Abstract
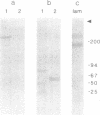
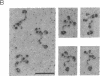
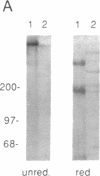
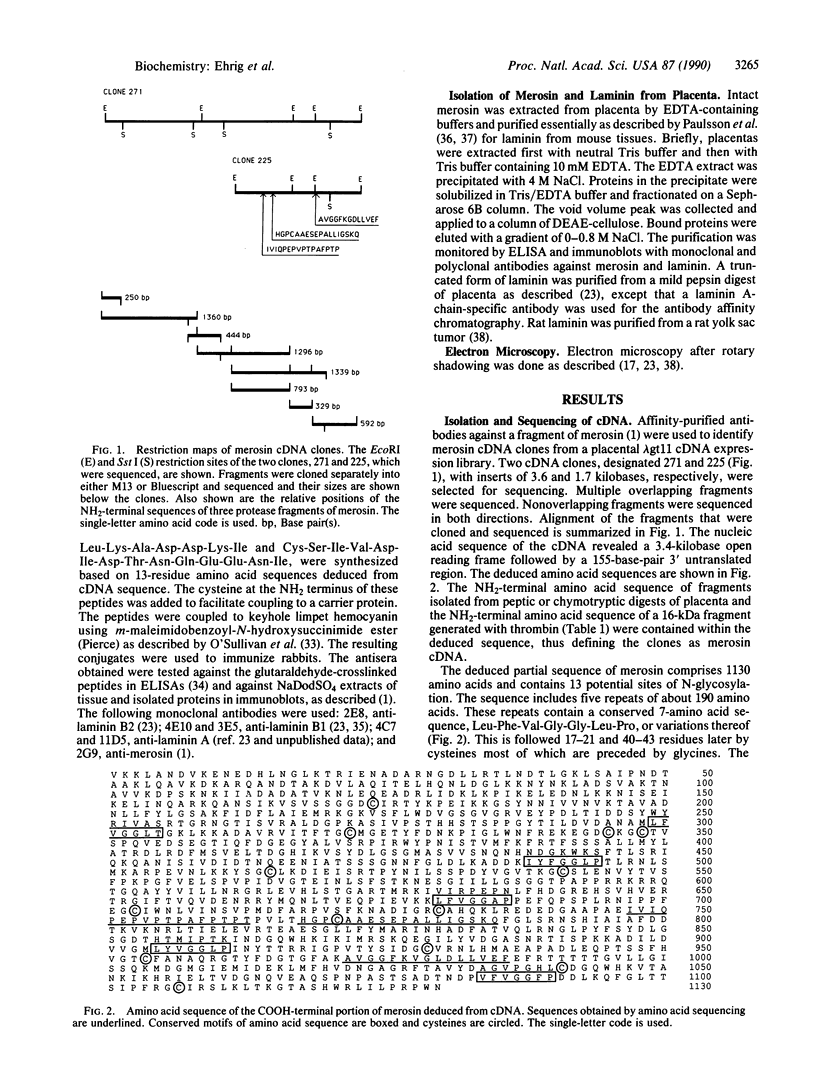
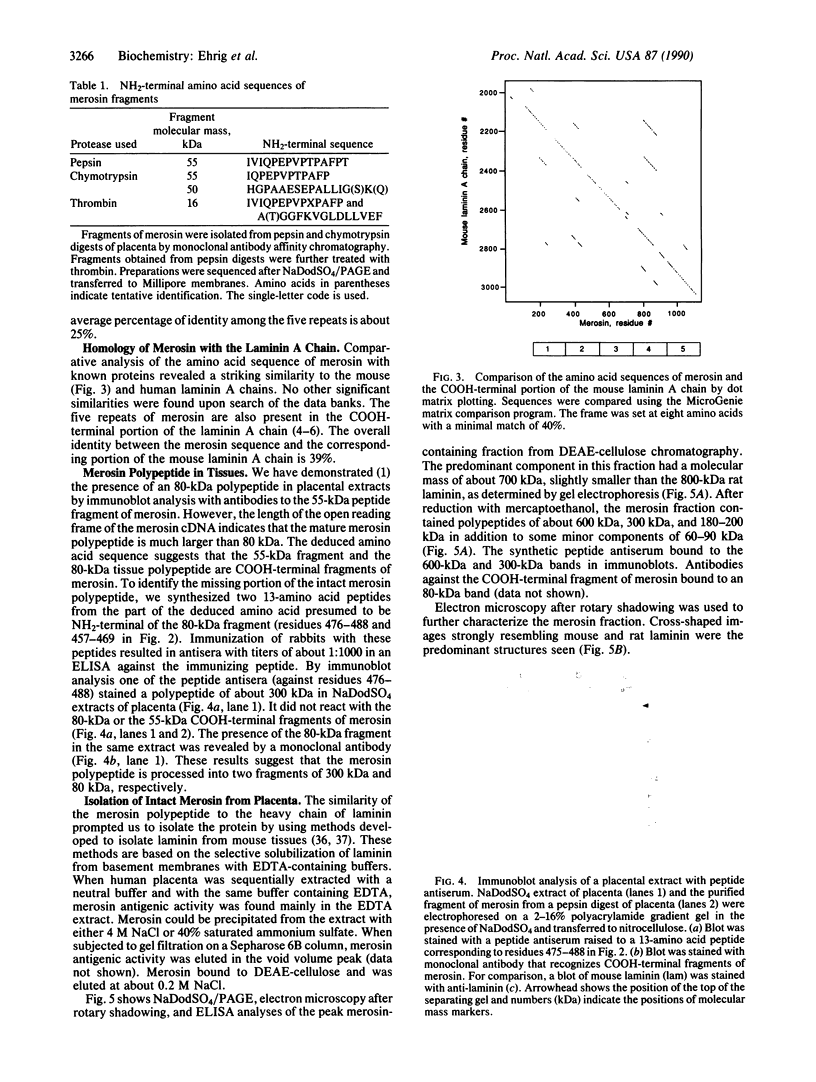
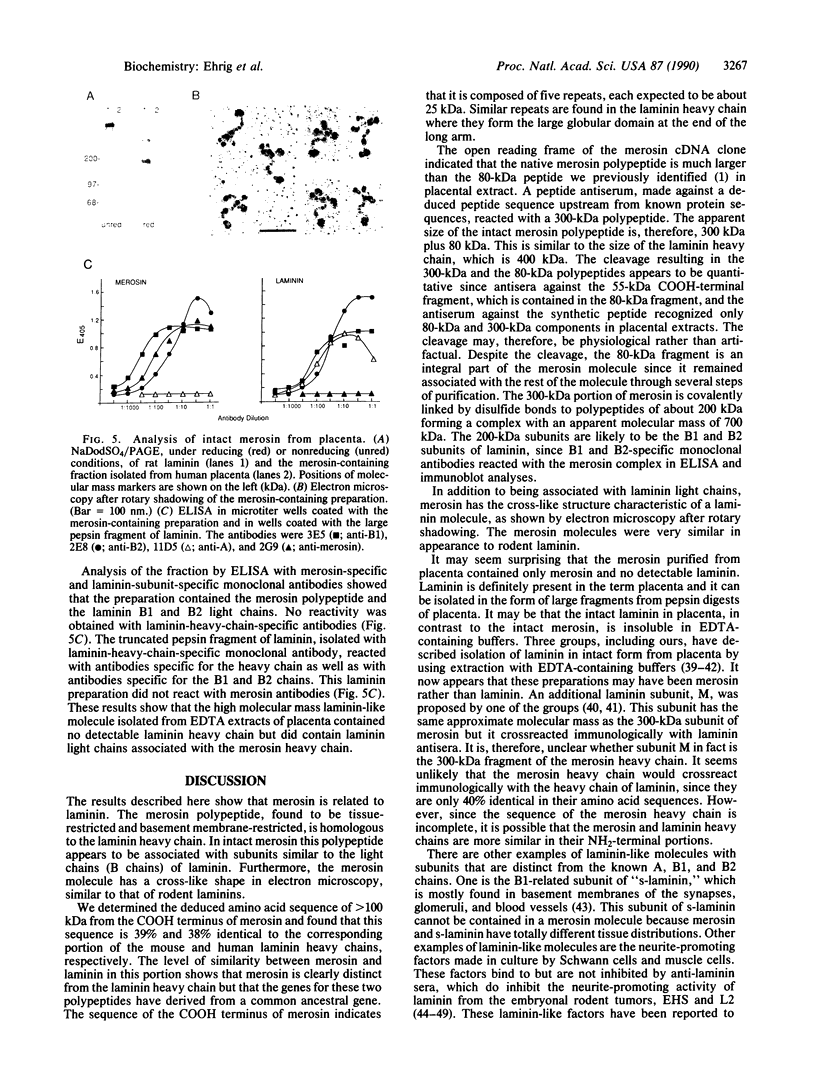
Merosin is a basement membrane-associated protein found in placenta, striated muscle, and peripheral nerve. A 3.6-kilobase merosin cDNA clone was isolated from a placental cDNA expression library. The clone contained a 3.4-kilobase open reading frame, the 3' portion of which includes protein sequences of proteolytic fragments of merosin. The deduced amino acid sequence of the merosin polypeptide was similar to that of the COOH-terminal region of the 400-kDa A chain of laminin. This part of laminin forms the large globule at the end of the long arm of the laminin cross and is thought to contain the neurite-promoting site and the major cell binding site(s) in laminin. The sequence identity between merosin and the laminin A chain in this region is nearly 40%. An antiserum against a synthetic peptide from the middle of the merosin cDNA sequence identified a 300-kDa polypeptide in placental extracts, indicating that the merosin polypeptide is similar in size to the laminin A chain. Intact merosin was isolated from placental extracts and shown to be covalently associated with the laminin B chains and to have a cross-like structure similar to that of laminin. The similarities between merosin and laminin show that both proteins are members of the same family of basement membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argraves W. S., Suzuki S., Arai H., Thompson K., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Amino acid sequence of the human fibronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aumailley M., Nurcombe V., Edgar D., Paulsson M., Timpl R. The cellular interactions of laminin fragments. Cell adhesion correlates with two fragment-specific high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11532–11538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. P., Green N. M., Kurkinen M., Hogan B. L. Sequencing of laminin B chain cDNAs reveals C-terminal regions of coiled-coil alpha-helix. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2355–2362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Kleinman H. K., Ohno S., Marangos P., Schwartz J. P., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Nerve growth factor, laminin, and fibronectin promote neurite growth in human fetal sensory ganglia cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):179–193. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi H. C., Hui C. F. Primary structure of the Drosophila laminin B2 chain and comparison with human, mouse, and Drosophila laminin B1 and B2 chains. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1543–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. E., Manthorpe M., Engvall E., Varon S. Isolation and characterization of rat schwannoma neurite-promoting factor: evidence that the factor contains laminin. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2662–2671. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02662.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutzmann R., Huber J., Schmetz K. A., Oberbäumer I., Hartl L. Structural study of long arm fragments of laminin. Evidence for repetitive C-terminal sequences in the A-chain, not present in the B-chains. