Abstract
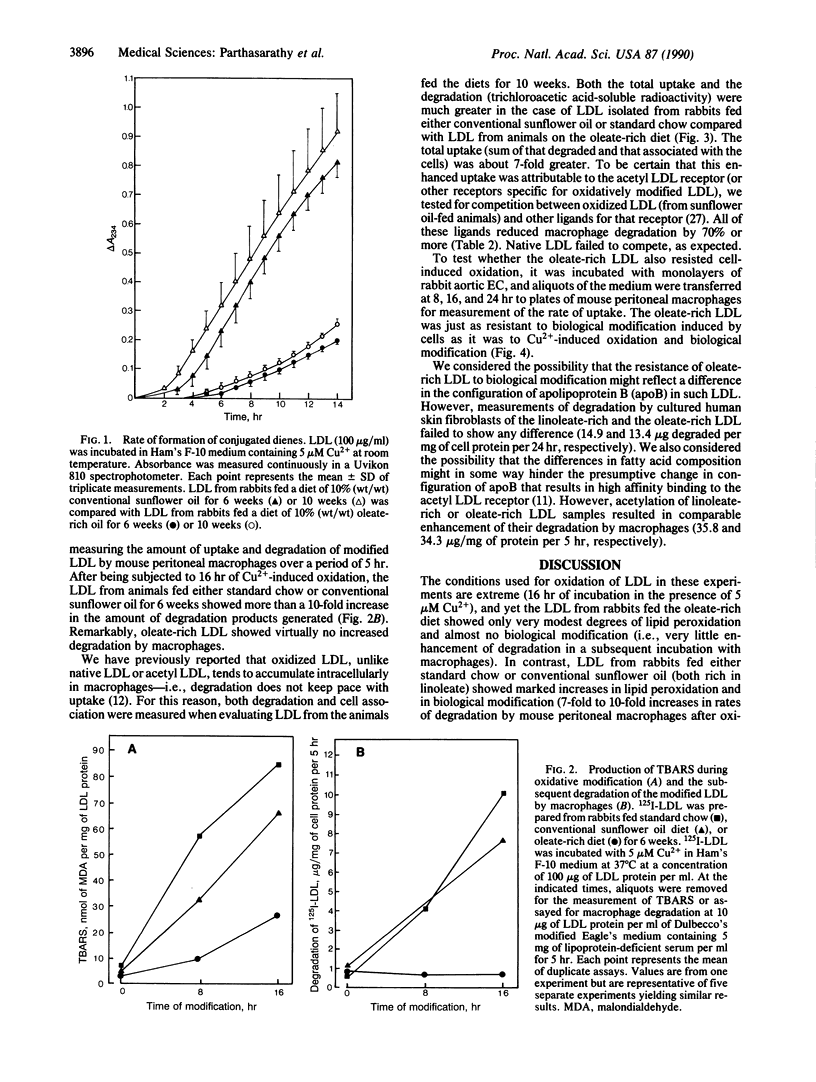
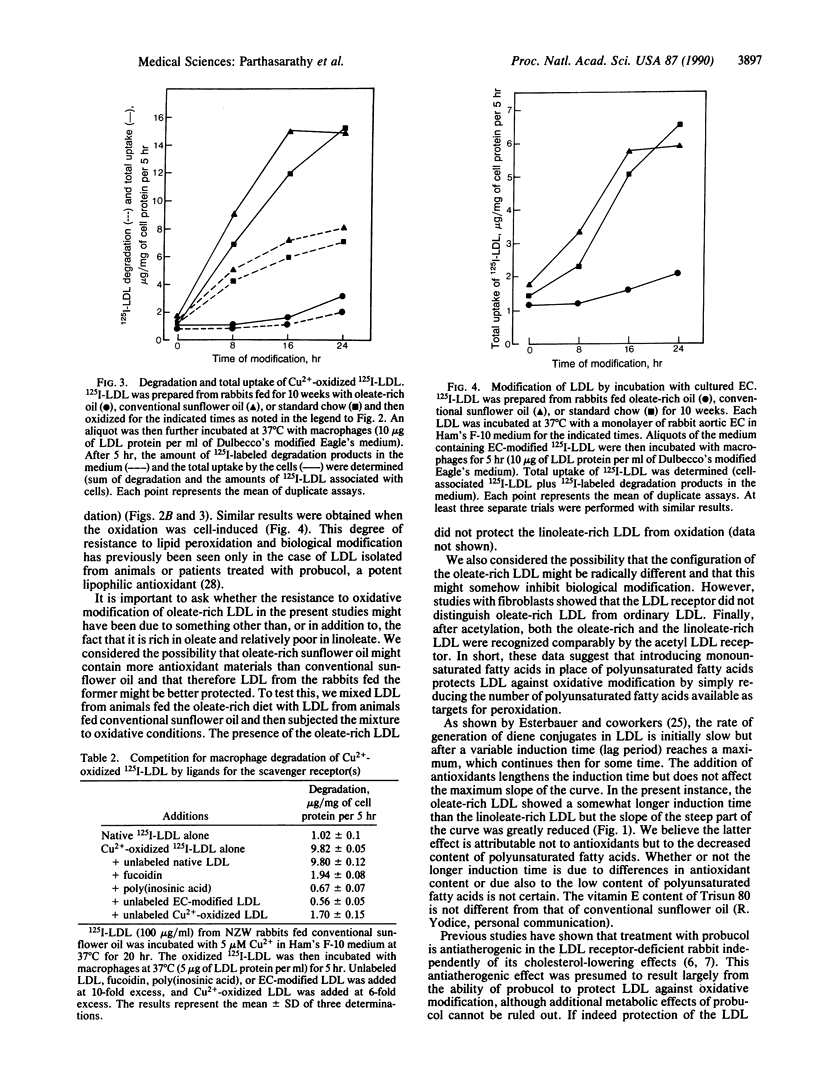
Oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein (LDL) enhances its potential atherogenicity in several ways, notably by enhancing its uptake into macrophages. In vivo studies in the rabbit show that inhibition of LDL oxidation slows the progression of atherosclerotic lesions. In the present studies, rabbits were fed either a newly developed variant sunflower oil (Trisun 80), containing more than 80% oleic acid and only 8% linoleic acid, or conventional sunflower oil, containing only 20% oleic acid and 67% linoleic acid. LDL isolated from the plasma of animals fed the variant sunflower oil was highly enriched in oleic acid and very low in linoleic acid. These oleate-rich LDL particles were remarkably resistant to oxidative modification. Even after 16-hr exposure to copper-induced oxidation or 24-hr incubation with cultured endothelial cells, macrophage uptake of the LDL was only marginally enhanced. The results suggest that diets sufficiently enriched in oleic acid, in addition to their LDL-lowering effect, may slow the progression of atherosclerosis by generating LDL that is highly resistant to oxidative modification.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Kita T., Yokode M., Narumiya S., Kawai C. Multiple receptors for modified low density lipoproteins in mouse peritoneal macrophages: different uptake mechanisms for acetylated and oxidized low density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1375–1382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson G. W., Brown M. S. Degradation of cationized low density lipoprotein and regulation of cholesterol metabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd H. C., Gown A. M., Wolfbauer G., Chait A. Direct evidence for a protein recognized by a monoclonal antibody against oxidatively modified LDL in atherosclerotic lesions from a Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1989 Nov;135(5):815–825. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Falck J. R., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The scavenger cell pathway for lipoprotein degradation: specificity of the binding site that mediates the uptake of negatively-charged LDL by macrophages. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):67–81. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. E., Schwenke D. C., Steinberg D. Antiatherogenic effect of probucol unrelated to its hypocholesterolemic effect: evidence that antioxidants in vivo can selectively inhibit low density lipoprotein degradation in macrophage-rich fatty streaks and slow the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7725–7729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Jürgens G., Quehenberger O., Koller E. Autoxidation of human low density lipoprotein: loss of polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E and generation of aldehydes. J Lipid Res. 1987 May;28(5):495–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Striegl G., Puhl H., Rotheneder M. Continuous monitoring of in vitro oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;6(1):67–75. doi: 10.3109/10715768909073429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M. Comparison of monounsaturated fatty acids and carbohydrates for lowering plasma cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 20;314(12):745–748. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603203141204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Fong D., Cheng L. Malondialdehyde-altered protein occurs in atheroma of Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.2455346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Lang J., Esterbauer H. Modification of human low-density lipoprotein by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A., WHYTE M., GOODMAN D. S. FATTY ACID ESTERIFICATION AND CHYLOMICRON FORMATION DURING FAT ABSORPTION. 1. TRIGLYCERIDES AND CHOLESTEROL ESTERS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jul;4:312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys A., Menotti A., Karvonen M. J., Aravanis C., Blackburn H., Buzina R., Djordjevic B. S., Dontas A. S., Fidanza F., Keys M. H. The diet and 15-year death rate in the seven countries study. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Dec;124(6):903–915. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Nagano Y., Yokode M., Ishii K., Kume N., Ooshima A., Yoshida H., Kawai C. Probucol prevents the progression of atherosclerosis in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit, an animal model for familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5928–5931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson F. H., Grundy S. M. Comparison of effects of dietary saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in man. J Lipid Res. 1985 Feb;26(2):194–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Ylä-Herttuala S., Gurtner G. C., Socher S. S., Butler S. W., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Low density lipoprotein undergoes oxidative modification in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1372–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Fong L. G., Otero D., Steinberg D. Recognition of solubilized apoproteins from delipidated, oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) by the acetyl-LDL receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):537–540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Young S. G., Witztum J. L., Pittman R. C., Steinberg D. Probucol inhibits oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):641–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI112349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh J., Fairclough G. F., Jr, Haschemeyer R. H. Oxygen-mediated heterogeneity of apo-low-density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3173–3177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow C. P., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. A macrophage receptor that recognizes oxidized low density lipoprotein but not acetylated low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2599–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P. Oxidation of human low density lipoprotein results in derivatization of lysine residues of apolipoprotein B by lipid peroxide decomposition products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3603–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Butler S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Evidence for the presence of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbit and man. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI114271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


