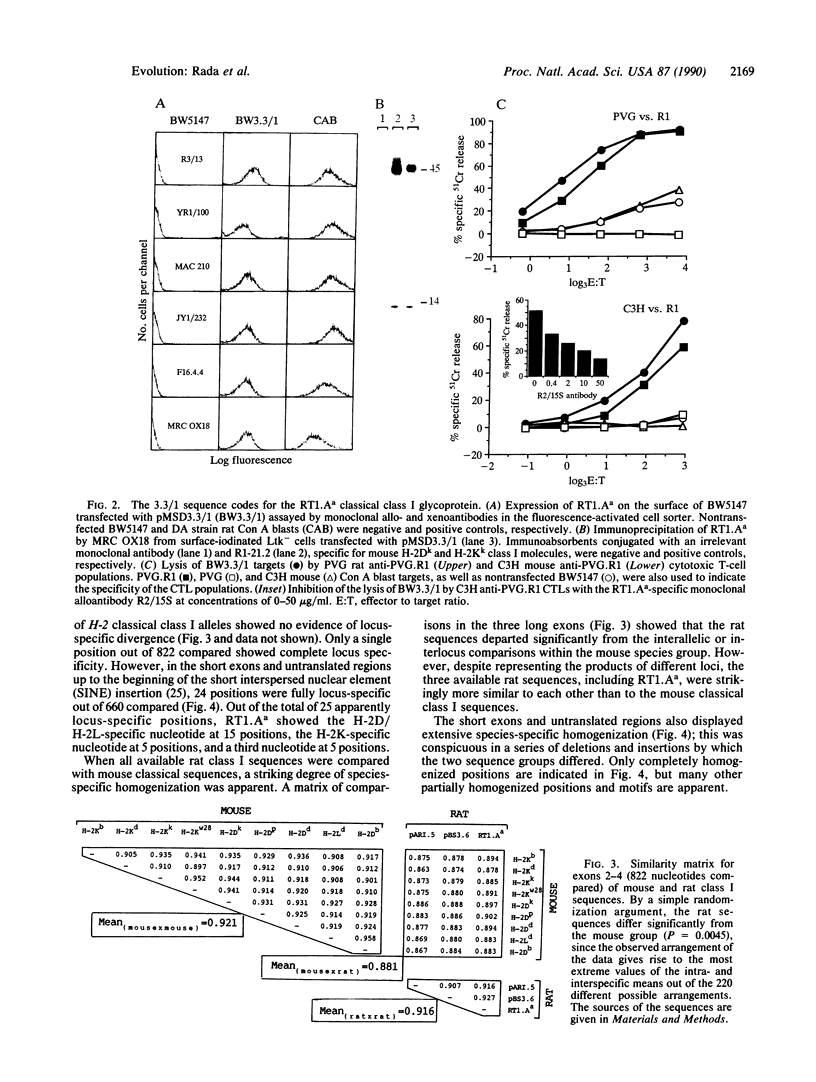
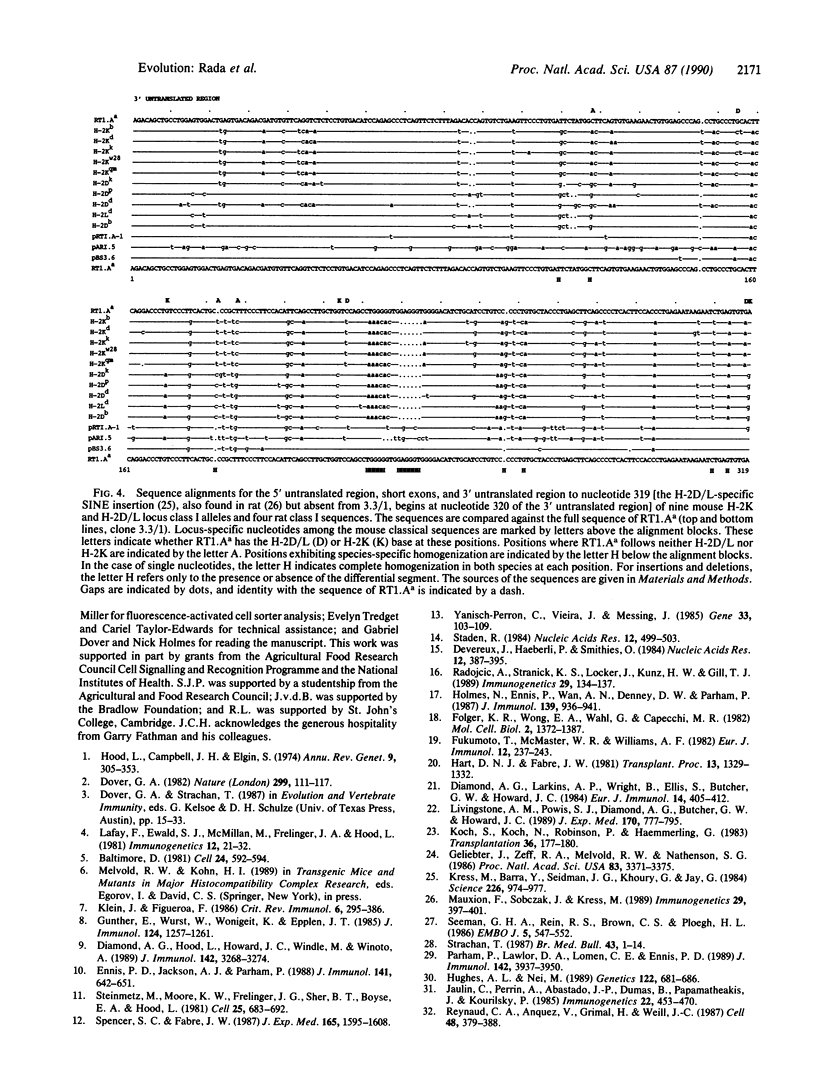
Abstract
Full-length cDNA sequences of two class I major histocompatibility complex molecules from the DA strain of Rattus norvegicus are reported. One codes for the classical class I restriction element RT1.Aa, which maps to the locus in the rat major histocompatibility complex homologous to H-2K in the mouse. The other probably codes for a soluble nonclassical class I molecule present in DA rat serum; a short deletion in the fifth exon implies that the translated product will terminate in the membrane-spanning region. These sequences have been compared with mouse classical class I sequences as well as with three published rat class I cDNA partial sequences. The results show, first, that "locus-specific" substitutions from the H-2K, H-2D, and H-2L data set are scrambled in the RT1.Aa molecule; a majority of these substitutions have H-2D/L-specific features. Second, the data show that the four rat sequences are strikingly similar to one another regardless of locus or haplotype of origin; they share a number of apparently species-specific features that distinguish them all from mouse classical class I sequences, which likewise share distinctive features of their own. The results suggest that segmental sequence exchange plays a major role in determining the evolution of sequence in class I major histocompatibility complex molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A. G., Hood L. E., Howard J. C., Windle M., Winoto A. The class II genes of the rat MHC. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3268–3274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A. G., Larkins A. P., Wright B., Ellis S. T., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. The alloantigenic organization of RT1Aa, a class I major histocompatibility complex molecule of the rat. Eur J Immunol. 1984 May;14(5):405–412. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis P. D., Jackson A. P., Parham P. Molecular cloning of bovine class I MHC cDNA. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):642–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto T., McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Mouse monoclonal antibodies against rat major histocompatibility antigens. Two Ia antigens and expression of Ia and class I antigens in rat thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):237–243. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geliebter J., Zeff R. A., Melvold R. W., Nathenson S. G. Mitotic recombination in germ cells generated two major histocompatibility complex mutant genes shown to be identical by RNA sequence analysis: Kbm9 and Kbm6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3371–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther E., Wurst W., Wonigeit K., Epplen J. T. Analysis of the rat major histocompatibility system by Southern blot hybridization. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1257–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. N., Fabre J. W. Problems in the use of erythrocytes for RT1.A typing studies, probably due to quantitative differences in RT1.A antigen expression in different strains. Transplant Proc. 1981 Jun;13(2):1329–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes N., Ennis P., Wan A. M., Denney D. W., Parham P. Multiple genetic mechanisms have contributed to the generation of the HLA-A2/A28 family of class I MHC molecules. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):936–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Campbell J. H., Elgin S. C. The organization, expression, and evolution of antibody genes and other multigene families. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:305–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Ancient interlocus exon exchange in the history of the HLA-A locus. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):681–686. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaulin C., Perrin A., Abastado J. P., Dumas B., Papamatheakis J., Kourilsky P. Polymorphism in mouse and human class I H-2 and HLA genes is not the result of random independent point mutations. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(5):453–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00418091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol. 1986;6(4):295–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch S., Koch N., Robinson P., Hämmerling G. Comparison of allogeneic and xenogeneic determinants on the H-2Kk molecule. Transplantation. 1983 Aug;36(2):177–180. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198308000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Barra Y., Seidman J. G., Khoury G., Jay G. Functional insertion of an Alu type 2 (B2 SINE) repetitive sequence in murine class I genes. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):974–977. doi: 10.1126/science.6095445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafay F., Ewald S. J., McMillan M., Frelinger J. A., Hood L. Tryptic peptide map analyses of mouse transplantation antigens. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(1-2):21–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01561648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone A. M., Powis S. J., Diamond A. G., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. A trans-acting major histocompatibility complex-linked gene whose alleles determine gain and loss changes in the antigenic structure of a classical class I molecule. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):777–795. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauxion F., Sobczak J., Kress M. Characterization of five distinct cDNA clones encoding for class I RT1 antigens. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(6):397–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00375868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Lawlor D. A., Lomen C. E., Ennis P. D. Diversity and diversification of HLA-A,B,C alleles. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3937–3950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radojcic A., Stranick K. S., Locker J., Kunz H. W., Gill T. J., 3rd Nucleotide sequence of a rat class I cDNA clone. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(2):134–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00395865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Anquez V., Grimal H., Weill J. C. A hyperconversion mechanism generates the chicken light chain preimmune repertoire. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann G. H., Rein R. S., Brown C. S., Ploegh H. L. Gene conversion-like mechanisms may generate polymorphism in human class I genes. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):547–552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. C., Fabre J. W. Identification in rat liver and serum of water-soluble class I MHC molecules possibly homologous to the murine Q10 gene product. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1595–1608. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A computer program to enter DNA gel reading data into a computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):499–503. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan T. Molecular genetics and polymorphism of class I HLA antigens. Br Med Bull. 1987 Jan;43(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