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):35–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner L., Dickerson K., Manthorpe M., Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. The neurite-promoting domain of human laminin promotes attachment and induces characteristic morphology in non-neuronal cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jul;177(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit S. N. Isolation, purification and characterization of intact and pepsin-derived fragments of laminin from human placenta. Connect Tissue Res. 1985;14(1):31–40. doi: 10.3109/03008208509089841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkin M. E., Bartos B. B., Liu S. H., Phillips S. L., Chung A. E. Primary structure of the mouse laminin B2 chain and comparison with laminin B1. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5198–5204. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. Structural requirements for the stimulation of neurite outgrowth by two variants of laminin and their inhibition by antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1299–1306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Davis G. E., Dickerson K., Ruoslahti E., Varon S., Manthorpe M. Mapping of domains in human laminin using monoclonal antibodies: localization of the neurite-promoting site. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2457–2465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Krusius T., Wewer U., Ruoslahti E. Laminin from rat yolk sac tumor: isolation, partial characterization, and comparison with mouse laminin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 15;222(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90562-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Dickerson K., Argraves W. S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Subunit structure of a laminin-binding integrin and localization of its binding site on laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19034–19038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Dillner L., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. The human laminin receptor is a member of the integrin family of cell adhesion receptors. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1228–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2970671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Deutzmann R., von der Mark K. Two distinct cell-binding domains in laminin can independently promote nonneuronal cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Miki N. Purification and characterization of a neurite outgrowth factor from chicken gizzard smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14269–14278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Greggs R., Decker C., Buck C. The cell substrate attachment (CSAT) antigen has properties of a receptor for laminin and fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2134–2144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. D., Shah V., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. A laminin-like adhesive protein concentrated in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):229–234. doi: 10.1038/338229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignatius M. J., Reichardt L. F. Identification of a neuronal laminin receptor: an Mr 200K/120K integrin heterodimer that binds laminin in a divalent cation-dependent manner. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., McDonald K. A., Vu M. P. Human melanoma cells express a novel integrin receptor for laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15642–15649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander A. D., Fujii D. K., Reichardt L. F. Laminin is associated with the "neurite outgrowth-promoting factors" found in conditioned media. