Abstract
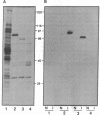
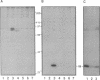
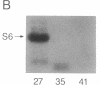
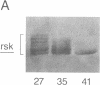
A recombinant baculovirus was constructed for the production of the serine-specific protein kinase, pp90rsk (where rsk is ribosomal S6 kinase), in insect cells. The Xenopus pp90rsk expressed in the infected cells had nearly undetectable enzyme activity in contrast to the same enzyme coproduced with the v-src oncogene product pp60v-src. The transforming gene product pp60v-src very effectively activated pp90rsk, whereas the products of c-src and the myristoylation-minus nontransforming virus NY315 were markedly less effective. Only a fraction of the total pp90rsk population was activated, and it could be partially separated from unactivated protein by ion-exchange chromatography. When compared to the unactivated form, the activated enzyme displayed about a 4000-fold increase in the capacity to phosphorylate the ribosomal protein S6. The enhanced enzymatic activity appeared to be due to phosphorylation of pp90rsk.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcorta D. A., Crews C. M., Sweet L. J., Bankston L., Jones S. W., Erikson R. L. Sequence and expression of chicken and mouse rsk: homologs of Xenopus laevis ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Siegmann M., Thomas G. S6 kinase in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells is activated by phosphorylation in response to serum treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Marshak D. R. Serum-stimulated cell growth causes oscillations in casein kinase II activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7345–7348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. In vivo phosphorylation and activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13711–13717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Stefanovic D., Blenis J., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Antibodies to Xenopus egg S6 kinase II recognize S6 kinase from progesterone- and insulin-stimulated Xenopus oocytes and from proliferating chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3147–3155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Collett M. S., Brugge J. S. Molecular events in cells transformed by Rous Sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):319–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Matsukawa T., Nurse P., Maller J. Dephosphorylation and activation of Xenopus p34cdc2 protein kinase during the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):626–629. doi: 10.1038/339626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmer T. M., Parsons J. T., Erikson R. L. Construction of plasmids for expression of Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, p60src, in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2152–2156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A tail of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Johnson P. J., Shalloway D. Regulation by the autophosphorylation site in overexpressed pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4541–4546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N., Kuenzel E. A., Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Lüscher B., Sommercorn J. Casein kinase II as a potentially important enzyme concerned with signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow V. A., Summers M. D. High level expression of nonfused foreign genes with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Williams N. G., Cheng S. H., Roberts T. M. Regulation of pp60c-src and its interaction with polyomavirus middle T antigen in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.61-68.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Garcia de Herreros A., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a bovine liver S6 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):891–899. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G. The structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:719–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]