Abstract
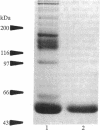
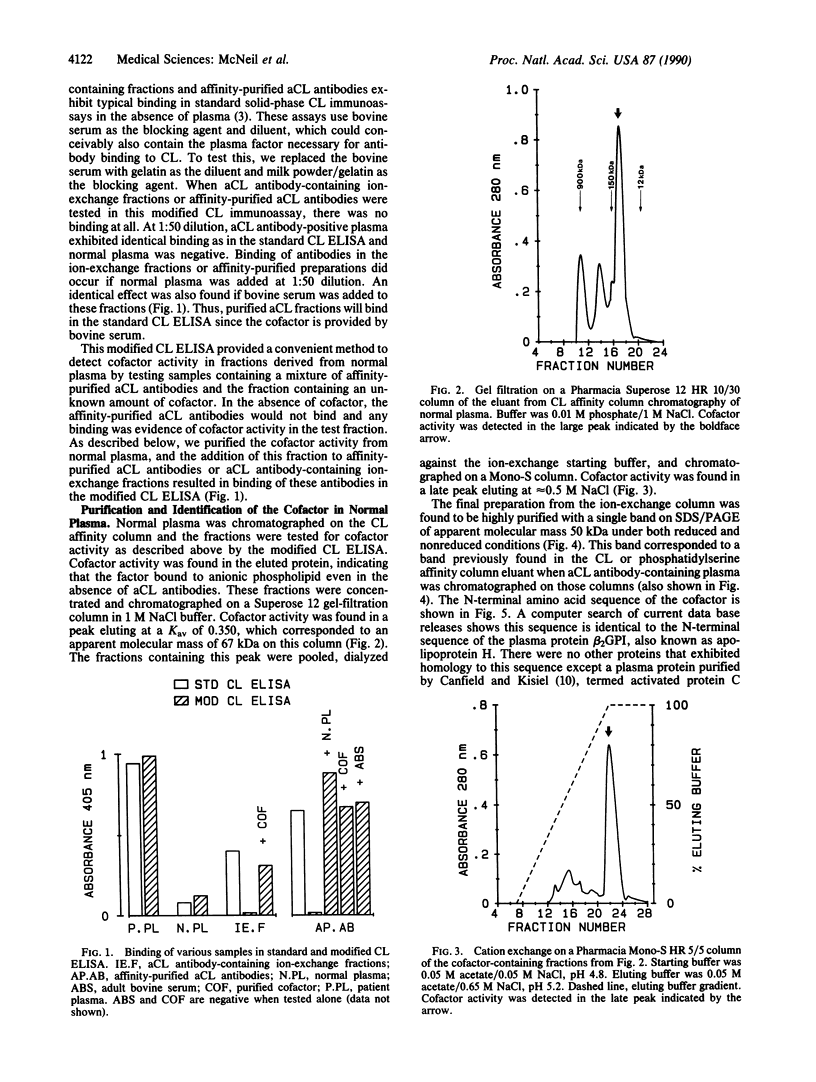
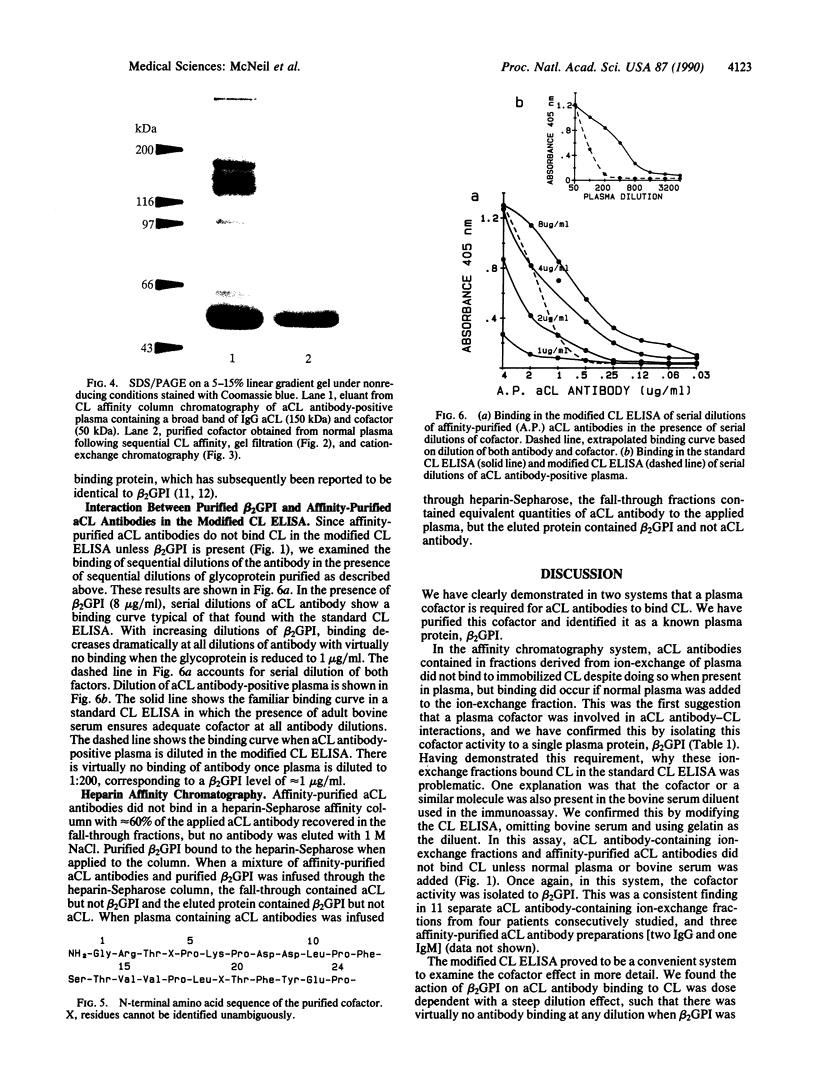
Anti-phospholipid (aPL) antibodies that exhibit binding in cardiolipin (CL) ELISA can be purified to greater than 95% purity by sequential phospholipid affinity and ion-exchange chromatography. However, these highly purified aPL antibodies do not bind to the CL antigen when assayed by a modified CL ELISA in which the blocking agent does not contain bovine serum, nor do they bind to phospholipid affinity columns. Binding to the phospholipid antigen will only occur if normal human plasma, human serum, or bovine serum is present, suggesting that the binding of aPL antibodies to CL requires the presence of a plasma/serum cofactor. Using sequential phospholipid affinity, gel-filtration, and ion-exchange chromatography, we have purified this cofactor to homogeneity and shown that the binding of aPL antibodies to CL requires the presence of this cofactor in a dose-dependent manner. N-terminal region sequence analysis of the molecule has identified the cofactor as beta 2-glycoprotein I (beta 2GPI) (apolipoprotein H), a plasma protein known to bind to anionic phospholipids. These findings indicate that the presence of beta 2GPI is an absolute requirement for antibody-phospholipid interaction, suggesting that bound beta 2GPI forms the antigen to which aPL antibodies are directed. Recent evidence indicates that beta 2GPI exerts multiple inhibitory effects on the coagulation pathway and platelet aggregation. Interference with the function of beta 2GPI by aPL antibodies could explain the thrombotic diathesis seen in association with these antibodies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canfield W. M., Kisiel W. Evidence of normal functional levels of activated protein C inhibitor in combined Factor V/VIII deficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1260–1272. doi: 10.1172/JCI110725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: isotype distribution and phospholipid specificity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Capra J. D. Automated amino acid sequence of small peptides utilizing Polybrene. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):126–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J., Larsen J. K., Loft H., Ezban M., Wallevik K., Faber M. DNA-binding proteins in Yoshida ascites tumor fluid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 15;434(2):490–501. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma beta 2-glycoprotein I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anticardiolipin antibodies and lupus anticoagulants comprise separate antibody subgroups with different phospholipid binding characteristics. Br J Haematol. 1989 Dec;73(4):506–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Binding specificity of lupus anticoagulants and anticardiolipin antibodies. Thromb Res. 1988 Dec 15;52(6):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Krilis S. A., Chesterman C. N. Purification of antiphospholipid antibodies using a new affinity method. Thromb Res. 1988 Dec 15;52(6):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya Y., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Activation of human post heparin lipoprotein lipase by apolipoprotein H (beta 2-glycoprotein I). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91595-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Bevers E. M., Bomans P. H., Till U., Wurm H., Kostner G. M., Zwaal R. F. Prothrombinase activity of human platelets is inhibited by beta 2-glycoprotein-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 29;884(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Wurm H., Kostner G. M. Beta 2-glycoprotein-I (apo-H) inhibits the release reaction of human platelets during ADP-induced aggregation. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Feb;63(2-3):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Kostner G. M. The binding of beta 2-glycoprotein-I to human serum lipoproteins: distribution among density fractions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Wurm H., Kostner G. M. Investigations on beta 2-glycoprotein-I in the rat: isolation from serum and demonstration in lipoprotein density fractions. Int J Biochem. 1980;11(3-4):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90229-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Binding of beta 2-glycoprotein I to platelets: effect of adenylate cyclase activity. Thromb Res. 1980 Jul 1;19(1-2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. Purification, characterization and identification of an agglutinin in human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 28;579(2):396–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. beta 2-Glycoprotein I: a plasma inhibitor of the contact activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1086–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm H. beta 2-Glycoprotein-I (apolipoprotein H) interactions with phospholipid vesicles. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(5):511–515. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]