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2183–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Languino L. R., Gehlsen K. R., Wayner E., Carter W. G., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Endothelial cells use alpha 2 beta 1 integrin as a laminin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2455–2462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivo I., Engvall E., Laurila P., Miettinen M. Distribution of merosin, a laminin-related tissue-specific basement membrane protein, in human Schwann cell neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1989 Oct;61(4):426–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivo I., Engvall E. Merosin, a protein specific for basement membranes of Schwann cells, striated muscle, and trophoblast, is expressed late in nerve and muscle development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1544–1548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivo I., Laurila P., Wahlström T., Engvall E. Expression of merosin, a tissue-specific basement membrane protein, in the intermediate trophoblast cells of choriocarcinoma and placenta. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):783–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthorpe M., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Longo F. M., Davis G. E., Varon S. Laminin promotes neuritic regeneration from cultured peripheral and central neurons. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1882–1890. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R. Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Palm S. L., Furcht L. T. Migration by haptotaxis of a Schwann cell tumor line to the basement membrane glycoprotein laminin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):772–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell D. J., Goodman C. S. Drosophila substrate adhesion molecule: sequence of laminin B1 chain reveals domains of homology with mouse. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):463–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M. J., Gnemmi E., Morris D., Chieregatti G., Simmonds A. D., Simmons M., Bridges J. W., Marks V. Comparison of two methods of preparing enzyme-antibody conjugates: application of these conjugates for enzyme immunoassay. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Martinez-Hernandez A., Ohno N., Kefalides N. A. Isolation of laminin from human placental basement membranes: amnion, chorion and chorionic microvessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):1091–1098. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91730-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Martinez-Hernandez A., Ohno N., Kefalides N. A. Laminin M is found in placental basement membranes, but not in basement membranes of neoplastic origin. Connect Tissue Res. 1986;15(3):199–207. doi: 10.3109/03008208609167143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D., Nagayoshi T., Fazio M., Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Sanborn D., Sasaki T., Kuivaniemi H., Chu M. L., Deutzmann R. Human laminin: cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding A, B1 and B2 chains, and expression of the corresponding genes in human skin and cultured cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):772–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., End P., Aumailley M., Timpl R., Engel J. Domains of laminin with growth-factor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90987-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Aumailley M., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Beck K., Engel J. Laminin-nidogen complex. Extraction with chelating agents and structural characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Saladin K. Mouse heart laminin. Purification of the native protein and structural comparison with Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm tumor laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18726–18732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen T., Eddy R., Fukushima Y., Byers M., Shows T., Pihlajaniemi T., Saraste M., Tryggvason K. Human laminin B1 chain. A multidomain protein with gene (LAMB1) locus in the q22 region of chromosome 7. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10454–10462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen T., Kallunki T., Tryggvason K. Human laminin B2 chain. Comparison of the complete amino acid sequence with the B1 chain reveals variability in sequence homology between different structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6751–6758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Terranova V., Rohrbach D., Crowley C., Rizzino H. The effects of laminin on the growth and differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells in defined media. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(2):243–253. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. L., Letourneau P. C., Palm S. L., McCarthy J., Furcht L. T. Neurite extension by peripheral and central nervous system neurons in response to substratum-bound fibronectin and laminin. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):212–220. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandrock A. W., Jr, Matthew W. D. Identification of a peripheral nerve neurite growth-promoting activity by development and use of an in vitro bioassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kato S., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Sequence of the cDNA encoding the laminin B1 chain reveals a multidomain protein containing cysteine-rich repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Yamada Y. The laminin B2 chain has a multidomain structure homologous to the B1 chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17111–17117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Modderman P. W., Hogervorst F. Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):487–489. doi: 10.1038/336487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. G., Dalton B. A. Neurite-promoting activity from fetal skeletal muscle: immunological comparison with laminin. J Neurosci Res. 1987;17(2):119–127. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490170205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro K., Sephel G. C., Weeks B., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y. A synthetic peptide containing the IKVAV sequence from the A chain of laminin mediates cell attachment, migration, and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16174–16182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A., Russo R. G., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment and metastasis of murine tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2265–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U., Albrechtsen R., Manthorpe M., Varon S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Human laminin isolated in a nearly intact, biologically active form from placenta by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12654–12660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]