Abstract
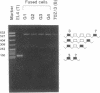
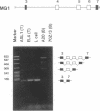
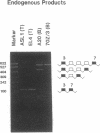
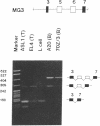
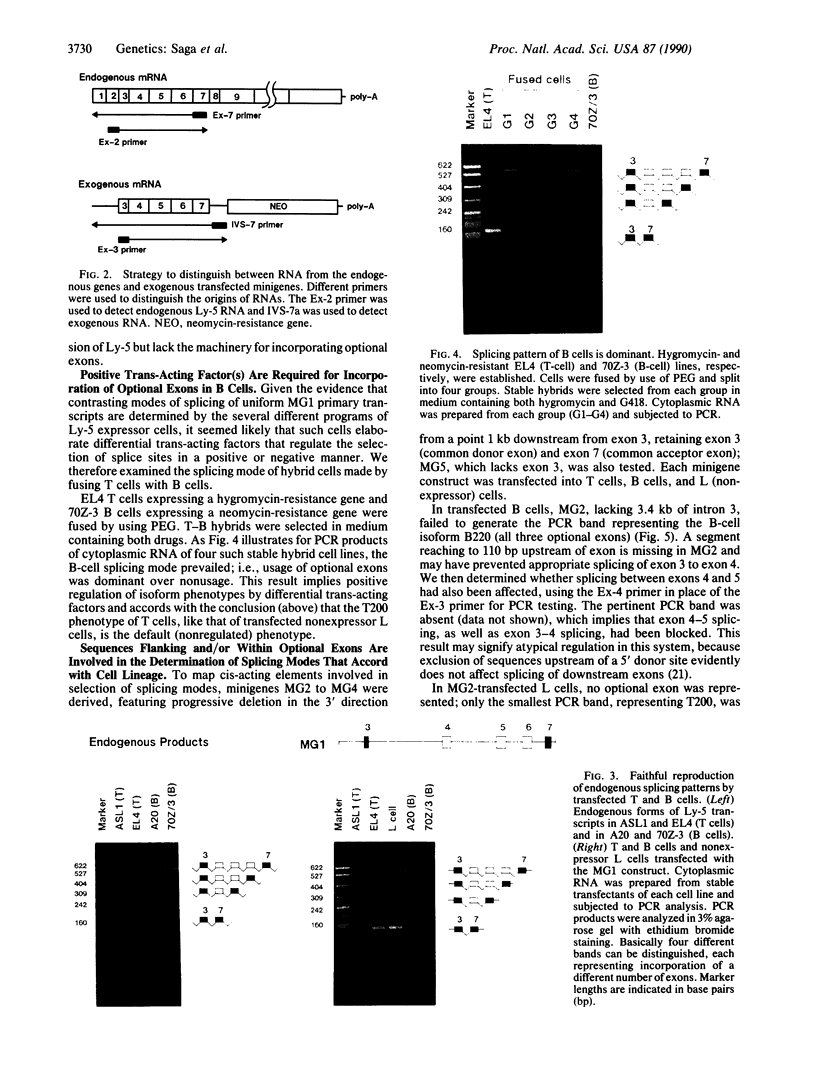
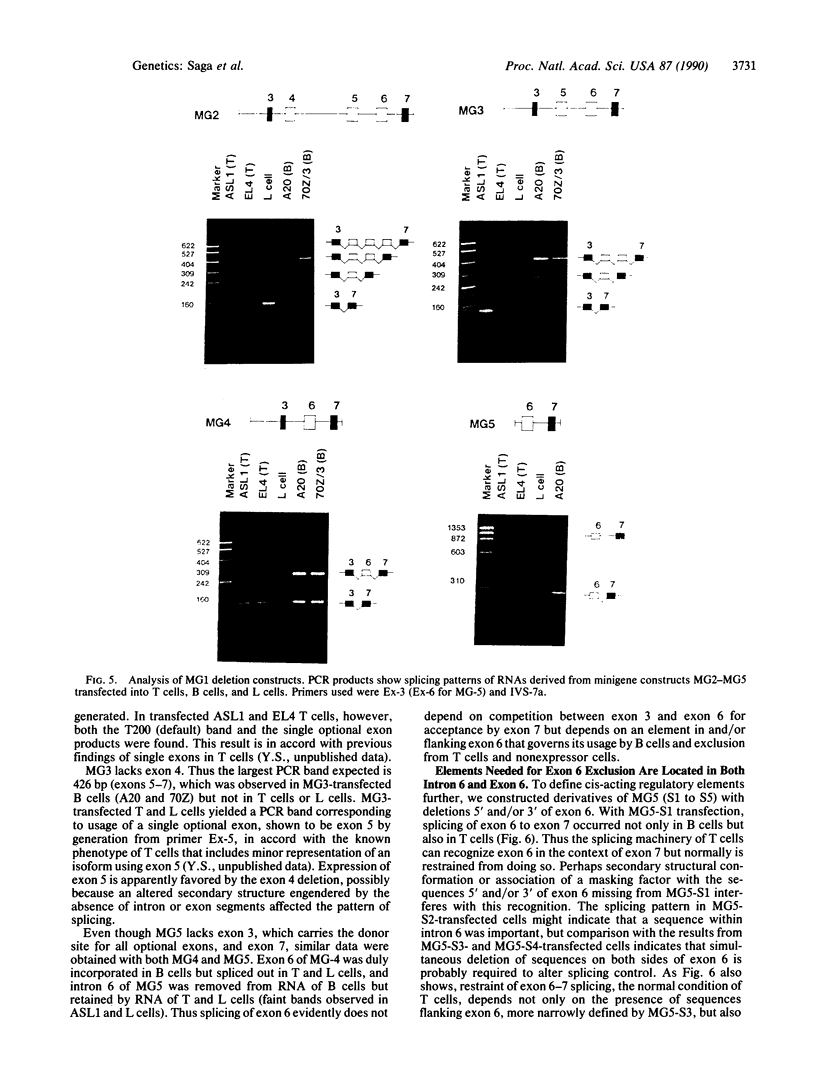
Alternative splicing generates various Ly-5 glycoprotein isoforms of the cell surface that typify different cell lineages and stages of hematopoietic differentiation in the mouse; exons 4-6 are incorporated to generate a B-cell isoform (B220) and excluded from a T-cell isoform (T200), the other coding exons (3 and 7-33) being shared. As a first step to understanding the mechanisms regulating Ly-5 alternative splicing, and thus determining Ly-5 isoforms, a minigene representing exons 3-7 was transfected into Ly-5-expressor T cells and B cells and into nonexpressor L cells for comparison of splicing patterns. We conclude that all the information required for faithful splice-site selection according to cell type is contained within the resulting pre-mRNA. The splicing pattern manifested by nonexpressor L cells may represent a default and nonregulated type. We postulate trans-acting factor(s) to account for the selection of appropriate exons, and we provide support for this interpretation from analysis of fused hybrid T-B cells, which exhibited B-cell specific Ly-5 transcripts. Splicing patterns were well conserved despite substantial disruption of constructs. However, extensive deletion analyses suggested that cis sequences flanking and within exon 6 affect the exclusion of that exon in T cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay A. N., Jackson D. I., Willis A. C., Williams A. F. Lymphocyte specific heterogeneity in the rat leucocyte common antigen (T200) is due to differences in polypeptide sequences near the NH2-terminus. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1259–1264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. L., Zaroukian M. H., Esselman W. J. T200 alternate exon use in murine lymphoid cells determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. R., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. Complete exon-intron organization of the human leukocyte common antigen (CD45) gene. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2781–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson R. K., La Follette L., Rottman F. M. Alternative processing of bovine growth hormone mRNA is influenced by downstream exon sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1604–1610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon H. J., Sebastio G., Baralle F. E. A role for exon sequences in alternative splicing of the human fibronectin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7725–7733. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph S. J., Thomas M. L., Morton C. C., Trowbridge I. S. Structural variants of human T200 glycoprotein (leukocyte-common antigen). EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1251–1257. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Specific and stable intron-factor interactions are established early during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saga Y., Tung J. S., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A. Alternative use of 5' exons in the specification of Ly-5 isoforms distinguishing hematopoietic cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saga Y., Tung J. S., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A. Sequences of Ly-5 cDNA: isoform-related diversity of Ly-5 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6940–6944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saga Y., Tung J. S., Shen F. W., Pancoast T. C., Boyse E. A. Organization of the Ly-5 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4889–4895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Nadal-Ginard B. Mutually exclusive splicing of alpha-tropomyosin exons enforced by an unusual lariat branch point location: implications for constitutive splicing. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Saito H. Regulation of tissue-specific alternative splicing: exon-specific cis-elements govern the splicing of leukocyte common antigen pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):787–796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L., Reynolds P. J., Chain A., Ben-Neriah Y., Trowbridge I. S. B-cell variant of mouse T200 (Ly-5): evidence for alternative mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5360–5363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Scheid M. P., Pierotti M. A., Hämmerling U., Boyse E. A. Structural features and selective expression of three Ly-5+ cell-surface molecules. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(1-2):101–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00344303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]