):284–294. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Mitchell E. Impaired mobility of human T lymphocyte surface molecules during inactive systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to a defective cAMP pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):88–98. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. The adenylate cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A pathway and regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandler R., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H., Kammer G. M., Rudolph S. A. Abnormal adenosine-induced immunosuppression and cAMP metabolism in T lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Reich E. Gene expression and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogreid D., Døskeland S. O., Gorman K. B., Steinberg R. A. Mutations that prevent cyclic nucleotide binding to binding sites A or B of type I cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17397–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Krueger B. K. Endogenous protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:107–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. A., Kammer G. M., Rudolph S. A. Characterization of the human T lymphocyte adenosine receptor: comparison of normal and systemic lupus erythematosus cells. FASEB J. 1988 Mar 1;2(3):244–250. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.3.3258258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S. Protein phosphorylation: hormones, drugs, and bioregulation. FASEB J. 1988 Sep;2(12):2753–2764. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.12.2842213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slungaard A., Confer D. L., Schubach W. H. Rapid transcriptional down-regulation of c-myc expression during cyclic adenosine monophosphate-promoted differentiation of leukemic cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1542–1547. doi: 10.1172/JCI112987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., van Daalen Wetters T., Coffino P. Kinase-negative mutants of S49 mouse lymphoma cells carry a trans-dominant mutation affecting expression of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Kipnis D. M., Utiger R., Parker C. Radioimmunoassay for the measurement of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):367–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]