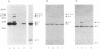Abstract
A radioactive and photoactivatable derivative of NAD+, 2-azido-[adenylate-32P]NAD+, has been synthesized and used with pertussis toxin to ADP-ribosylate Cys347 of the alpha subunit (alpha T) of GT, the retinal guanine nucleotide-binding protein. ADP-ribosylation of alpha T followed by light activation of the azide moiety of 2-azido-[adenylate-32P]ADP-ribose produced four crosslinked species involving the alpha and gamma subunits of the GT heterotrimer: an alpha trimer (alpha-alpha-alpha), and alpha-alpha-gamma crosslink, an alpha dimer (alpha-alpha), and an alpha-gamma crosslink. The alpha trimer, alpha-alpha-gamma complex, alpha dimer, and alpha-gamma complexes were immunoreactive with alpha T antibodies. The alpha-alpha-gamma and the alpha-gamma complexes were immunoreactive with antisera recognizing gamma subunits. No evidence was found for crosslinking of alpha T to beta T subunits. Hydrolysis of the thioglycosidic bond between Cys347 and 2-azido-[adenylate-32P]ADP-ribose using mercuric acetate resulted in the transfer of radiolabel from Cys347 of alpha T in the crosslinked oligomers to alpha monomers, indicative of intermolecular photocrosslinking, and to gamma monomers, indicative of either intermolecular crosslinked complexes (between heterotrimers) or intramolecular crosslinked complexes (within the heterotrimer). These results demonstrate that GT exists as an oligomer and that ADP-ribosylated Cys347, which is four residues from the alpha T-carboxyl terminus, is oriented toward and in close proximity to the gamma subunit.
Full text
PDF
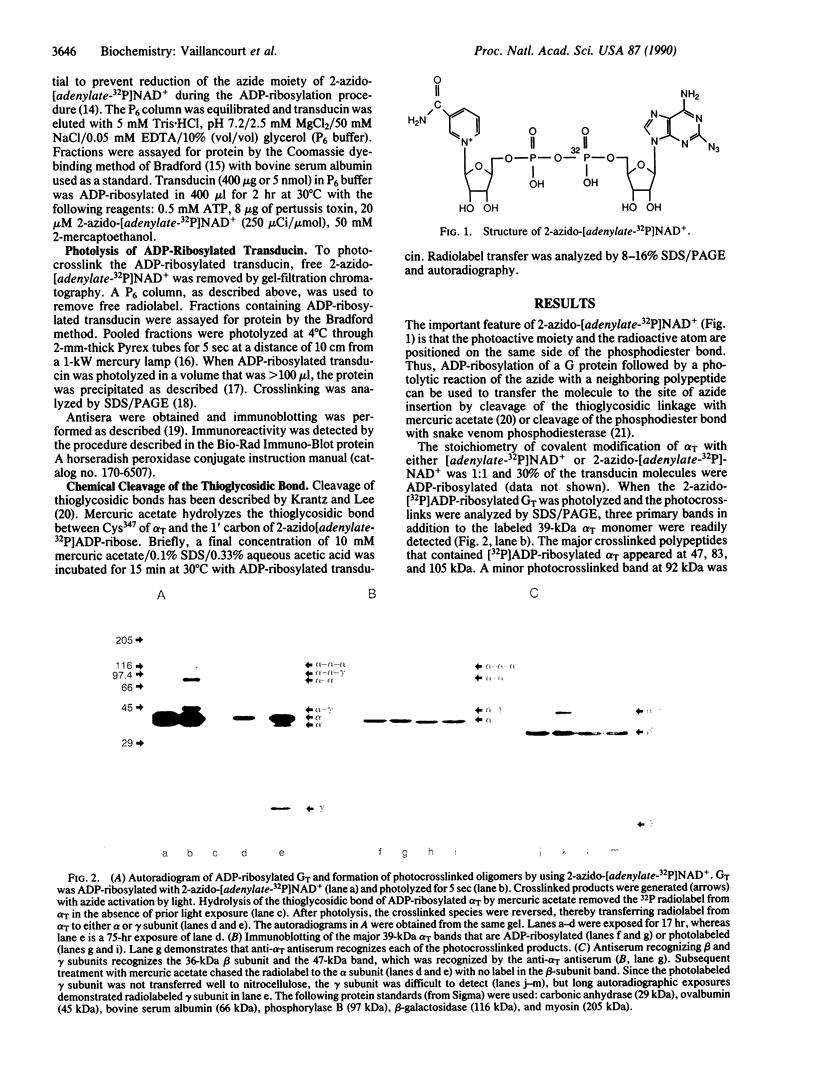

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Pedersen S. E., Scott C. W., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of catecholamine-stimulated binding of guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) to the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5460–5467. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Morita E. A., Swanson R. J., Applebury M. L. Characterization of bovine rod outer segment G-protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6452–6460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Dalbon P., Vignais P. V. Photoaffinity labeling of mitochondrial adenosinetriphosphatase by 2-azidoadenosine 5'-[alpha-32P]diphosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7372–7379. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Hutchinson D. W., Armstrong V. W. The reaction between thiols and 8-azidoadenosine derivatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2331–2339. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Kroll S., Rajaram R., Unson C., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. M. An antibody directed against the carboxyl-terminal decapeptide of the alpha subunit of the retinal GTP-binding protein, transducin. Effects on transducin function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9345–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhanasekaran N., Wessling-Resnick M., Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L., Ruoho A. E. Mapping of the carboxyl terminus within the tertiary structure of transducin's alpha subunit using the heterobifunctional cross-linking reagent, 125I-N-(3-iodo-4-azidophenylpropionamido-S-(2-thiopyridyl) cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17942–17950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOARD D. E., OTT D. G. CONVERSION OF MONO- AND OLIGODEOXYRIBONUCLEOTIDES TO 5-TRIPHOSPHATES. