Abstract
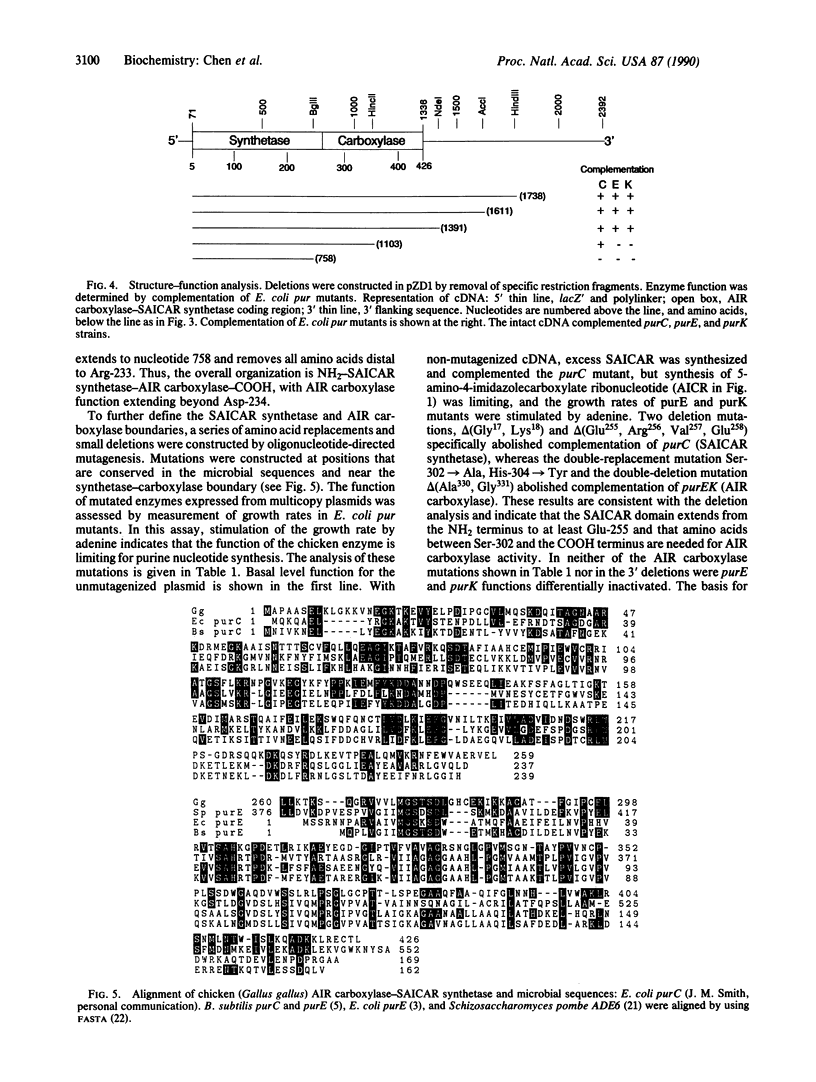
We have used functional complementation of Escherichia coli pur mutants to clone avian cDNA encoding 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR) carboxylase-5-aminoimidazole-4-N-succinocarboxamide ribonucleotide (SAICAR) synthetase, the bifunctional enzyme catalyzing steps 6 and 7 in the pathway for de novo purine nucleotide synthesis. Mutational analyses have been used to establish the structure-function relationship: NH2-SAICAR synthetase-AIR carboxylase-COOH. The amino acid sequence of the SAICAR synthetase domain is homologous to that of bacterial purC-encoded enzymes, and the sequence of the following AIR carboxylase domain is homologous to that of bacterial purE-encoded enzymes. In E. coli, AIR carboxylase is the product of genes purEK with the purK subunit postulated to have a role in CO2 binding. The avian enzyme lacks sequences corresponding to purK yet functions in E. coli. Functional complementation of E. coli pur mutants can be used to clone additional avian cDNAs for de novo purine nucleotide synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss G. R., Seegmiller J. E. Genetic defects in human purine and pyrimidine metabolism. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:297–328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart F. R., Huberman E. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human and Chinese hamster inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15769–15772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbole D. J., Zalkin H. Cloning and characterization of a 12-gene cluster from Bacillus subtilis encoding nine enzymes for de novo purine nucleotide synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8274–8287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbole D. J., Zalkin H. Interaction of a putative repressor protein with an extended control region of the Bacillus subtilis pur operon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3553–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Multifunctional polypeptides for purine de novo synthesis. Bioessays. 1987 Jan;6(1):8–13. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patey C. A., Shaw G. Purification and properties of an enzyme duet, phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase and phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthetase, involved in the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides de novo. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):543–545. doi: 10.1042/bj1350543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfes R. J., Zalkin H. Escherichia coli gene purR encoding a repressor protein for purine nucleotide synthesis. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and interaction with the purF operator. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19653–19661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schendel F. J., Mueller E., Stubbe J., Shiau A., Smith J. M. Formylglycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase from Escherichia coli: cloning, sequencing, overproduction, isolation, and characterization. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2459–2471. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Brake A. J., Kiefer M. C., Young D., Barr P. J. Cloning of three human multifunctional de novo purine biosynthetic genes by functional complementation of yeast mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Daum H. A., 3rd Nucleotide sequence of the purM gene encoding 5'-phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole synthetase of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10632–10636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szankasi P., Heyer W. D., Schuchert P., Kohli J. DNA sequence analysis of the ade6 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Wild-type and mutant alleles including the recombination host spot allele ade6-M26. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedeman A. A., Keyhani J., Kamholz J., Daum H. A., 3rd, Gots J. S., Smith J. M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the purEK operon encoding 5'-phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole carboxylase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):205–212. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.205-212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Zalkin H., van Cleemput M., Yanofsky C., Smith J. M. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli purF and deduced amino acid sequence of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3525–3531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L., Andrews P. C., Hermodson M. A., Dixon J. E., Zalkin H. Cloning and structural characterization of porcine heart aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2814–2821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]