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Apr 20;87:1785–1788. doi: 10.1021/ja01086a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani V. N., Ho Y. K. Fluorescent labeling of signal-transducing G-proteins. Pertussis toxin-catalyzed etheno-ADP ribosylation of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19804–19808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani V. N., Tobias D. T., Henderson J. T., Ho Y. K. Chemical cross-linking of bovine retinal transducin and cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6916–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Transducin inhibition of light-dependent rhodopsin phosphorylation: evidence for beta gamma subunit interaction with rhodopsin. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;34(4):452–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz M. J., Lee Y. C. Quantitative hydrolysis of thioglycosides. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):318–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok-Keung Fung B., Stryer L. Photolyzed rhodopsin catalyzes the exchange of GTP for bound GDP in retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. R., Fraser B. A., Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. ADP-ribosylation of transducin by islet-activation protein. Identification of asparagine as the site of ADP-ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):749–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon S. E., Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. Participation of the amino-terminal region of T alpha in subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15746–15751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E. Iodoazidobenzylpindolol, a photoaffinity probe for the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Kempner E. S., Rodbell M. Activation of adenylate cyclase in hepatic membranes involves interactions of the catalytic unit with multimeric complexes of regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5168–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F. Cytochalasin B. A natural photoaffinity ligand for labeling the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7290–7293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Yamanaka G., Steinberg F., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Stryer L., Bourne H. R. ADP-ribosylation of transducin by pertussis toxin blocks the light-stimulated hydrolysis of GTP and cGMP in retinal photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessling-Resnick M., Johnson G. L. Allosteric behavior in transducin activation mediated by rhodopsin. Initial rate analysis of guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3697–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessling-Resnick M., Johnson G. L. Evidence for oligomeric forms of transducins alpha subunit: formation of intermolecular alpha-alpha disulfide linkages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):651–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessling-Resnick M., Johnson G. L. Transducin interactions with rhodopsin. Evidence for positive cooperative behavior. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12444–12447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Moss J., Vaughan M., Liu T., Liu T. Y. Pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of transducin. Cysteine 347 is the ADP-ribose acceptor site. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14428–14430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M., Kato T. Studies of phosphorylation. I. Phosphorylation of 2',3'-o-isopropylidene nucleoside by phosphoryl chloride. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1967 Dec;40(12):2849–2853. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.40.2849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]